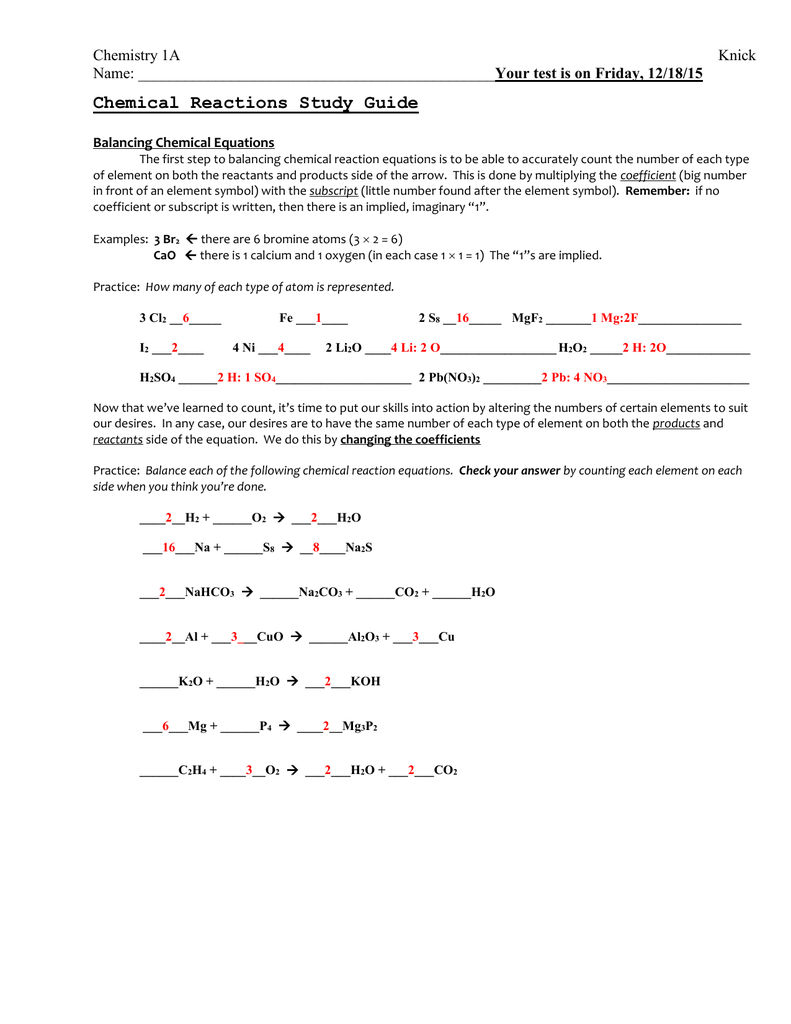
Chemical Reactions Worksheet Answers Made Easy
Understanding Chemical Reactions: A Comprehensive Guide
Chemical reactions are the building blocks of chemistry, and understanding them is crucial for any student or enthusiast of the subject. However, navigating the complex world of chemical reactions can be daunting, especially when it comes to worksheets and assignments. In this article, we’ll break down the key concepts and provide answers to common chemical reaction worksheet questions, making it easier for you to master this fundamental aspect of chemistry.
What is a Chemical Reaction?
A chemical reaction is a process in which one or more substances (reactants) are converted into new substances (products). This transformation involves the breaking and forming of chemical bonds between atoms, resulting in changes to the chemical composition of the reactants.
Types of Chemical Reactions
There are several types of chemical reactions, including:
- Synthesis reactions: Two or more reactants combine to form a new compound.
- Decomposition reactions: A single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances.
- Replacement reactions: One element replaces another element in a compound.
- Combustion reactions: A substance reacts with oxygen to produce heat and light.
Chemical Reaction Worksheet Answers
Here are some common chemical reaction worksheet questions and answers:
1. What is the difference between a reactant and a product?
A reactant is a substance that is consumed in the course of a chemical reaction, while a product is a substance that is formed as a result of the reaction.
