Understanding Atoms: Protons Neutrons and Electrons Made Easy
Understanding Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
Atoms are the fundamental units of matter, and understanding their structure is essential for grasping various concepts in physics, chemistry, and other sciences. In this article, we will delve into the world of atoms, exploring their composition, properties, and behavior. By the end of this journey, you will have a comprehensive understanding of protons, neutrons, and electrons, making it easier to navigate the fascinating realm of atomic physics.
The Atomic Structure: A Review
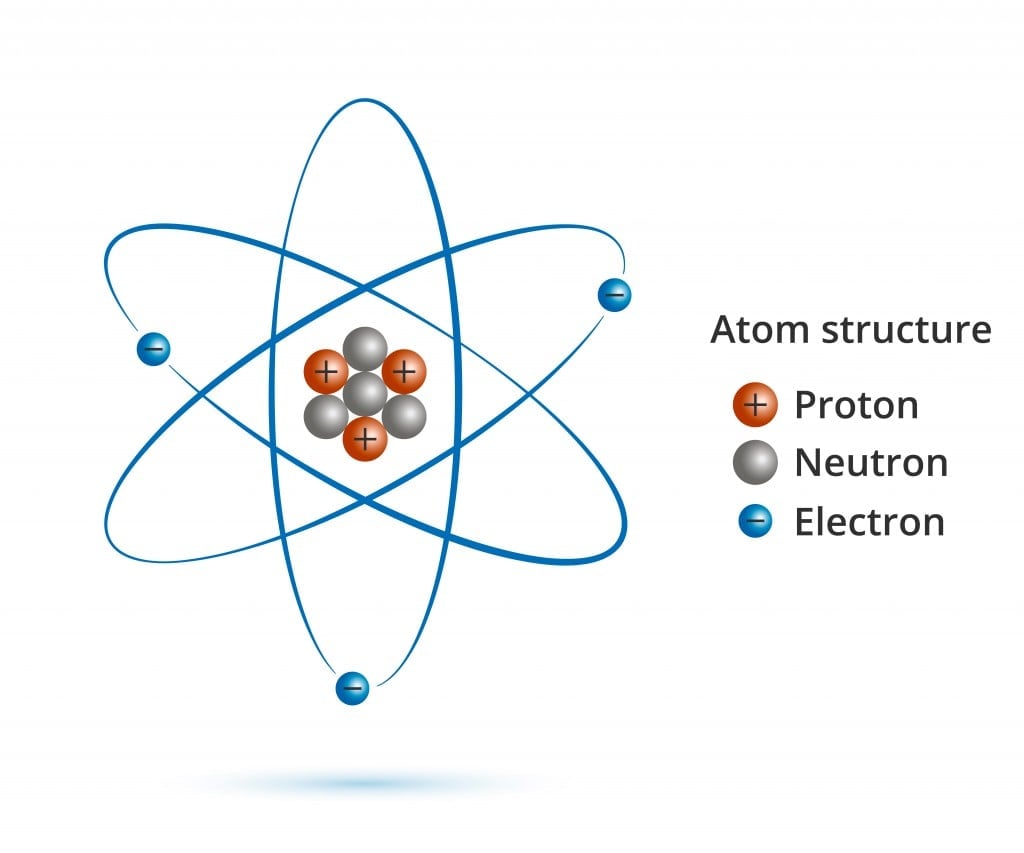
An atom consists of three primary components: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Each of these particles plays a vital role in determining the atom’s properties and behavior.
- Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus (center) of the atom. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, leading to different isotopes (atoms of the same element with varying numbers of neutrons) of an element.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, and this number determines the chemical properties of an element.
The Proton: A Closer Look
Protons are positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
- Proton Charge: The charge of a proton is +1 elementary charge, which is equal to 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs.
- Proton Mass: The mass of a proton is approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu), which is equal to 1.672 x 10^-27 kilograms.
- Proton Spin: Protons have a spin of 1⁄2, which means they can rotate around their axis in two different directions.
The Neutron: A Neutral Component
Neutrons are particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, leading to different isotopes (atoms of the same element with varying numbers of neutrons) of an element.
- Neutron Charge: Neutrons have no charge, which means they do not contribute to the overall charge of an atom.
- Neutron Mass: The mass of a neutron is approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu), which is equal to 1.675 x 10^-27 kilograms.
- Neutron Spin: Neutrons have a spin of 1⁄2, which means they can rotate around their axis in two different directions.
The Electron: A Negatively Charged Particle
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. The number of electrons in an atom is equal to the number of protons, and this number determines the chemical properties of an element.
- Electron Charge: The charge of an electron is -1 elementary charge, which is equal to -1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs.
- Electron Mass: The mass of an electron is approximately 1⁄1836 that of a proton, which is equal to 9.109 x 10^-31 kilograms.
- Electron Spin: Electrons have a spin of 1⁄2, which means they can rotate around their axis in two different directions.
Atomic Models: A Historical Perspective
Over the years, scientists have proposed various models to describe the structure of atoms. Some of the most notable models include:
- Rutherford Model: Proposed by Ernest Rutherford in 1911, this model describes the atom as a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons.
- Bohr Model: Proposed by Niels Bohr in 1913, this model describes the atom as a small, dense nucleus surrounded by electrons in specific energy levels or shells.
- Quantum Mechanical Model: This model describes the atom as a complex system of particles, with electrons exhibiting both wave-like and particle-like behavior.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the structure and properties of atoms is essential for grasping various concepts in physics, chemistry, and other sciences. By exploring the world of protons, neutrons, and electrons, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate and fascinating realm of atomic physics.
What is the charge of a proton?
+
The charge of a proton is +1 elementary charge, which is equal to 1.602 x 10^-19 coulombs.
What is the mass of a neutron?
+
The mass of a neutron is approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu), which is equal to 1.675 x 10^-27 kilograms.
What is the spin of an electron?
+
Electrons have a spin of 1⁄2, which means they can rotate around their axis in two different directions.