5 Tips to Master Solubility Curves
Understanding Solubility Curves: A Key to Mastering Chemical Reactions
Solubility curves are graphical representations of the relationship between the solubility of a substance and temperature. Mastering solubility curves is crucial for chemists, chemical engineers, and students to predict and control the outcomes of various chemical reactions. In this article, we will explore five essential tips to help you understand and work with solubility curves like a pro.
Tip 1: Know Your Axes
A solubility curve typically consists of two axes: temperature (x-axis) and solubility (y-axis). The x-axis represents the temperature range, usually in degrees Celsius (°C), while the y-axis represents the solubility of the substance, often expressed in grams per 100 grams of solvent (g/100g). Understanding the units and scales of both axes is vital to accurately interpret and work with solubility curves.
💡 Note: Always check the units and scales of the axes before analyzing a solubility curve.
Tip 2: Identify the Types of Solubility Curves
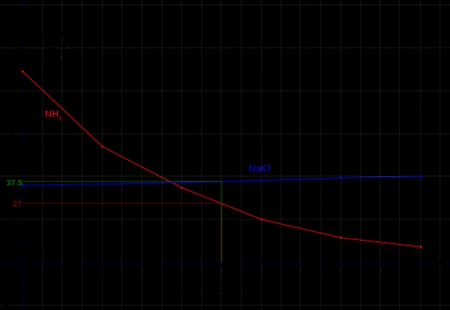
There are two primary types of solubility curves: normal and retrograde. Normal solubility curves exhibit a positive slope, indicating that the solubility of the substance increases with temperature. Retrograde solubility curves, on the other hand, have a negative slope, showing that the solubility decreases with temperature. Recognizing the type of solubility curve is essential to predict the behavior of a substance in different temperature conditions.
| Type of Solubility Curve | Description |
|---|---|
| Normal Solubility Curve | Positive slope, solubility increases with temperature |
| Retrograde Solubility Curve | Negative slope, solubility decreases with temperature |
Tip 3: Determine the Solubility of a Substance at a Given Temperature
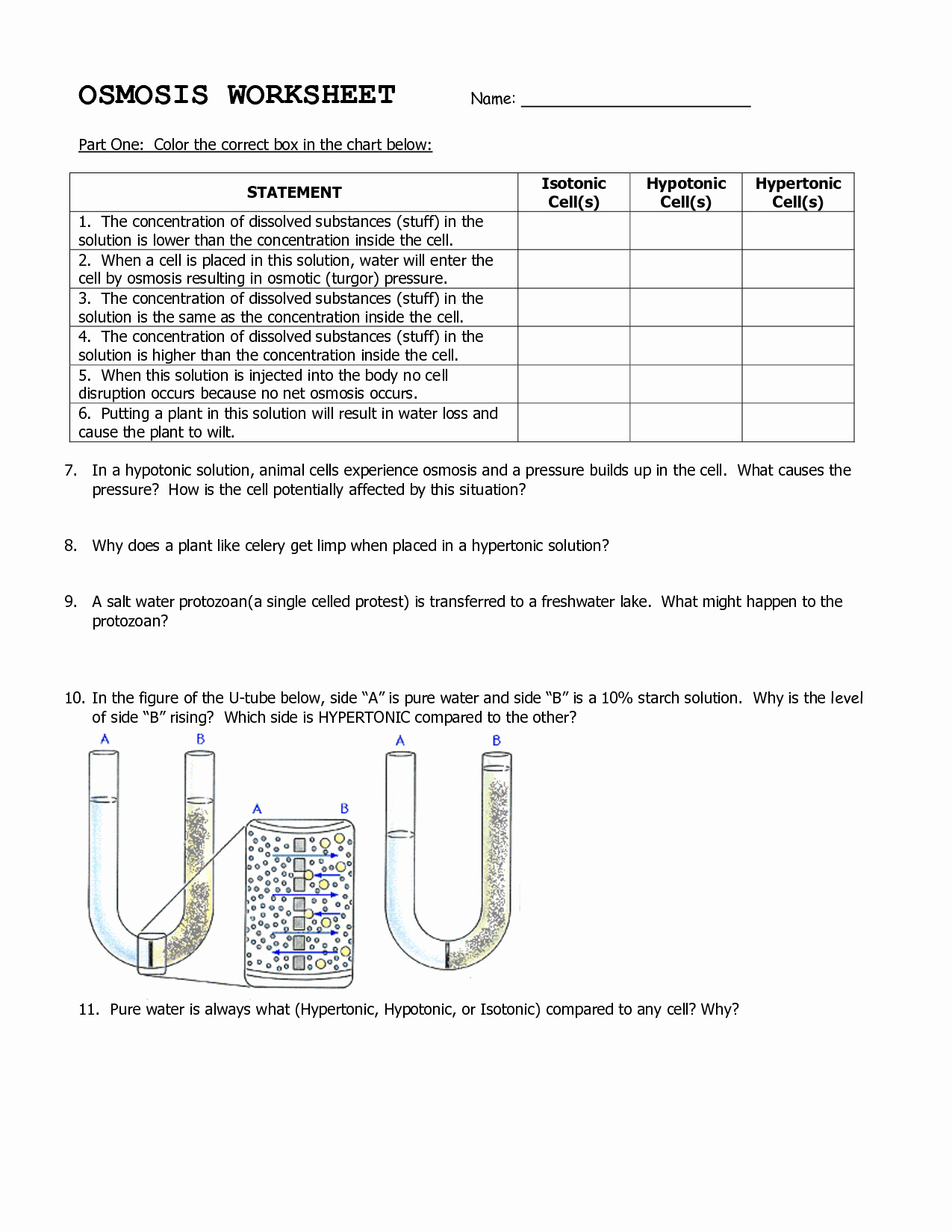
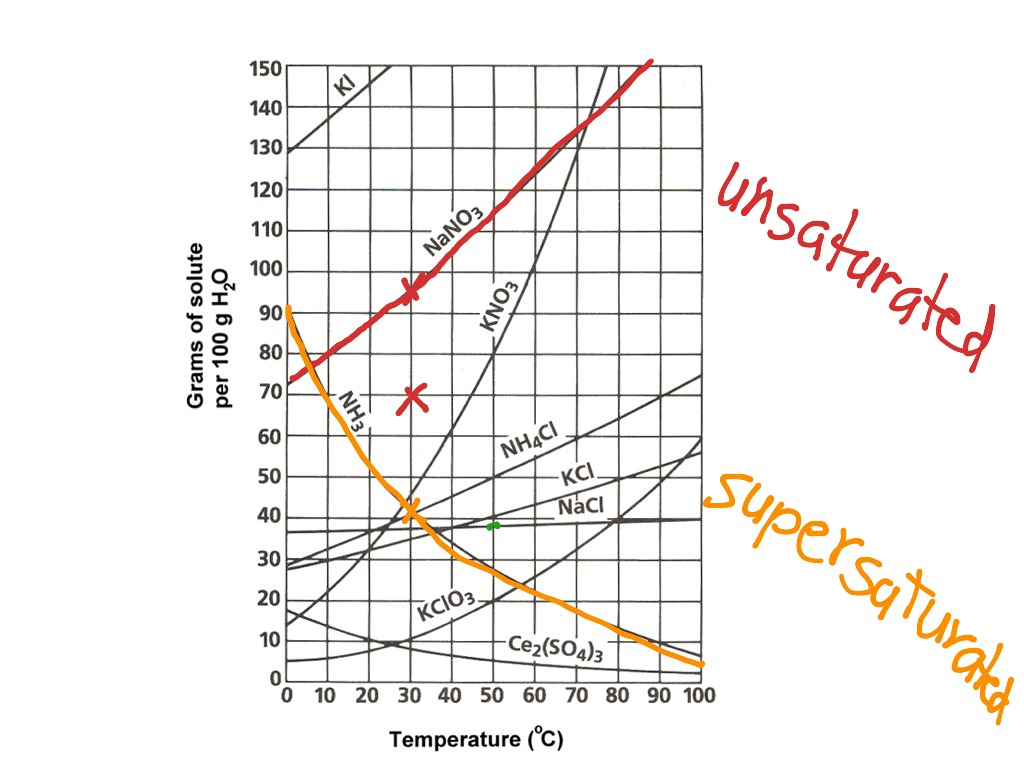
To determine the solubility of a substance at a specific temperature, locate the temperature on the x-axis and draw a vertical line to the solubility curve. The point where the line intersects the curve represents the solubility of the substance at that temperature. This information is crucial for predicting the outcome of chemical reactions and designing experiments.
Tip 4: Analyze the Shape of the Solubility Curve
