Subatomic Particles Worksheet Answers Explained Simply
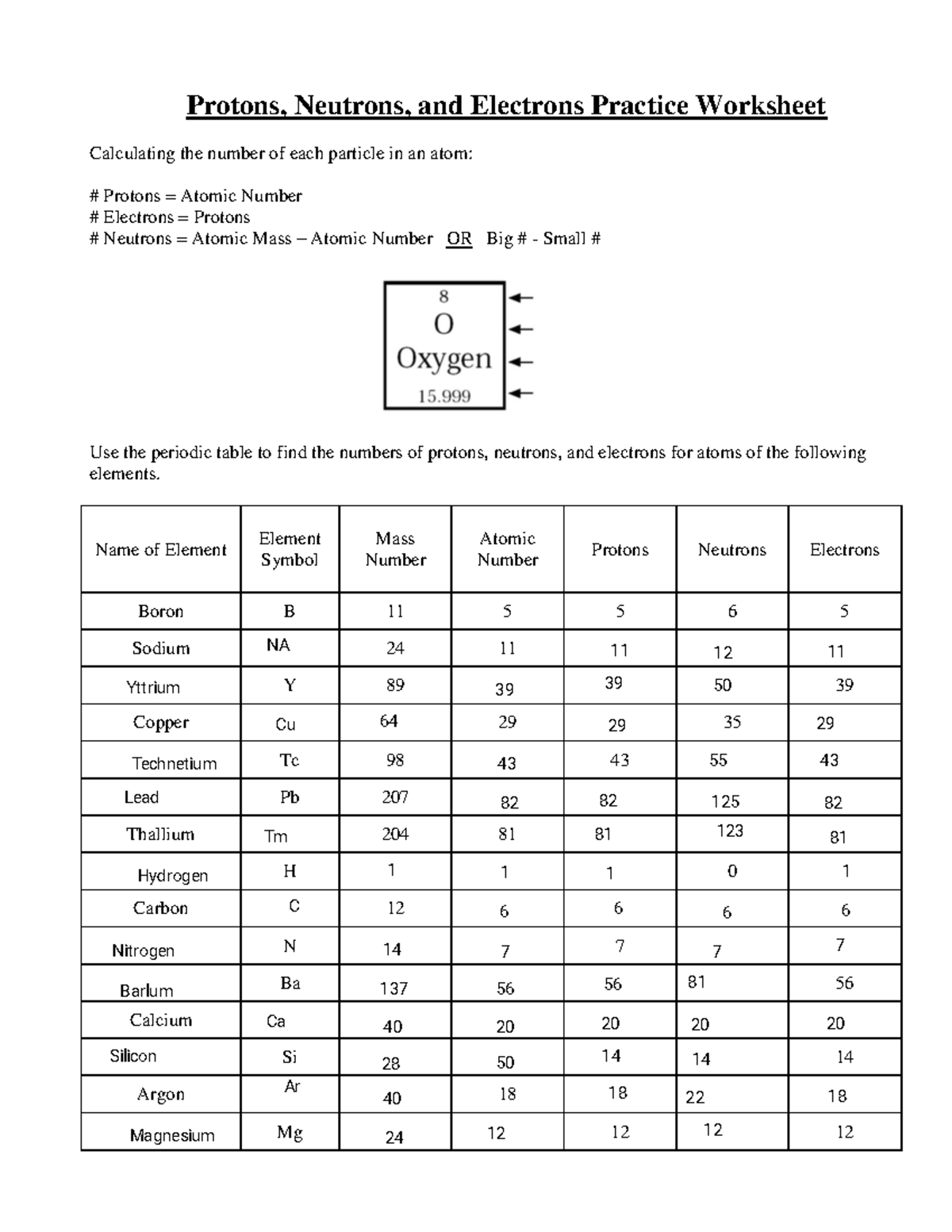
Understanding Subatomic Particles: A Comprehensive Guide
Subatomic particles are the building blocks of matter, and understanding them is crucial for any student of physics or chemistry. In this post, we will delve into the world of subatomic particles, exploring their types, properties, and importance. We will also provide answers to common worksheet questions, explaining each concept in a simple and easy-to-understand manner.
What are Subatomic Particles?
Subatomic particles are tiny particles that make up atoms, which are the basic units of matter. These particles are too small to be seen with the naked eye, but they play a vital role in the structure and properties of atoms. There are three main types of subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Protons
Protons are positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms. Protons have a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu).
Neutrons
Neutrons are particles that have no charge and reside in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, leading to different isotopes of an element. Neutrons have a mass slightly larger than that of protons.
Electrons
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus of an atom. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, and this number determines the chemical properties of an element. Electrons have a very small mass compared to protons and neutrons.
Properties of Subatomic Particles
Subatomic particles have several important properties that affect the behavior of atoms.
- Charge: Protons have a positive charge, electrons have a negative charge, and neutrons have no charge.
- Mass: Protons and neutrons have a mass of approximately 1 amu, while electrons have a much smaller mass.
- Spin: Subatomic particles can rotate around their axis, and this rotation is known as spin.
Importance of Subatomic Particles
Subatomic particles play a vital role in the structure and properties of atoms, which in turn affect the behavior of matter.
- Atomic Structure: The arrangement of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom determines its chemical properties.
- Chemical Reactions: The interaction between electrons and nuclei of atoms determines the chemical reactions that occur.
- Radioactivity: The decay of unstable nuclei leads to radioactivity, which has important applications in medicine and industry.
Worksheet Answers Explained
Here are answers to common worksheet questions on subatomic particles, explained in a simple and easy-to-understand manner.
- What is the charge of a proton? A proton has a positive charge.
- What is the mass of an electron? An electron has a very small mass, approximately 1⁄1836 that of a proton.
- What is the role of neutrons in an atom? Neutrons reside in the nucleus along with protons and play a crucial role in determining the stability of an atom.
- What is the difference between an isotope and an element? An element is a substance with a unique number of protons, while an isotope is a variant of an element with a different number of neutrons.
💡 Note: Understanding subatomic particles is essential for any student of physics or chemistry. These particles play a vital role in the structure and properties of atoms, which in turn affect the behavior of matter.
Conclusion
In conclusion, subatomic particles are the building blocks of matter, and understanding them is crucial for any student of physics or chemistry. By grasping the concepts of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and their properties and importance, students can gain a deeper understanding of the structure and behavior of atoms.
What is the smallest subatomic particle?
+The smallest subatomic particle is the electron, with a mass of approximately 1⁄1836 that of a proton.
What is the role of protons in an atom?
+Protons reside in the nucleus of an atom and determine the element of an atom. Each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
What is the difference between a proton and a neutron?
+A proton has a positive charge, while a neutron has no charge. Protons and neutrons have approximately the same mass, but neutrons have a slightly larger mass than protons.
Related Terms:
- Subatomic Particles Worksheet PDF
- Subatomic particles worksheet PDF answers
- Atomic Structure Worksheet answers
- Subatomic Particles homework
- Atomic Structure Worksheet answers pdf
- Subatomic particles practice



