Points Lines And Planes Worksheet
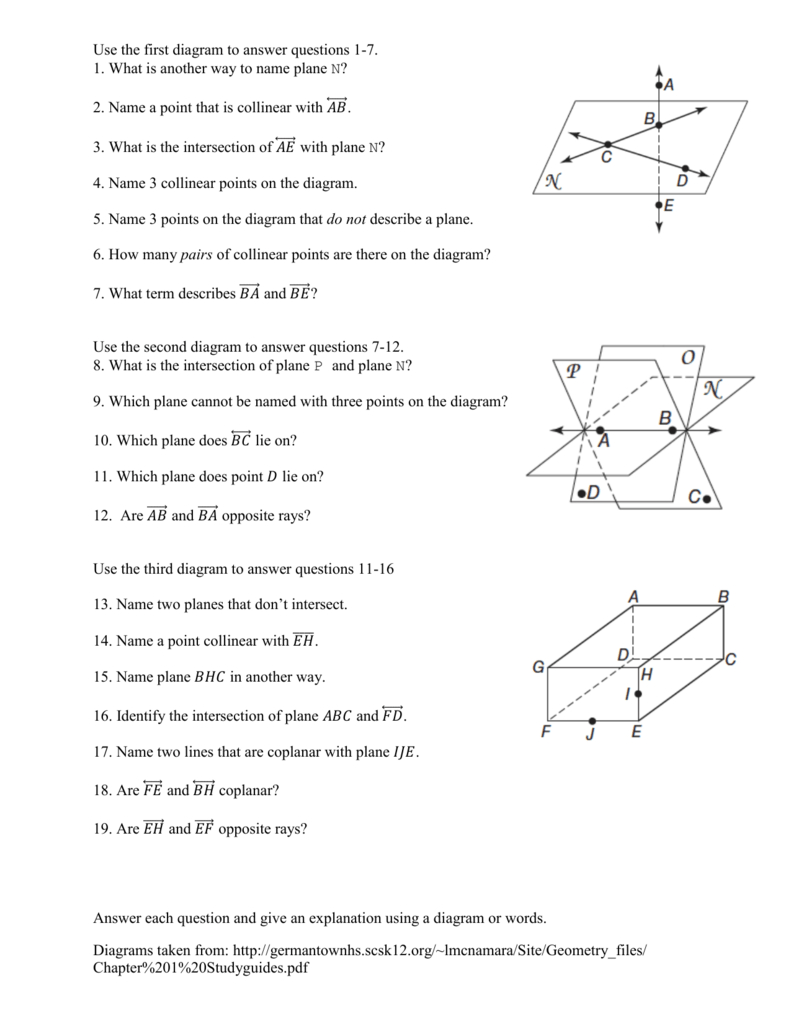
Understanding Points, Lines, and Planes
In geometry, points, lines, and planes are the fundamental building blocks of all shapes and objects. Understanding these concepts is crucial for problem-solving and critical thinking in mathematics and real-world applications.
Points
A point is a location in space, represented by a set of coordinates. It has no size or dimension, only position. Points are usually represented by a dot (•) on a coordinate plane.
Key Characteristics of Points:
- A point has no size or dimension.
- A point is represented by a set of coordinates (x, y, z).
- Points are used to define the position of objects in space.
Lines
A line is a set of points that extend infinitely in two directions. It has no thickness or width, only length. Lines can be straight or curved.
Key Characteristics of Lines:
- A line has no thickness or width.
- A line extends infinitely in two directions.
- Lines can be straight or curved.
- Lines can be represented by two points (A and B).
Planes
A plane is a flat surface that extends infinitely in all directions. It has no thickness, only length and width. Planes can be oriented at different angles.
Key Characteristics of Planes:
- A plane has no thickness.
- A plane extends infinitely in all directions.
- Planes can be oriented at different angles.
- Planes can be represented by three points (A, B, and C).
Relationships Between Points, Lines, and Planes
Points, lines, and planes are related in several ways:
- A line is defined by two points.
- A plane is defined by three points.
- A line can intersect a plane at a single point.
- A plane can contain multiple lines and points.
Real-World Applications
Understanding points, lines, and planes is essential in various real-world applications, such as:
- Architecture: designing buildings and bridges.
