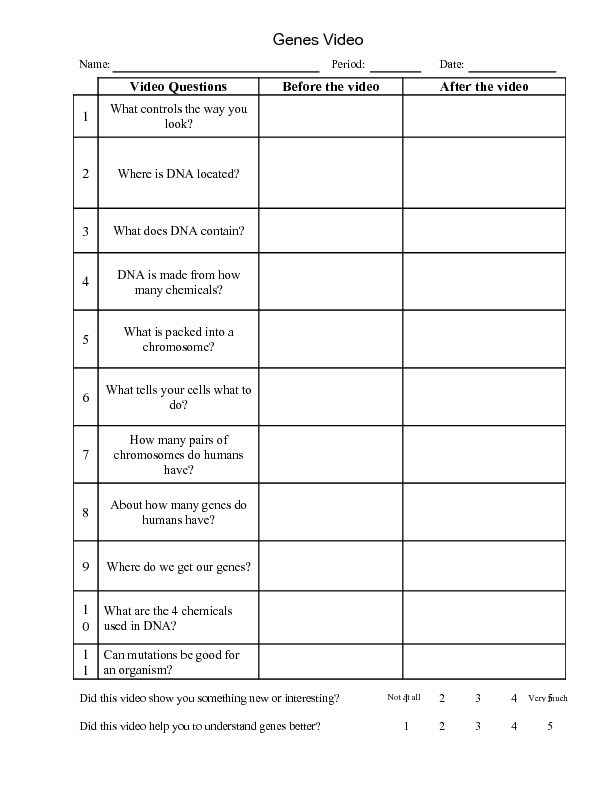
Read Blood Pressure Like a Pro with Sphygmomanometer

Understanding Blood Pressure and Sphygmomanometer
Blood pressure is a crucial indicator of our cardiovascular health, and monitoring it regularly can help us identify potential issues before they become severe. A sphygmomanometer, also known as a blood pressure monitor, is a device used to measure blood pressure. In this article, we will delve into the world of blood pressure and sphygmomanometers, teaching you how to read blood pressure like a pro.
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure is the force exerted by blood on the walls of our arteries as it circulates throughout the body. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is expressed as two numbers: systolic pressure and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure is the higher number, representing the pressure in the arteries when the heart beats, while diastolic pressure is the lower number, representing the pressure in the arteries between beats.
What is a Sphygmomanometer?
A sphygmomanometer is a device used to measure blood pressure. It consists of an inflatable cuff, a pressure gauge, and a stethoscope. The cuff is wrapped around the upper arm, and the pressure gauge measures the pressure in the cuff as it is inflated and deflated. The stethoscope is used to listen to the sounds of the blood flowing through the arteries.
How to Use a Sphygmomanometer
Using a sphygmomanometer is a relatively simple process. Here are the steps to follow:
- Sit comfortably with your back straight and your arm at heart level.
- Wrap the cuff around your upper arm, making sure it is not too tight or too loose.
- Place the stethoscope on the inside of your elbow, just above the artery.
- Inflate the cuff by squeezing the bulb until the pressure gauge reads 180-200 mmHg.
- Slowly deflate the cuff by releasing the air from the bulb.
- Listen to the sounds of the blood flowing through the arteries with the stethoscope.
- Note the pressure reading on the gauge when you first hear the sounds of the blood flowing (systolic pressure) and when the sounds disappear (diastolic pressure).
How to Read Blood Pressure
Reading blood pressure is a straightforward process. Here are the steps to follow:
- Look at the pressure gauge and note the systolic pressure (the higher number).
- Look at the pressure gauge and note the diastolic pressure (the lower number).
- Record your blood pressure reading as systolic pressure/diastolic pressure (e.g., 120⁄80 mmHg).
What Do the Numbers Mean?
The numbers on the pressure gauge represent the pressure in the arteries. Here is what the numbers mean:
- Systolic pressure:
- Less than 90 mmHg: too low
- 90-119 mmHg: normal
- 120-139 mmHg: elevated
- 140 mmHg or higher: high
- Diastolic pressure:
- Less than 60 mmHg: too low
- 60-79 mmHg: normal
- 80-89 mmHg: elevated
- 90 mmHg or higher: high
👍 Note: Blood pressure readings can vary depending on the time of day, physical activity, and other factors. It is essential to take multiple readings at different times to get an accurate picture of your blood pressure.
Tips for Accurate Blood Pressure Readings
Here are some tips to ensure accurate blood pressure readings:
- Use a high-quality sphygmomanometer.
- Use the correct cuff size.
- Sit comfortably with your back straight and your arm at heart level.
- Avoid smoking, caffeine, and exercise before taking a reading.
- Take multiple readings at different times.
Conclusion
Reading blood pressure with a sphygmomanometer is a simple process that can help you monitor your cardiovascular health. By following the steps outlined in this article, you can become a pro at reading blood pressure and take control of your health.
What is a normal blood pressure reading?
+A normal blood pressure reading is typically less than 120⁄80 mmHg.
How often should I check my blood pressure?
+It is recommended to check your blood pressure at least once a day, ideally at the same time each day.
What can affect blood pressure readings?
+Blood pressure readings can be affected by various factors, including physical activity, smoking, caffeine, and stress.
Related Terms:
- Blood pressure Worksheet PDF
- Blood pressure practice worksheet
- Blood pressure Worksheet answers
- Blood pressure Practice quiz
- Blood pressure Simulator online free
- Practice blood pressure simulator online