5 Ways to Master Diffusion and Osmosis
Understanding the Basics of Diffusion and Osmosis
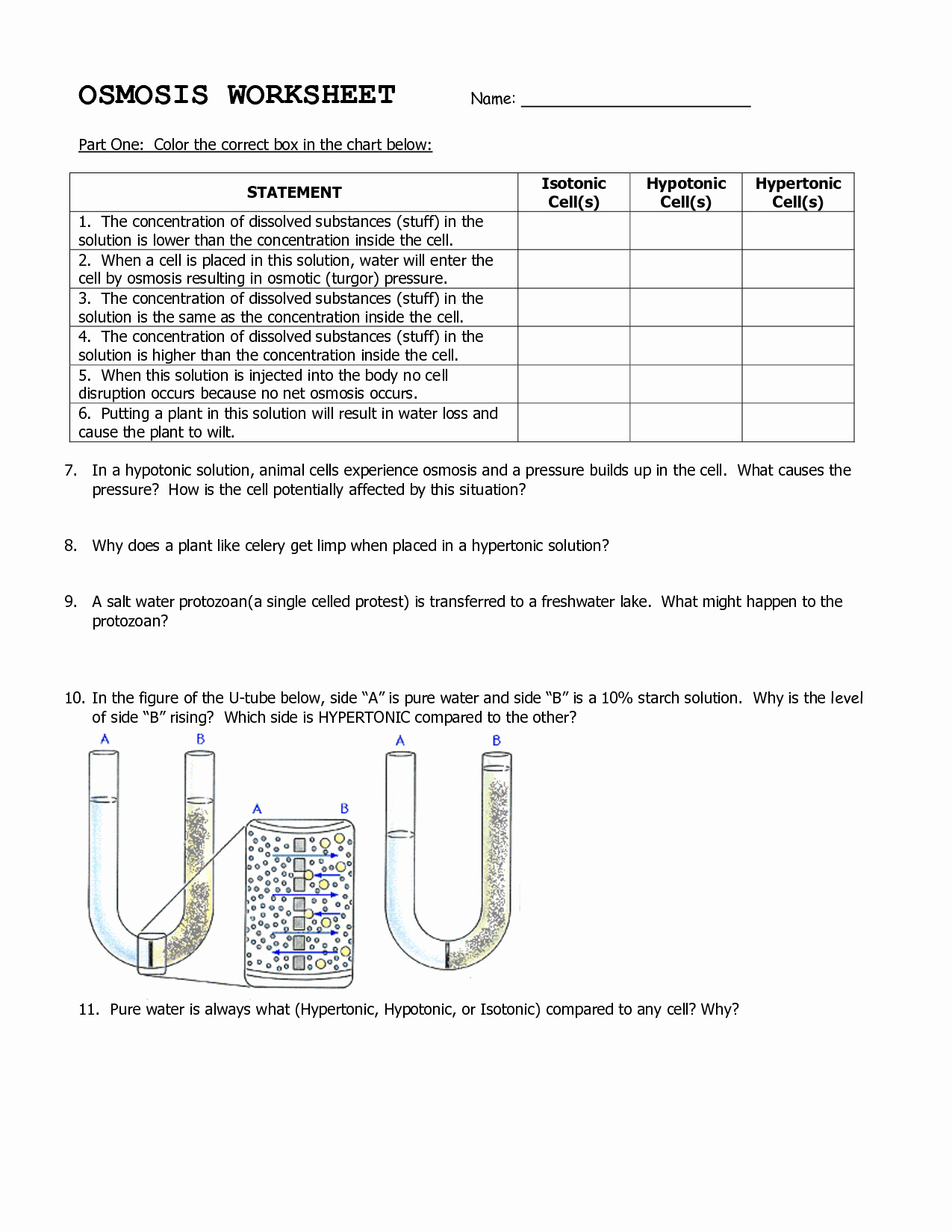
Diffusion and osmosis are two fundamental biological processes that play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of fluids within living organisms. Diffusion is the passive movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, resulting in uniform distribution. On the other hand, osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
1. Visualize the Process with Analogies
One of the most effective ways to master diffusion and osmosis is to visualize the process using analogies. For instance, imagine a crowded room where people are moving randomly. As the crowd disperses, people move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, resulting in uniform distribution. This is similar to how diffusion works.