- Engineering: designing roads, bridges, and electronic circuits.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD): creating 2D and 3D models.
- Physics: describing the motion of objects in space.
Worksheet
Now, let’s practice identifying and working with points, lines, and planes with the following worksheet:
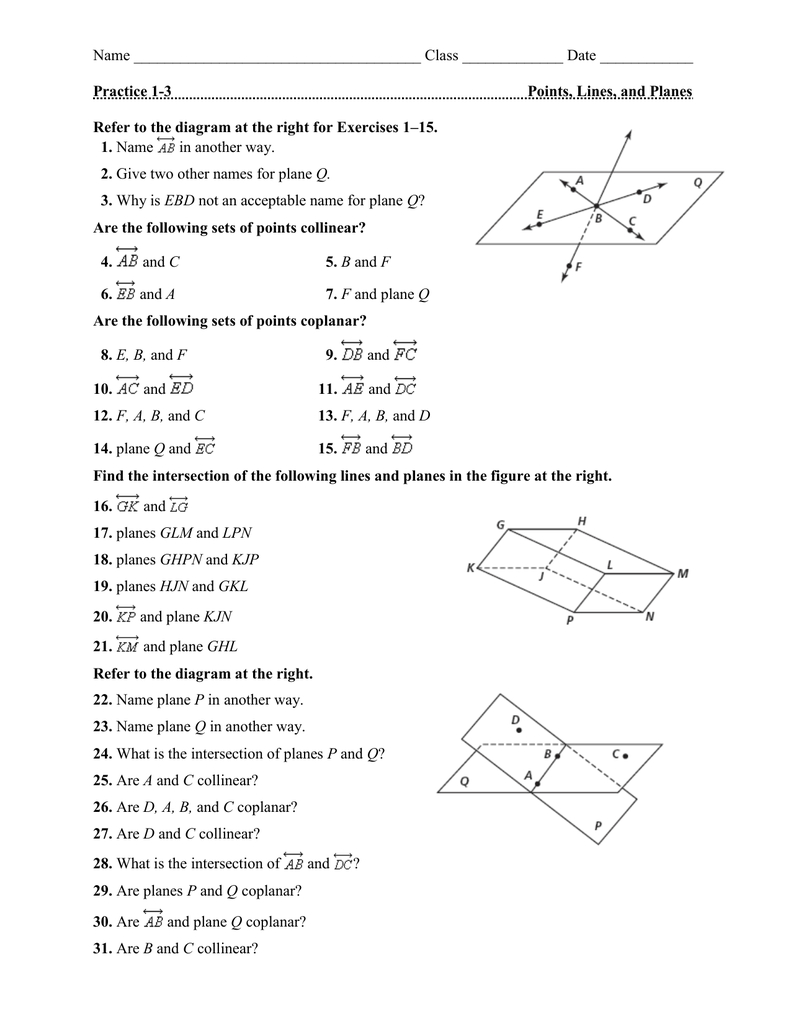
| Problem | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is the definition of a point in geometry? | A point is a location in space, represented by a set of coordinates. |
| What are the key characteristics of a line? | A line has no thickness or width, extends infinitely in two directions, and can be straight or curved. |
| How many points are needed to define a plane? | Three points are needed to define a plane. |
| What is the relationship between a line and a plane? | A line can intersect a plane at a single point. |
📝 Note: For more practice problems and exercises, refer to your geometry textbook or online resources.
Solutions
Answers to the worksheet problems are provided above. Make sure to review the concepts and practice more problems to reinforce your understanding of points, lines, and planes.
In this blog post, we explored the fundamental concepts of points, lines, and planes in geometry. Understanding these building blocks is crucial for problem-solving and critical thinking in mathematics and real-world applications. By practicing and applying these concepts, you’ll become proficient in geometry and develop a strong foundation for more advanced math topics.
What is the difference between a point and a line?
+A point is a location in space, represented by a set of coordinates, while a line is a set of points that extend infinitely in two directions.
How many points are needed to define a line?
+Two points are needed to define a line.
What is the relationship between a point and a plane?
+A point can be part of a plane, and a plane can contain multiple points.