7 Key Differences: Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic Cells
Cellular Structure: Unveiling the Differences Between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
Cells are the fundamental building blocks of life, and they come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. These two cell types have distinct characteristics that set them apart from each other. Understanding the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is crucial in the fields of biology, medicine, and research. In this article, we will delve into the 7 key differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
1. Cell Size and Complexity
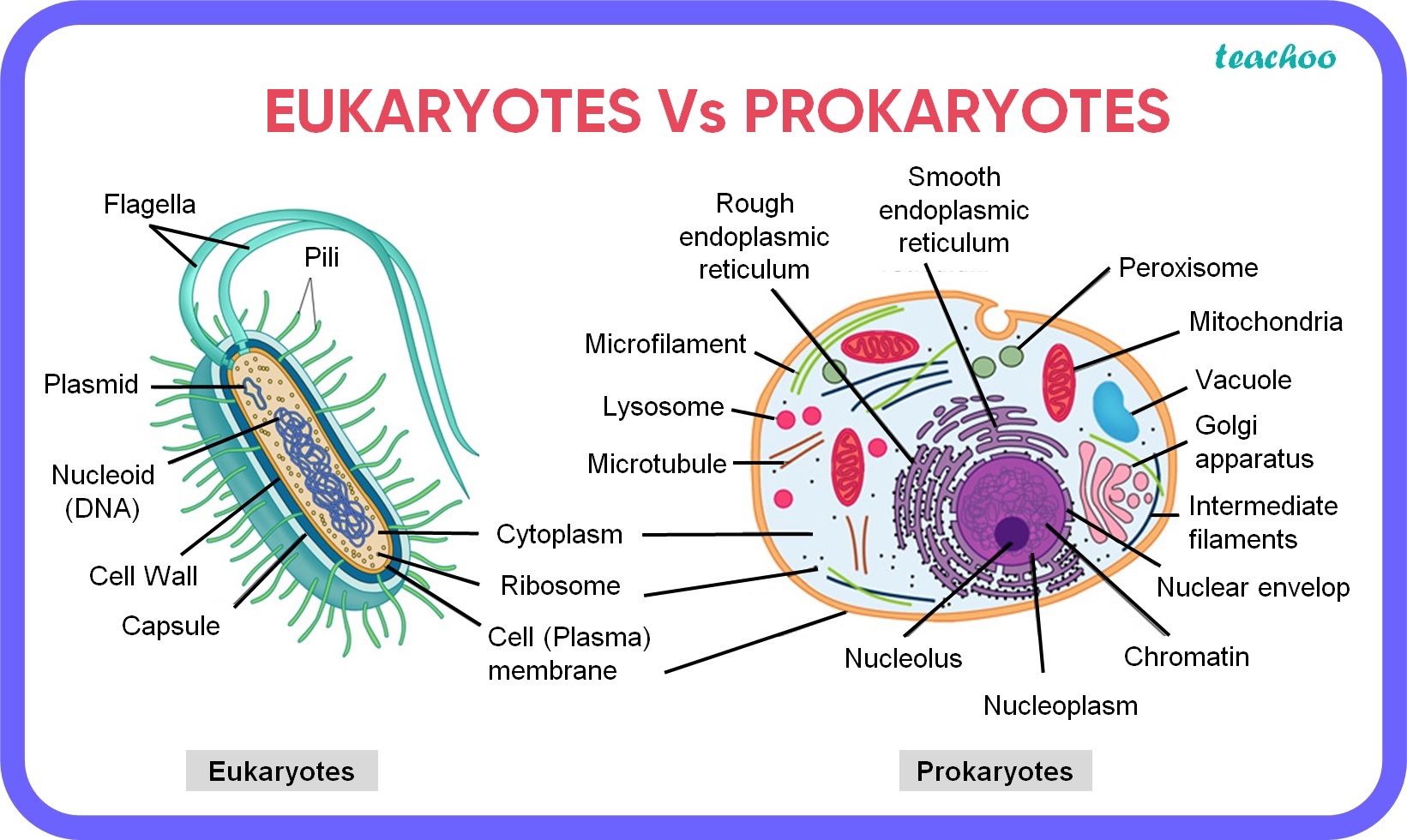
Prokaryotic cells are relatively small, typically ranging from 0.5 to 5.0 micrometers in diameter. They have a simple structure, with a single circular chromosome and no membrane-bound organelles. In contrast, eukaryotic cells are larger, ranging from 10 to 100 micrometers in diameter. They have a more complex structure, with multiple linear chromosomes and various membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and a nucleus.