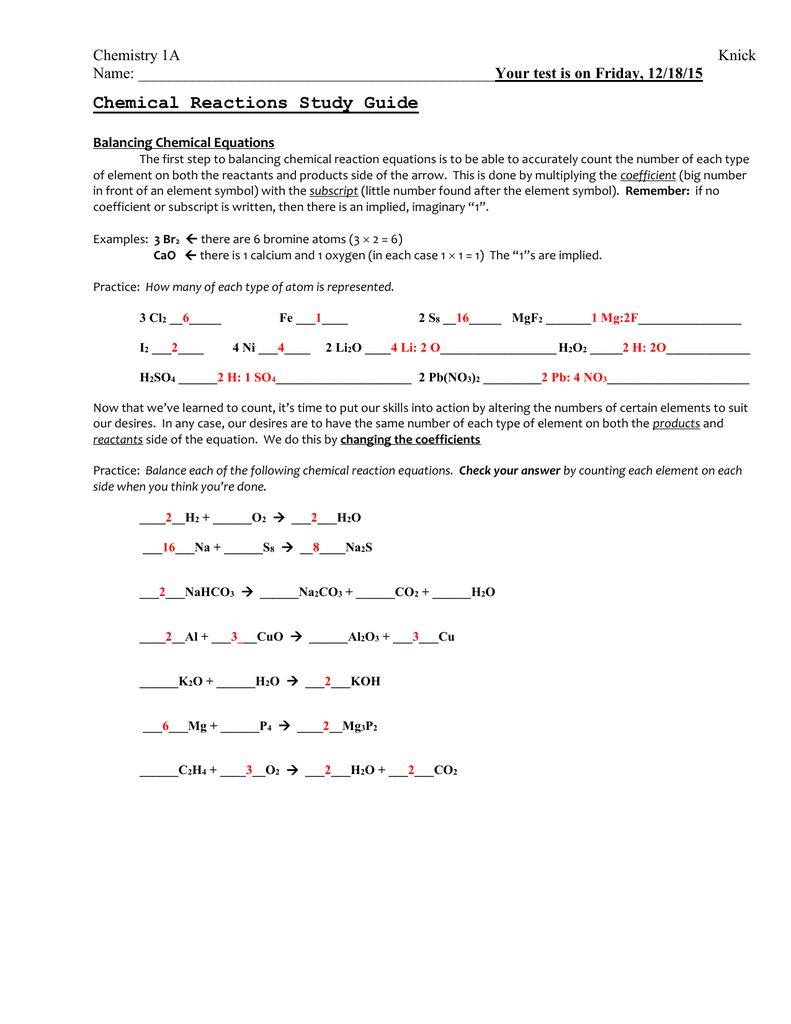
2. What is the balanced equation for the combustion of methane?
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
3. What type of chemical reaction is the following equation an example of?
2Na + Cl₂ → 2NaCl
Answer: Synthesis reaction
4. What is the law of conservation of mass, and how does it relate to chemical reactions?
The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products.
5. What is the difference between a catalyst and a reactant?
A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process, while a reactant is a substance that is consumed in the course of the reaction.
💡 Note: Catalysts are not reactants, and they do not affect the equilibrium of the reaction.
Chemical Reaction Stoichiometry
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions. It involves calculating the amounts of substances required for a reaction to occur, as well as the amounts of products formed.
Stoichiometry Example:
Calculate the number of moles of oxygen required to react with 2 moles of methane (CH₄) in the following reaction:
CH₄ + 2O₂ → CO₂ + 2H₂O
Answer: 4 moles of oxygen
| Reactant | Stoichiometric Coefficient | Number of Moles |
|---|---|---|
| CH₄ | 1 | 2 |
| O₂ | 2 | 4 |
Conclusion
Mastering chemical reactions requires a deep understanding of the underlying principles and concepts. By breaking down the key concepts and providing answers to common worksheet questions, we hope to have made chemical reactions more accessible and easier to understand. Remember to practice, practice, practice, and you’ll be solving chemical reaction worksheets like a pro in no time!
What is the difference between a chemical reaction and a physical change?
+A chemical reaction involves the breaking and forming of chemical bonds, resulting in changes to the chemical composition of the reactants. A physical change, on the other hand, involves a change in the state of a substance (e.g., solid to liquid) without any changes to its chemical composition.
What is the purpose of a catalyst in a chemical reaction?
+A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction without being consumed in the process. It works by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, allowing the reaction to proceed faster and more efficiently.
What is the law of conservation of mass, and how does it relate to chemical reactions?
+The law of conservation of mass states that matter cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction. This means that the total mass of the reactants must equal the total mass of the products. This law is a fundamental principle of chemistry and is essential for balancing chemical equations.
Related Terms:
- Chemical reactions Worksheet answers pdf
- Balancing chemical reactions worksheet pdf
- Chemical reaction Worksheet pdf
- Identifying chemical reactions Worksheet