Cell Diagram Worksheet: Explore Plant and Animal Cells
Understanding Cell Structure: A Comprehensive Guide
Cells are the basic building blocks of life, and understanding their structure and function is crucial for any biology student. In this worksheet, we will explore the cell diagrams of plant and animal cells, highlighting their similarities and differences.
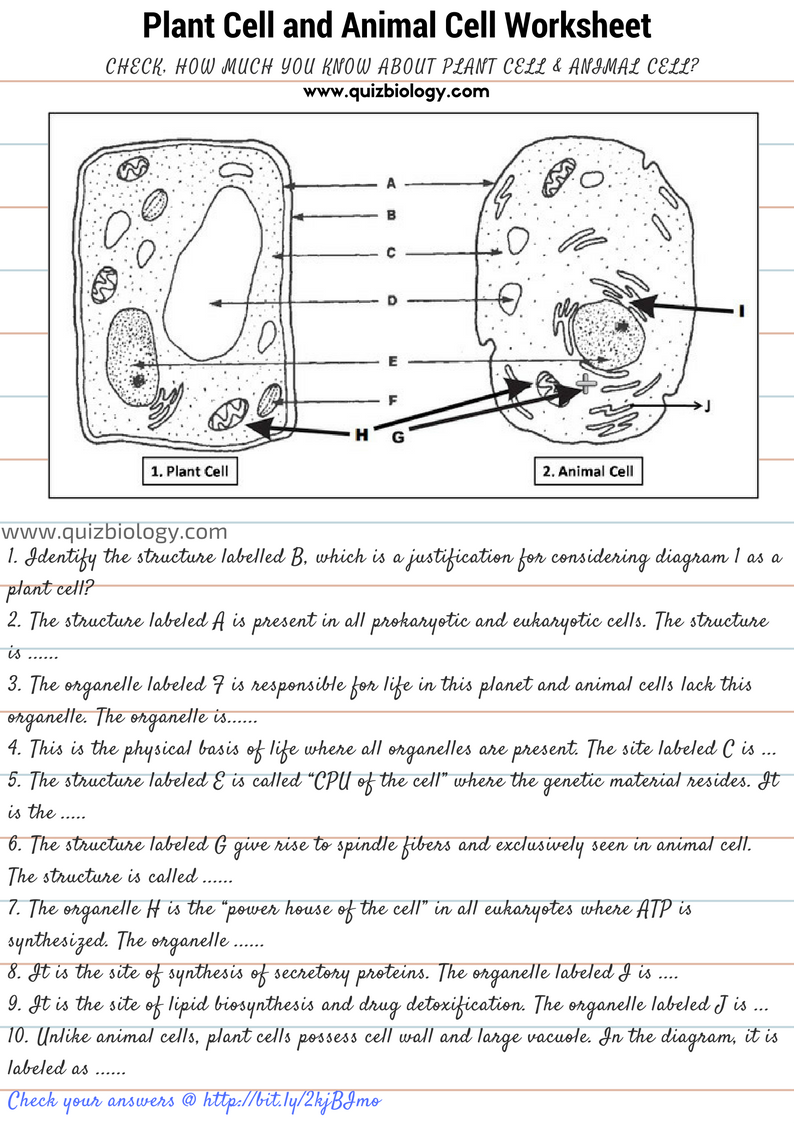
Plant Cell Diagram
Plant cells are eukaryotic cells that are part of plants and are characterized by the presence of a cell wall. The following is a labeled diagram of a plant cell:
| Cell Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Cell Wall | A rigid layer outside the cell membrane that provides support and protection |
| Cell Membrane | A semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of substances in and out |
| Cytoplasm | A jelly-like substance inside the cell membrane where many metabolic processes take place |
| Nucleus | The control center of the cell where DNA is stored |
| Chloroplasts | Organelles responsible for photosynthesis, found only in plant cells |
| Vacuoles | Storage organelles that contain water, salts, and other substances |
Animal Cell Diagram
Animal cells are also eukaryotic cells, but they do not have a cell wall. The following is a labeled diagram of an animal cell:
| Cell Component | Description |
|---|---|
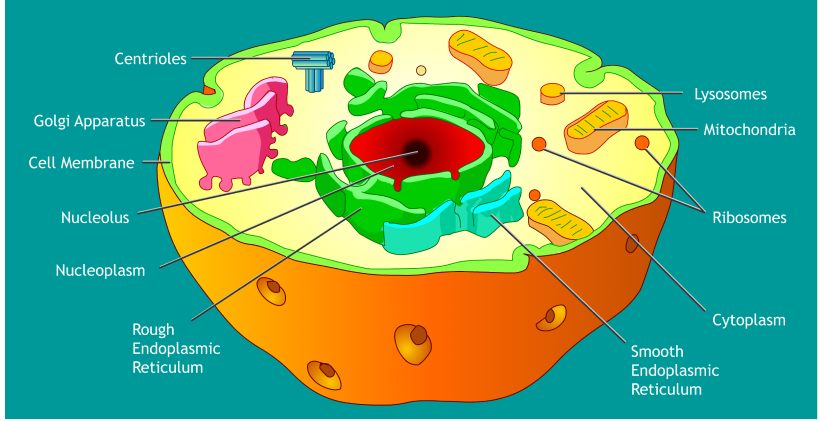
| Cell Membrane | A semi-permeable membrane that surrounds the cell and regulates the movement of substances in and out |
| Cytoplasm | A jelly-like substance inside the cell membrane where many metabolic processes take place |
| Nucleus | The control center of the cell where DNA is stored |
| Mitochondria | Organelles responsible for generating energy for the cell through cellular respiration |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | A network of membranous tubules and cisternae that transport materials throughout the cell |
| Lysosomes | Membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes |
Similarities and Differences between Plant and Animal Cells
While both plant and animal cells are eukaryotic cells, there are several similarities and differences between them. Some of the similarities include:
- Both have a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleus
- Both have mitochondria for energy production
- Both have endoplasmic reticulum for transporting materials
However, there are also several differences:
- Plant cells have a cell wall, while animal cells do not
- Plant cells have chloroplasts for photosynthesis, while animal cells do not
- Plant cells have vacuoles for storage, while animal cells have lysosomes for digestion
📝 Note: It's essential to understand the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells to appreciate their unique structures and functions.
In conclusion, understanding the structure and function of plant and animal cells is crucial for any biology student. By studying cell diagrams and identifying the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells, students can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and diversity of life on Earth.
What is the main difference between plant and animal cells?
+The main difference between plant and animal cells is the presence of a cell wall in plant cells, which is absent in animal cells.
What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
+Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis, the process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
What is the function of lysosomes in animal cells?
+Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles that contain digestive enzymes, responsible for breaking down and recycling cellular waste and foreign substances.