Another analogy for osmosis is a sponge soaking up water. When a sponge is placed in a container of water, the water molecules move from the container into the sponge, equalizing the concentration of water molecules inside and outside the sponge.
Key Takeaways:
- Diffusion and osmosis are essential biological processes that maintain fluid balance.
- Analogies can help visualize and understand the processes.
💡 Note: Visualizing complex biological processes with analogies can make them easier to understand and remember.
2. Understand the Role of Concentration Gradients
Concentration gradients play a vital role in both diffusion and osmosis. A concentration gradient is the gradual change in concentration of particles or substances from one area to another. In diffusion, particles move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, down the concentration gradient.
In osmosis, water molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. The direction of osmosis depends on the concentration gradient of solutes, which are substances dissolved in the solution.

| Concentration Gradient | Direction of Diffusion | Direction of Osmosis |
|---|---|---|
| High → Low | From high to low concentration | Into the cell (endosmosis) |
| Low → High | From low to high concentration | Out of the cell (exosmosis) |
Key Takeaways:
- Concentration gradients determine the direction of diffusion and osmosis.
- Understanding concentration gradients is crucial for mastering diffusion and osmosis.
3. Explore the Role of Selectively Permeable Membranes
Selectively permeable membranes play a crucial role in osmosis, allowing certain substances to pass through while restricting others. These membranes have tiny pores that permit water molecules to pass through, but restrict larger particles and solutes.
The selectively permeable membrane acts as a filter, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. In osmosis, water molecules move through the membrane from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, equalizing the concentration of solutes inside and outside the cell.
Key Takeaways:
- Selectively permeable membranes control the movement of substances in and out of cells.
- Understanding the role of selectively permeable membranes is essential for mastering osmosis.
4. Use Real-World Examples to Illustrate the Processes
Using real-world examples can help illustrate the processes of diffusion and osmosis. For instance, the absorption of nutrients by cells in the small intestine is an example of facilitated diffusion, where nutrients are absorbed through a selectively permeable membrane.
Another example of osmosis is the process of plasmolysis, where a plant cell loses water and shrinks due to high salt concentrations in the surrounding solution.
Key Takeaways:
- Real-world examples can help illustrate the processes of diffusion and osmosis.
- Using examples can make the processes more relatable and easier to understand.
5. Practice with Diagrams and Illustrations
Practicing with diagrams and illustrations can help solidify understanding of diffusion and osmosis. Drawing diagrams of cells and selectively permeable membranes can help visualize the processes and identify key components.
Using illustrations to show the movement of particles and water molecules can also help clarify the processes and make them more memorable.
Key Takeaways:
- Practicing with diagrams and illustrations can help solidify understanding of diffusion and osmosis.
- Visualizing the processes can make them easier to remember and understand.
In summary, mastering diffusion and osmosis requires a combination of understanding the basics, visualizing the processes, and practicing with real-world examples and diagrams. By following these steps, you can gain a deeper understanding of these essential biological processes.
What is the main difference between diffusion and osmosis?
+Diffusion is the passive movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, while osmosis is the movement of water molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
What is the role of concentration gradients in diffusion and osmosis?
+Concentration gradients determine the direction of diffusion and osmosis. In diffusion, particles move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration, down the concentration gradient. In osmosis, water molecules move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration through a selectively permeable membrane.
What is the purpose of selectively permeable membranes in osmosis?
+Selectively permeable membranes control the movement of substances in and out of cells. They allow certain substances to pass through while restricting others, regulating the movement of water molecules and solutes.