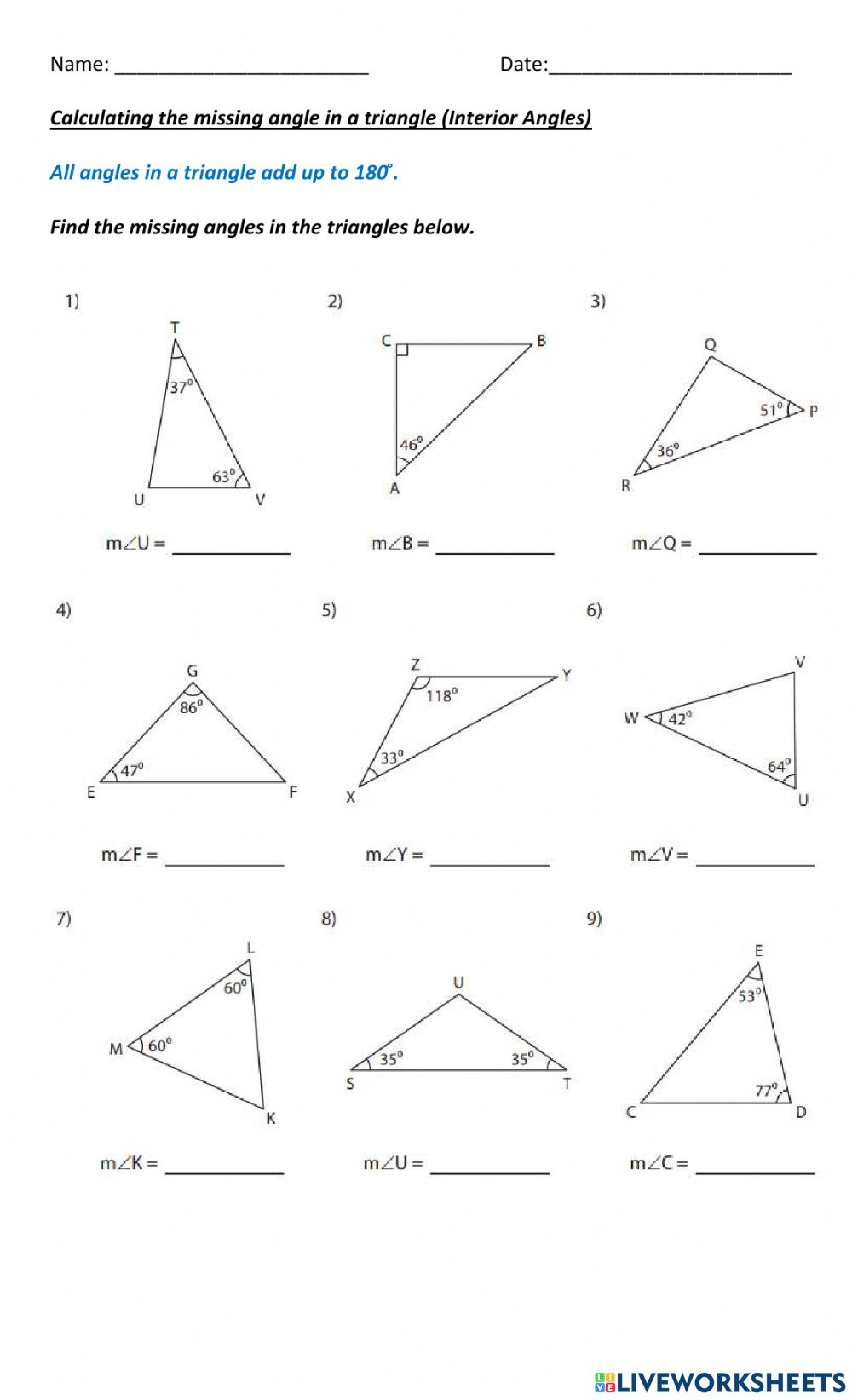
6 Essential Parts of a Plant Cell to Label

Exploring the Fundamental Components of a Plant Cell
Plant cells are the basic structural and functional units of plants, and they play a crucial role in the growth, development, and reproduction of plants. Understanding the different parts of a plant cell is essential for botany and biology students, as well as for anyone interested in the natural world. In this article, we will delve into the six essential parts of a plant cell that you should label.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance within the plant cell, surrounding the organelles and providing a medium for chemical reactions to occur. It is a vital component of the cell, responsible for maintaining the cell’s shape and providing mechanical support. The cytoplasm is composed of water, salts, sugars, and various organic molecules.
Cell Wall
The cell wall is a rigid layer outside the cell membrane that provides structural support and protection to the plant cell. It is composed of cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin, which are complex carbohydrates that give the cell wall its strength and rigidity. The cell wall also plays a role in cell signaling and communication.
Chloroplasts
Chloroplasts are organelles found in plant cells that are responsible for photosynthesis, the process of converting light energy into chemical energy. Chloroplasts contain the pigment chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy and transfers it to other molecules, resulting in the production of glucose and oxygen. Chloroplasts are unique to plant cells and are essential for plant growth and development.
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are membrane-bound organelles that are responsible for storing water, salts, and other substances. They play a crucial role in maintaining the cell’s turgor pressure and providing structural support to the plant cell. Vacuoles also contain enzymes that break down and recycle cellular waste.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the control center of the plant cell, containing most of the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. The nucleus regulates cell growth, division, and differentiation, and it is responsible for transmitting genetic information from one generation to the next. The nucleus is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of membranous tubules and cisternae that is responsible for transporting materials throughout the plant cell. The ER is involved in the synthesis and transport of proteins, lipids, and other molecules. It also plays a role in cell signaling and communication.
