Mastering Atomic Structure: Protons Neutrons and Electrons Worksheet
Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter: Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
The atomic structure is the foundation of chemistry, and it’s essential to understand the three main components that make up an atom: protons, neutrons, and electrons. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of atomic structure, exploring the roles of protons, neutrons, and electrons, and provide a comprehensive worksheet to help you master this fundamental concept.
The Atomic Structure: A Brief Overview
An atom is the smallest unit of a chemical element, and it’s composed of three primary particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. The protons and neutrons are found in the nucleus, which is the central part of the atom, while the electrons orbit around the nucleus.
- Protons: Positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
- Neutrons: Particles with no charge that reside in the nucleus along with protons. The number of neutrons in an atom can vary, leading to different isotopes of the same element.
- Electrons: Negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
The Role of Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
Protons, neutrons, and electrons play crucial roles in the atomic structure:
- Protons: Determine the element of an atom and contribute to the overall positive charge of the nucleus.
- Neutrons: Contribute to the mass of an atom and help stabilize the nucleus.
- Electrons: Determine the chemical properties of an element and participate in chemical bonding.
Worksheet: Mastering Atomic Structure
Now that you have a solid understanding of the atomic structure, it’s time to practice with a worksheet. Complete the following exercises to reinforce your knowledge:
Exercise 1: Identifying Protons, Neutrons, and Electrons
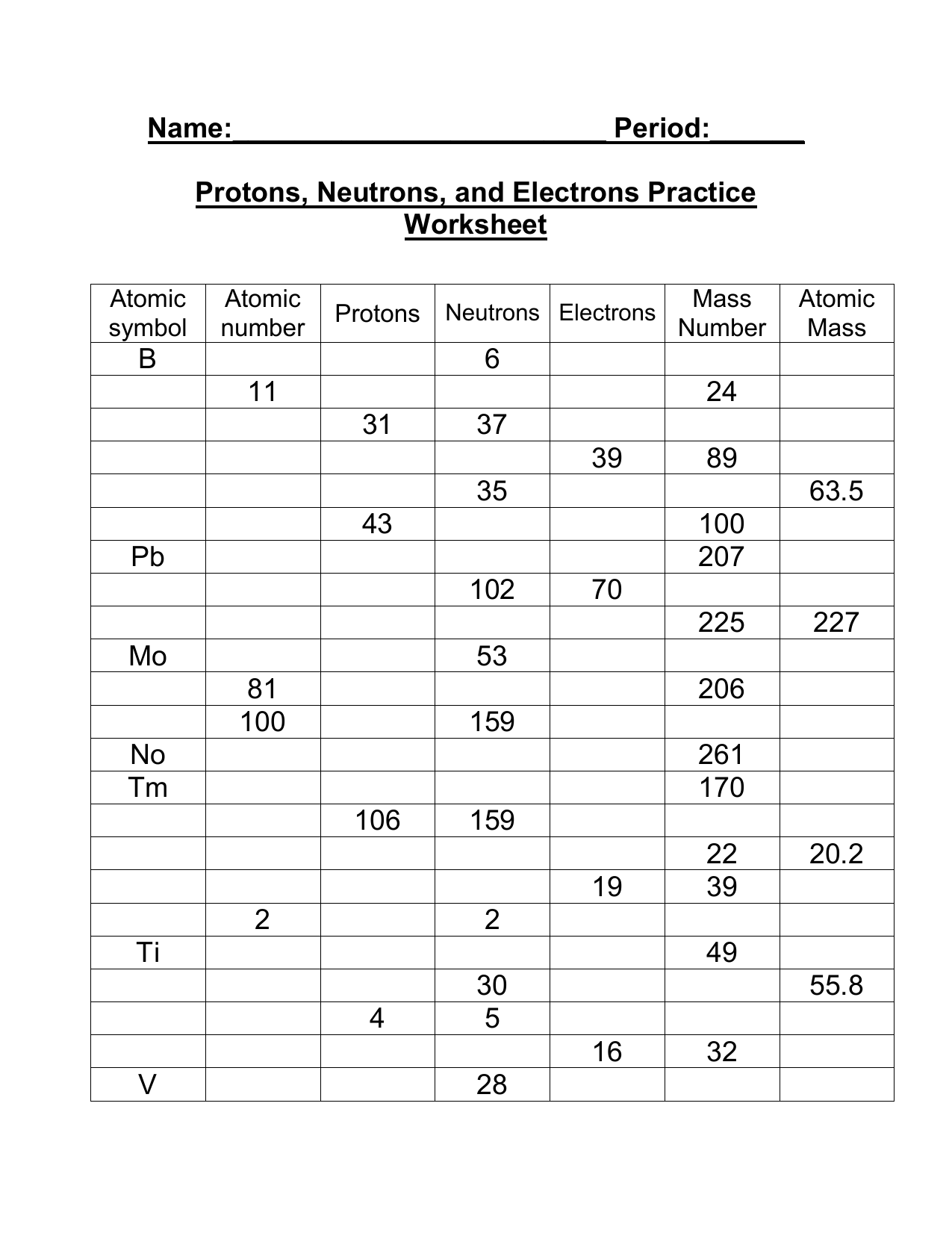
| Element | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Helium | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Nitrogen | 7 | 7 | 7 |
Exercise 2: Calculating Atomic Mass
The atomic mass of an element is the sum of protons and neutrons. Calculate the atomic mass of the following elements:
| Element | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 6 | 6 | ? |
