5 Key Differences Between Prokaryote and Eukaryote Cells
Understanding the Building Blocks of Life: Cells
Cells are the basic structural and functional units of living organisms. They are the smallest units of life that can replicate independently, and they are the foundation of all life on Earth. There are two main types of cells: prokaryote and eukaryote cells. While both types of cells are essential for life, they have many distinct differences. In this article, we will explore the 5 key differences between prokaryote and eukaryote cells.
1. Cell Structure
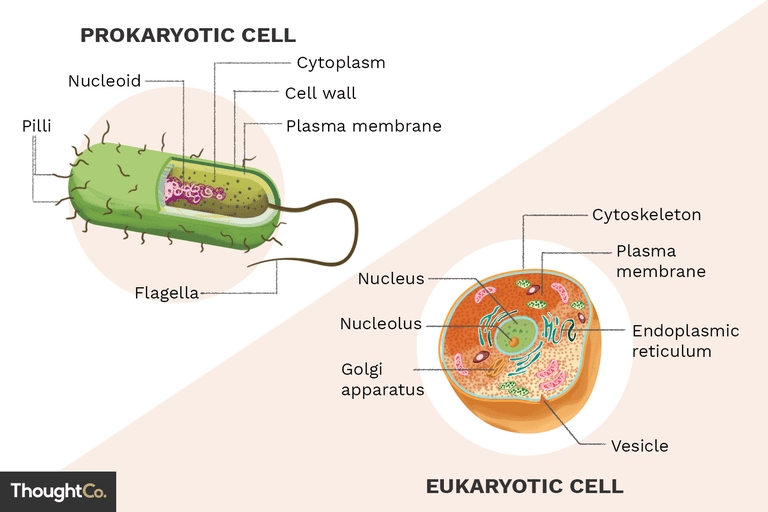
One of the most significant differences between prokaryote and eukaryote cells is their structure. Prokaryote cells, also known as prokaryotes, lack a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. They have a simple structure consisting of a cell wall, a plasma membrane, and a single circular chromosome. On the other hand, eukaryote cells, also known as eukaryotes, have a complex structure with a true nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and a golgi apparatus.
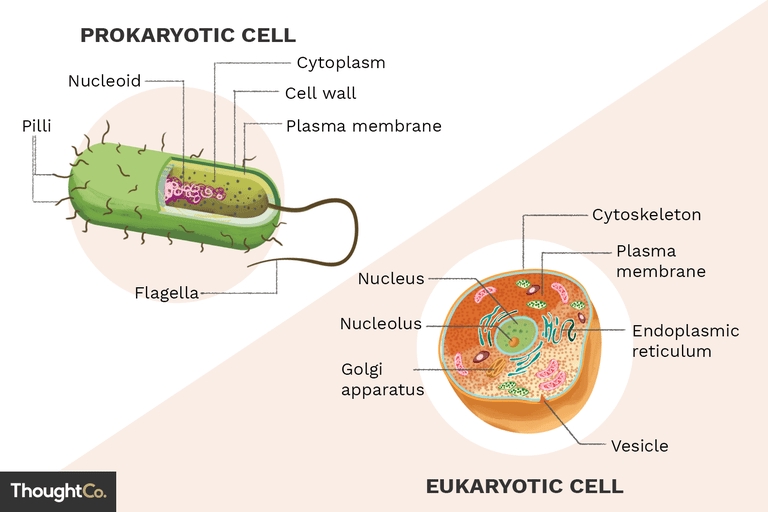
| Prokaryote Cells | Eukaryote Cells |
|---|---|
| No true nucleus | True nucleus with a nuclear membrane |
| No membrane-bound organelles | Membrane-bound organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and golgi apparatus |
| Single circular chromosome | Multiple linear chromosomes |
2. Cell Size
Prokaryote cells are generally smaller than eukaryote cells. Prokaryote cells typically range in size from 1-5 micrometers in diameter, while eukaryote cells can range in size from 10-100 micrometers in diameter. This size difference is due to the complexity of eukaryote cells, which require more space to accommodate their multiple organelles and larger nuclei.
3. Reproduction
Prokaryote cells reproduce by a process called binary fission, where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. Eukaryote cells, on the other hand, reproduce by a process called mitosis, where the cell divides into two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
4. Metabolism
Prokaryote cells have a simple metabolism and are able to survive in a wide range of environments. They are able to perform photosynthesis, respiration, and fermentation, and are able to survive in extreme environments such as high temperatures and high salinity. Eukaryote cells, on the other hand, have a more complex metabolism and are able to perform a wider range of functions, including photosynthesis, respiration, and the synthesis of complex molecules.
5. Evolution
Prokaryote cells are thought to have evolved first, around 3.5 billion years ago. They were able to survive in a wide range of environments and were able to evolve into different species. Eukaryote cells, on the other hand, are thought to have evolved around 2 billion years ago, and are thought to have evolved from a group of prokaryote cells called archaea.
🔬 Note: The exact timing of the evolution of eukaryote cells is still a topic of debate among scientists.
In conclusion, prokaryote and eukaryote cells are two distinct types of cells that have many differences in terms of their structure, size, reproduction, metabolism, and evolution. Understanding these differences is essential for understanding the complexity of life on Earth.
What is the main difference between prokaryote and eukaryote cells?
+The main difference between prokaryote and eukaryote cells is the presence or absence of a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Which type of cell is thought to have evolved first?
+Prokaryote cells are thought to have evolved first, around 3.5 billion years ago.
What is the process by which eukaryote cells reproduce?
+Eukaryote cells reproduce by a process called mitosis, where the cell divides into two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.