5 Essential Steps to Master Mitosis and Meiosis

Understanding the Fundamentals of Cell Division
Mitosis and meiosis are two fundamental processes in cell biology that are essential for the survival and reproduction of living organisms. Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell, while meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four non-identical daughter cells that are necessary for reproduction. Mastering these processes is crucial for anyone studying biology, medicine, or related fields. In this article, we will break down the five essential steps to master mitosis and meiosis.
Step 1: Understanding the Cell Cycle
Before diving into the specifics of mitosis and meiosis, it is essential to understand the cell cycle. The cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell, from the moment it is formed until it divides into two daughter cells. The cell cycle consists of three main stages: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. Interphase is the longest stage of the cell cycle, during which the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division. Mitosis is the stage where the replicated DNA is divided equally between two daughter cells. Cytokinesis is the final stage, where the cytoplasm divides, and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
🔍 Note: The cell cycle is a continuous process, and cells can exit the cycle at any stage if they are not needed for growth or repair.
Step 2: Mastering Mitosis
Mitosis is a critical process that ensures genetic continuity between generations of cells. It consists of five stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. During prophase, the chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope breaks down. In metaphase, the chromosomes line up at the center of the cell, attached to the spindle fibers. Anaphase is the stage where the sister chromatids separate, and telophase is where the nuclear envelope reforms, and the chromosomes uncoil. Cytokinesis is the final stage, where the cytoplasm divides, and the cell splits into two daughter cells.
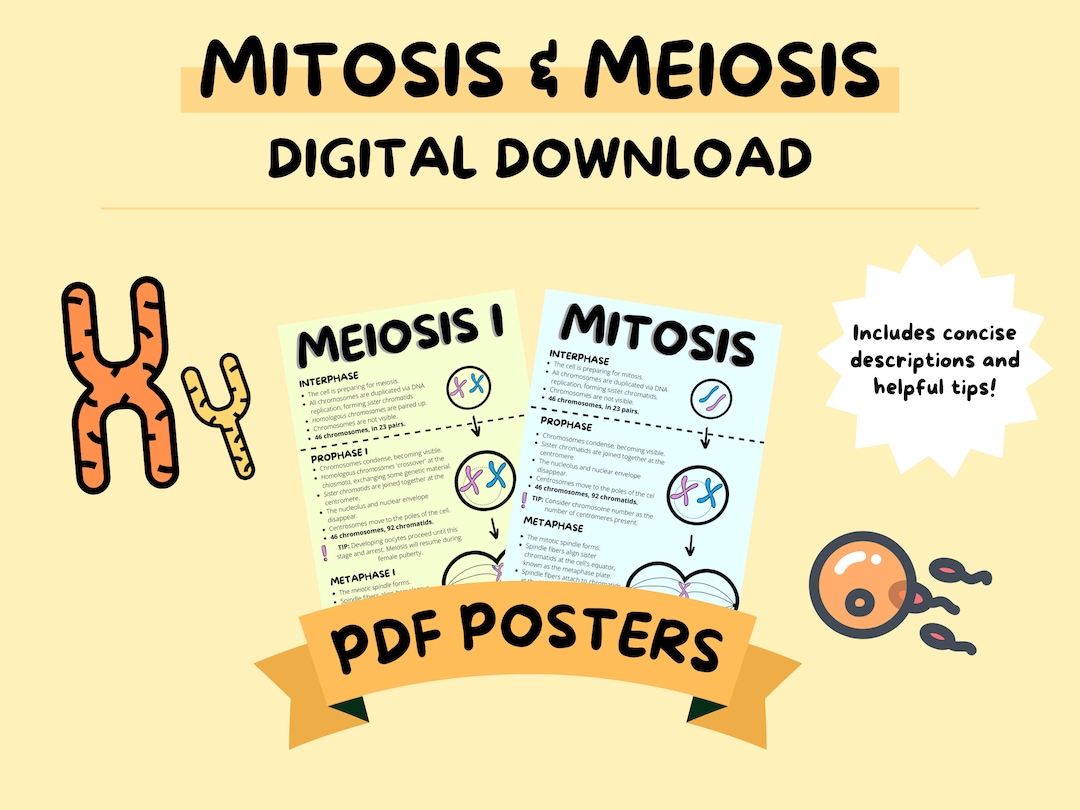
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Prophase | Chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, nuclear envelope breaks down |
| Metaphase | Chromosomes line up at the center of the cell, attached to spindle fibers |
| Anaphase | Sister chromatids separate |
| Telophase | Nuclear envelope reforms, chromosomes uncoil |
| Cytokinesis | Cytoplasm divides, cell splits into two daughter cells |
Step 3: Understanding Meiosis
Meiosis is a specialized type of cell division that reduces the number of chromosomes in the daughter cells by half. This process is essential for the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells) in sexually reproducing organisms. Meiosis consists of two successive cell divisions, meiosis I and meiosis II, each with its own stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. During meiosis I, homologous chromosomes separate, and during meiosis II, sister chromatids separate.
🔍 Note: Meiosis is a critical process that increases genetic diversity by shuffling the genetic material between homologous chromosomes.
Step 4: Comparing Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitosis and meiosis are both types of cell division, but they have distinct differences. Mitosis is a type of cell division that results in two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis is a type of cell division that results in four non-identical daughter cells. Mitosis occurs in somatic cells, while meiosis occurs in reproductive cells.
- Mitosis:
- Results in two genetically identical daughter cells
- Occurs in somatic cells
- Consists of one round of cell division
- Meiosis:
- Results in four non-identical daughter cells
- Occurs in reproductive cells
- Consists of two successive rounds of cell division
Step 5: Applying Your Knowledge
Mastering mitosis and meiosis requires practice and application. Try drawing diagrams of the different stages of mitosis and meiosis, and label the key structures. Practice identifying the different stages of cell division under a microscope. Apply your knowledge to real-world scenarios, such as understanding how genetic disorders occur or how cancer develops.
By following these five essential steps, you can master mitosis and meiosis and gain a deeper understanding of the complex processes that govern cell biology.
The cell cycle and cell division are critical processes that govern the life of a cell. Mastering these processes is essential for anyone studying biology, medicine, or related fields. By understanding the cell cycle, mastering mitosis, understanding meiosis, comparing mitosis and meiosis, and applying your knowledge, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex processes that govern life.
What is the main difference between mitosis and meiosis?
+The main difference between mitosis and meiosis is the number of daughter cells produced. Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four non-identical daughter cells.
What is the purpose of the cell cycle?
+The cell cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell, from the moment it is formed until it divides into two daughter cells. The purpose of the cell cycle is to ensure genetic continuity between generations of cells.
What is the significance of meiosis in sexually reproducing organisms?
+Meiosis is a critical process that increases genetic diversity by shuffling the genetic material between homologous chromosomes. This process is essential for the production of gametes (sperm and egg cells) in sexually reproducing organisms.