👍 Note: When labeling a plant cell, it's essential to include these six essential parts to ensure that you have a complete and accurate representation of the cell's structure and function.
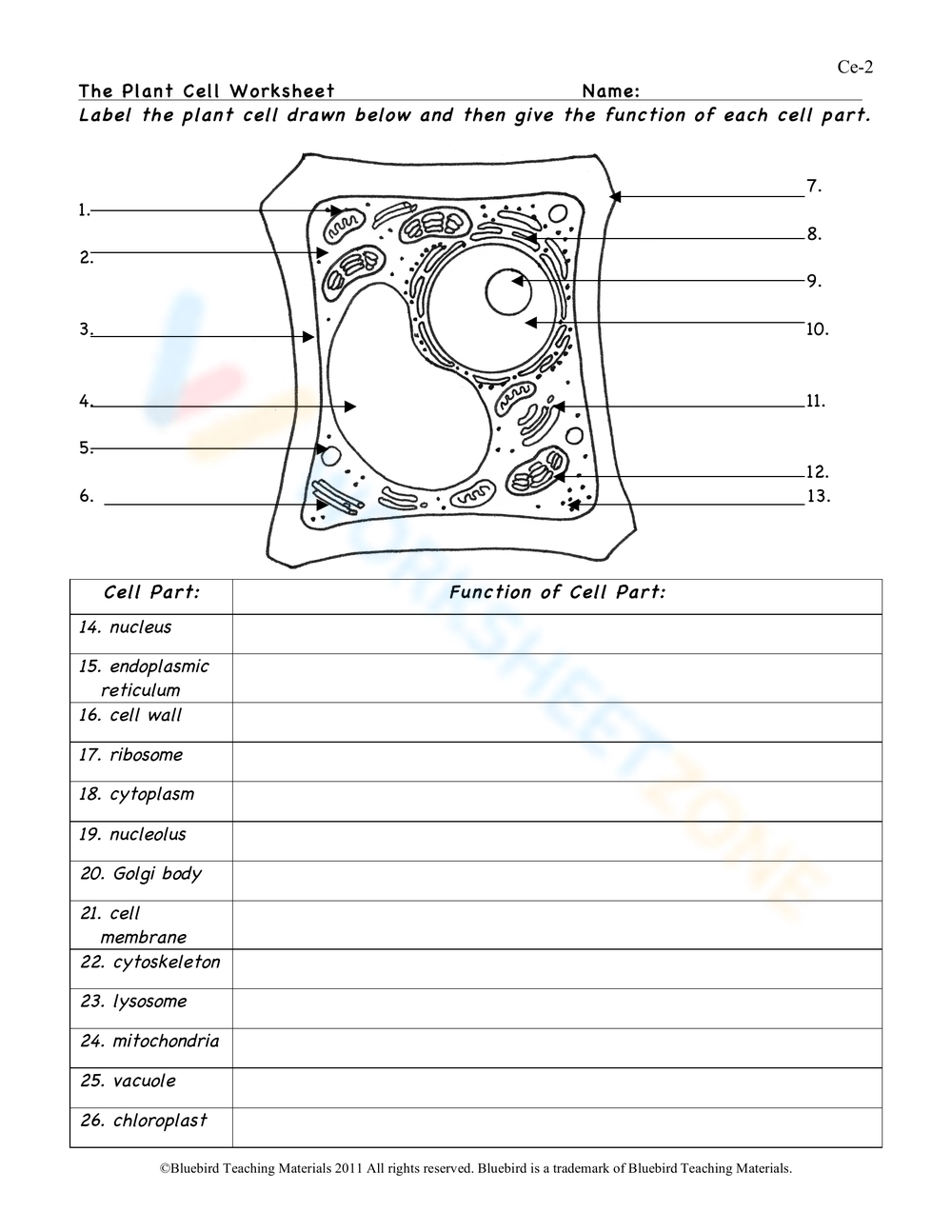
| Part of the Plant Cell | Description |
|---|---|
| Cytoplasm | Jelly-like substance surrounding the organelles |
| Cell Wall | Rigid layer outside the cell membrane providing structural support |
| Chloroplasts | Organelles responsible for photosynthesis |
| Vacuoles | Membrane-bound organelles storing water, salts, and other substances |
| Nucleus | Control center of the plant cell containing genetic material |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER) | Network of membranous tubules and cisternae transporting materials |
In summary, labeling a plant cell requires attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the different parts that make up the cell. By including the cytoplasm, cell wall, chloroplasts, vacuoles, nucleus, and endoplasmic reticulum, you can ensure that you have a complete and accurate representation of the plant cell’s structure and function.
What is the primary function of the cell wall in a plant cell?
+The primary function of the cell wall is to provide structural support and protection to the plant cell.
Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis in a plant cell?
+Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis in a plant cell.
What is the function of the nucleus in a plant cell?
+The nucleus is the control center of the plant cell, containing most of the cell’s genetic material and regulating cell growth, division, and differentiation.
Related Terms:
- The plant cell worksheet
- Plant cell worksheet With Answers
- Plant cell Worksheet PDF
- Animal cell diagram
- Animal cell worksheet
- Plant cell diagram