The shape of the solubility curve can provide valuable information about the substance’s behavior. For example, a steep slope indicates a significant change in solubility over a small temperature range, while a gentle slope suggests a more gradual change. Analyzing the shape of the curve can help you identify the optimal temperature range for a chemical reaction or process.
📊 Note: The shape of the solubility curve can also indicate the presence of impurities or other factors affecting the substance's solubility.
Tip 5: Consider the Effects of Pressure and Concentration
While temperature is the primary variable in solubility curves, pressure and concentration can also impact a substance’s solubility. For example, increasing pressure can increase the solubility of a gas, while high concentrations of a substance can lead to saturation. Considering these factors can help you refine your predictions and optimize chemical reactions.
By mastering these five tips, you’ll be well on your way to becoming an expert in working with solubility curves. Remember to always analyze the axes, identify the type of solubility curve, determine solubility at specific temperatures, analyze the curve’s shape, and consider the effects of pressure and concentration.
In conclusion, solubility curves are powerful tools for predicting and controlling chemical reactions. By following these tips, you’ll be able to unlock the full potential of solubility curves and take your chemistry skills to the next level.
What is the primary variable in a solubility curve?
+Temperature is the primary variable in a solubility curve.
What is the difference between a normal and retrograde solubility curve?
+A normal solubility curve has a positive slope, indicating that the solubility increases with temperature, while a retrograde solubility curve has a negative slope, indicating that the solubility decreases with temperature.
How can I determine the solubility of a substance at a specific temperature?
+To determine the solubility of a substance at a specific temperature, locate the temperature on the x-axis and draw a vertical line to the solubility curve. The point where the line intersects the curve represents the solubility of the substance at that temperature.
Related Terms:
- Solubility curve Worksheet Answers PDF
- Solubility Curves Worksheet Answers
- Solubility curve Worksheet PDF
- Solubility curve questions and answers
- Solubility Curves Worksheet CP answers
- Solubility Worksheet PDF