Physical Science Worksheet Conservation Of Energy #2

Understanding the Concept of Conservation of Energy
Conservation of energy is a fundamental concept in physical science that states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant over time. Energy can neither be created nor destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This concept is essential in understanding various phenomena in the physical world, from the simplest to the most complex systems.
Forms of Energy
Energy comes in various forms, including:
- Kinetic Energy: The energy of motion. An object possesses kinetic energy when it is moving.
- Potential Energy: The energy an object possesses due to its position or configuration. This can be gravitational (e.g., water stored behind a dam) or elastic (e.g., a stretched rubber band).
- Thermal Energy: The energy an object possesses due to the motion of its particles, which is related to its temperature.
- Electrical Energy: The energy associated with the movement of electrons.
- Chemical Energy: The energy stored in the bonds of chemical compounds. This energy is released or absorbed during chemical reactions.
- Radiant Energy: The energy of electromagnetic waves, including light and radio waves.
Transformations of Energy
Energy transformations occur when energy changes from one form to another. These transformations are essential for understanding how energy is conserved in various processes.
- Mechanical to Thermal: Friction is a classic example where mechanical energy (kinetic or potential) is transformed into thermal energy.
- Electrical to Light: A light bulb transforms electrical energy into radiant energy (light).
- Chemical to Mechanical: In a car engine, chemical energy from gasoline is transformed into mechanical energy (the movement of the car).
Work and Energy
Work is closely related to energy. When a force is applied to an object, causing it to move, work is done. The amount of work done is equal to the change in energy of the object.
- Work-Energy Theorem: States that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy.
Conservation of Energy in Real-World Scenarios
Understanding conservation of energy helps in analyzing and solving problems in various fields.
- Hydroelectric Power Plants: Water stored behind a dam has potential energy. As it falls, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy, which is then used to generate electrical energy.
- Solar Panels: Convert radiant energy (sunlight) into electrical energy.
🌟 Note: Conservation of energy is a fundamental principle that helps us understand and analyze energy transformations in various systems.
Calculating Energy
Energy calculations are crucial in understanding how energy is conserved and transformed.
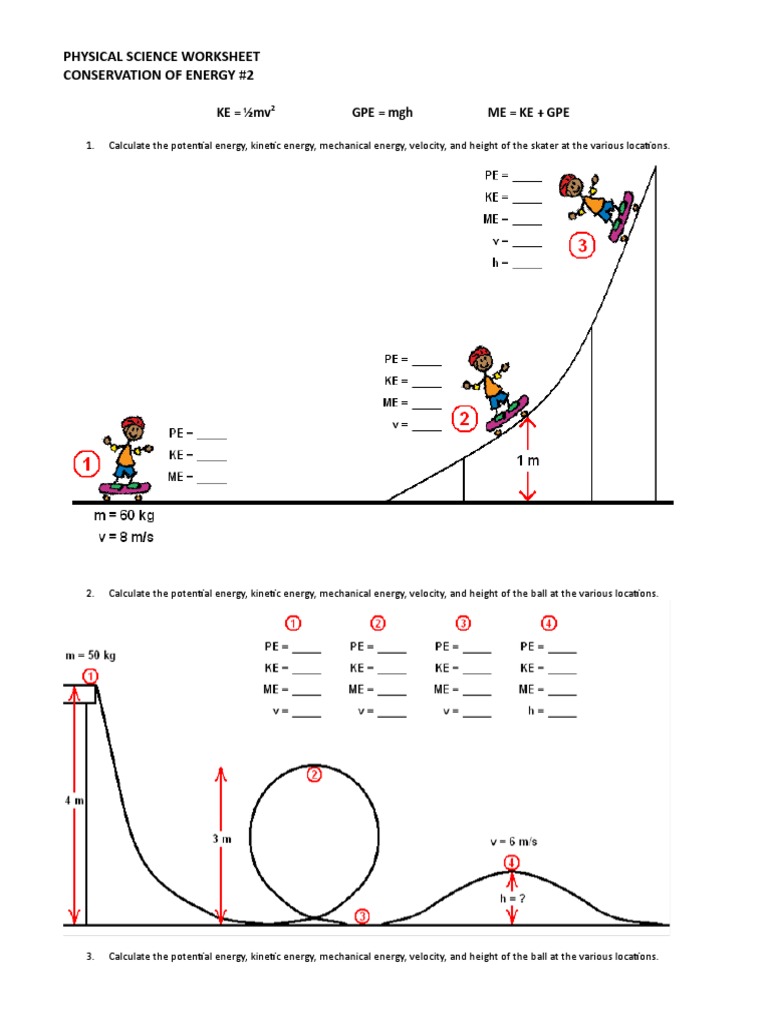
| Form of Energy | Formula |
|---|---|
| Kinetic Energy | (KE = \frac{1}{2}mv^2) |
| Potential Energy | (PE = mgh) |
| Thermal Energy | (Q = mc\Delta T) |
Conclusion
Conservation of energy is a powerful tool for understanding the world around us. By recognizing the various forms of energy and how they transform from one form to another, we can analyze and predict the behavior of complex systems. This concept is fundamental in science and engineering, enabling us to harness and utilize energy more efficiently.
What is the law of conservation of energy?
+The law of conservation of energy states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another.
Give an example of energy transformation.
+A light bulb transforms electrical energy into radiant energy (light) and thermal energy (heat).
What is the work-energy theorem?
+The work-energy theorem states that the net work done on an object is equal to its change in kinetic energy.