Mastering Line Graphs: A Step-by-Step Interpretation Guide
Understanding Line Graphs: A Comprehensive Guide
Line graphs are one of the most widely used data visualization tools, offering a simple yet effective way to display trends and patterns in data over time. They consist of a series of data points connected by line segments, making it easy to see the relationship between the data points and how they change over time. In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of line graphs, exploring how to read, interpret, and create them.
Components of a Line Graph
Before we dive into the interpretation of line graphs, it’s essential to understand the components that make up a line graph. The typical components of a line graph include:
- X-axis: The horizontal axis, which represents the independent variable, often time or categories.
- Y-axis: The vertical axis, which represents the dependent variable, often the value or quantity being measured.
- Data points: The individual points on the graph that represent the data values.
- Line segments: The lines that connect the data points, showing the trend or pattern in the data.
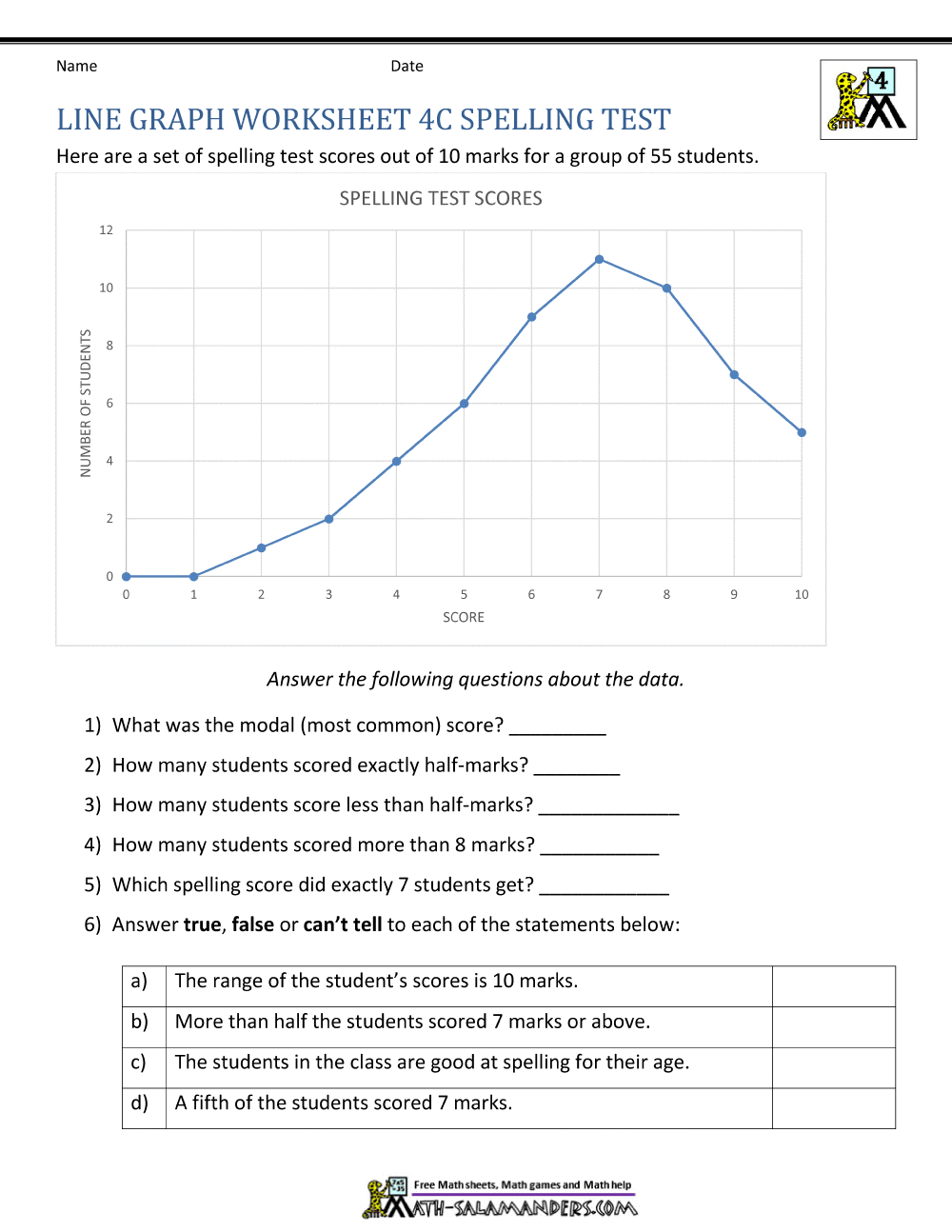
How to Read a Line Graph
Reading a line graph involves understanding the relationship between the data points and the trend or pattern they represent. Here are some steps to follow:
- Identify the x-axis and y-axis: Understand what the x-axis and y-axis represent, as this will help you interpret the data.
- Look for patterns and trends: Examine the line segments to identify any patterns or trends in the data. Are the values increasing or decreasing over time?
- Check for anomalies: Look for any unusual data points that may be outliers or anomalies.
- Compare data points: Compare the values of different data points to see how they relate to each other.
Interpreting Line Graphs
Interpreting line graphs requires a deeper understanding of the data and its implications. Here are some tips:
- Look for correlations: Identify any correlations between the data points and external factors, such as economic trends or seasonal changes.
- Identify turning points: Look for points where the trend changes direction, indicating a significant shift in the data.
- Analyze the slope: The slope of the line can indicate the rate of change in the data. A steep slope indicates a rapid change, while a shallow slope indicates a slower change.
📝 Note: When interpreting line graphs, it's essential to consider the context of the data and any external factors that may influence the trend or pattern.
Creating Line Graphs
Creating line graphs involves several steps:
- Collect and organize data: Gather the data and organize it in a table or spreadsheet.
- Choose a scale: Select a suitable scale for the x-axis and y-axis, ensuring that the data points are evenly spaced and easy to read.
- Plot the data points: Plot the data points on the graph, using a consistent marker or symbol.
- Draw the line segments: Draw the line segments to connect the data points, using a smooth curve or straight line.
Best Practices for Creating Line Graphs
Here are some best practices to keep in mind when creating line graphs:
- Use clear labels: Use clear and concise labels for the x-axis and y-axis.
- Choose a suitable color scheme: Select a color scheme that is easy to read and distinguish between different data sets.
- Avoid clutter: Avoid cluttering the graph with too many data points or unnecessary information.
📈 Note: When creating line graphs, it's essential to consider the audience and the purpose of the graph, ensuring that the design is clear and effective.
What is the primary purpose of a line graph?
+The primary purpose of a line graph is to display trends and patterns in data over time, making it easy to see the relationship between the data points and how they change over time.
What are the components of a line graph?
+The typical components of a line graph include the x-axis, y-axis, data points, and line segments.
How do I interpret a line graph?
+To interpret a line graph, identify the x-axis and y-axis, look for patterns and trends, check for anomalies, and compare data points.
In conclusion, mastering line graphs requires a deep understanding of the components, how to read and interpret the data, and best practices for creating effective line graphs. By following these guidelines, you’ll be well on your way to becoming proficient in creating and interpreting line graphs, unlocking the secrets of data visualization.
Related Terms:
- Interpreting line graphs worksheet PDF
- Year 5 line graphs worksheets
- Linear graph Worksheet pdf