2. Cell Membrane and Wall
Prokaryotic cells have a cell membrane composed of phospholipid bilayer, but they lack a true cell wall. Some prokaryotic cells, such as bacteria, have a peptidoglycan layer that provides structural support. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a cell membrane composed of phospholipid bilayer and a cell wall that is made of cellulose, chitin, or other polysaccharides.
3. Nucleus and Genetic Material
Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus, and their genetic material is found in a single circular chromosome that is located in the nucleoid region. Eukaryotic cells, by contrast, have a membrane-bound nucleus that contains multiple linear chromosomes. The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which regulates the movement of materials in and out of the nucleus.
4. Organelles
Prokaryotic cells lack membrane-bound organelles, whereas eukaryotic cells have various organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, endoplasmic reticulum, and golgi apparatus. These organelles perform specialized functions such as energy production, photosynthesis, and protein synthesis.
5. Cell Division
Prokaryotic cells divide by a process called binary fission, where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, undergo a more complex process called mitosis, where the cell divides into two daughter cells with identical genetic material.
6. Metabolism
Prokaryotic cells are mostly heterotrophic, meaning they rely on external sources of energy and nutrients. Eukaryotic cells, by contrast, can be autotrophic or heterotrophic, meaning they can produce their own energy and nutrients through photosynthesis or rely on external sources.
7. Evolutionary History
Prokaryotic cells are thought to have evolved first, with evidence suggesting that they existed around 3.5 billion years ago. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, are believed to have evolved around 2.1 billion years ago, with the development of membrane-bound organelles and a true nucleus.
📝 Note: The exact timing of the evolution of eukaryotic cells is still a topic of debate among scientists.
Comparison Table
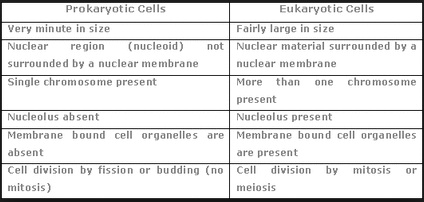
| Characteristics | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Size | 0.5-5.0 μm | 10-100 μm |
| Cell Membrane | Phospholipid bilayer | Phospholipid bilayer with a cell wall |
| Nucleus | No true nucleus | Membrane-bound nucleus |
| Organelles | No membrane-bound organelles | Various membrane-bound organelles |
| Cell Division | Binary fission | Mitosis |
| Metabolism | Heterotrophic | Autotrophic or heterotrophic |
| Evolutionary History | 3.5 billion years ago | 2.1 billion years ago |
In conclusion, prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells have distinct differences in terms of their structure, function, and evolutionary history. Understanding these differences is essential for understanding the complexity of life on Earth.
What is the main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
+The main difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells is the presence or absence of a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus and organelles, whereas eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and various organelles.
Which type of cell is thought to have evolved first?
+Prokaryotic cells are thought to have evolved first, with evidence suggesting that they existed around 3.5 billion years ago.
What is the difference between binary fission and mitosis?
+Binary fission is a process of cell division that occurs in prokaryotic cells, where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Mitosis, on the other hand, is a more complex process of cell division that occurs in eukaryotic cells, where the cell divides into two daughter cells with identical genetic material.