| Oxygen | 8 | 8 | ? |
| Nitrogen | 7 | 7 | ? |
Exercise 3: Determining the Number of Electrons
Determine the number of electrons in the following atoms:
| Element | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium | 11 | 12 | ? |
| Calcium | 20 | 20 | ? |
| Aluminum | 13 | 14 | ? |
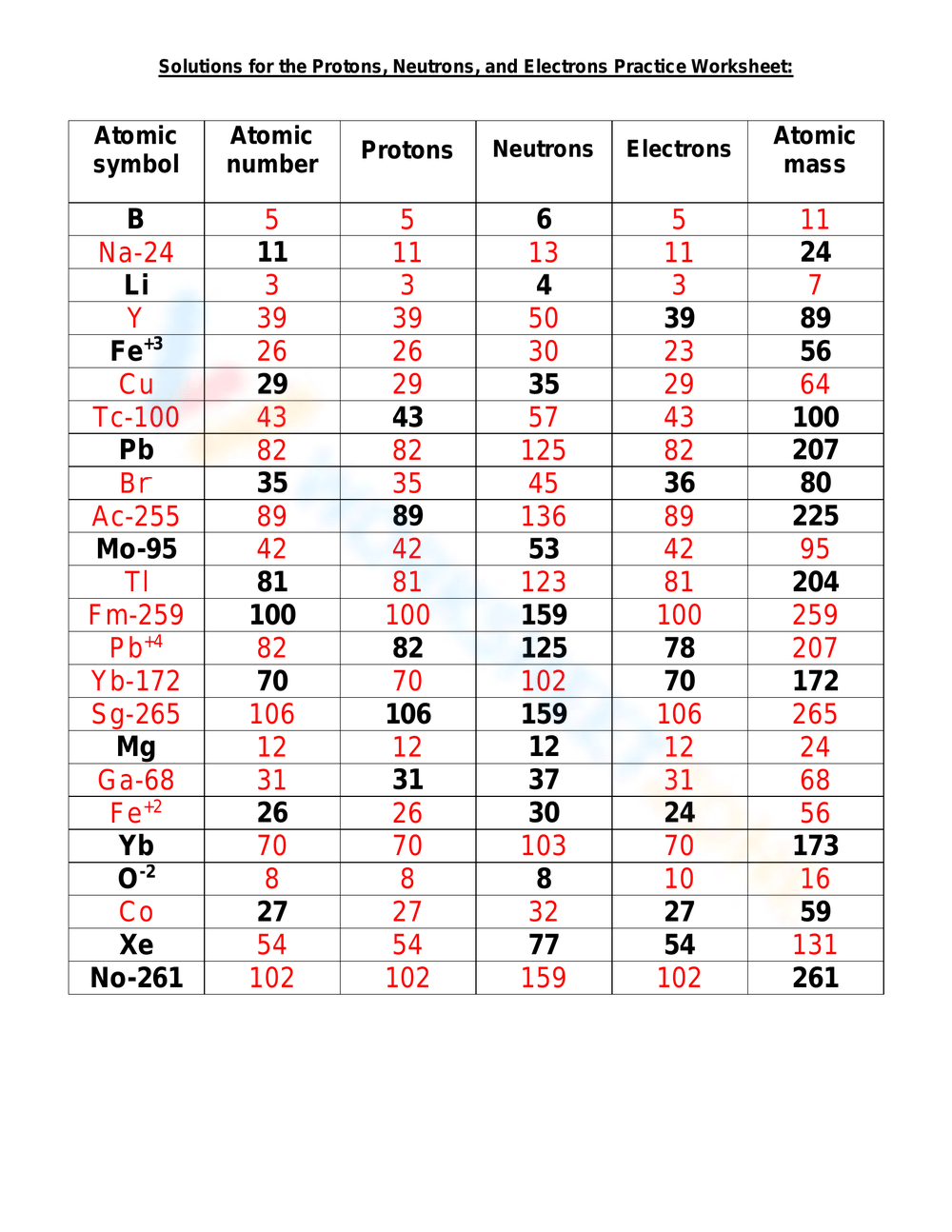
Answers
Exercise 1:
| Element | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| Helium | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Nitrogen | 7 | 7 | 7 |
Exercise 2:
| Element | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Atomic Mass |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | 6 | 6 | 12 |
| Oxygen | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| Nitrogen | 7 | 7 | 14 |
Exercise 3:
| Element | Number of Protons | Number of Neutrons | Number of Electrons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium | 11 | 12 | 11 |
| Calcium | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Aluminum | 13 | 14 | 13 |
📝 Note: The number of electrons in a neutral atom is equal to the number of protons.
Common Isotopes and Their Applications
Isotopes are atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons. Some common isotopes and their applications include:
- Carbon-14: Used in radiocarbon dating to determine the age of organic materials.
- Oxygen-18: Used in medical research to study oxygen metabolism.
- Nitrogen-15: Used in agricultural research to study nitrogen uptake in plants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the atomic structure is essential for understanding the building blocks of matter. By grasping the roles of protons, neutrons, and electrons, you’ll be better equipped to tackle more complex chemistry concepts. Remember to practice with worksheets and exercises to reinforce your knowledge.
What is the atomic structure composed of?
+
The atomic structure is composed of three primary particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What determines the element of an atom?
+
The number of protons in an atom determines the element.
What is the role of neutrons in the atomic structure?
+
Neutrons contribute to the mass of an atom and help stabilize the nucleus.
Related Terms:
- Ions Protons Neutrons Electrons worksheet
- Protons, neutrons and electrons pdf
- Chemistry worksheet for kids