7 Ways to Master Ionic Bonds in Chemistry
Understanding Ionic Bonds: A Comprehensive Guide
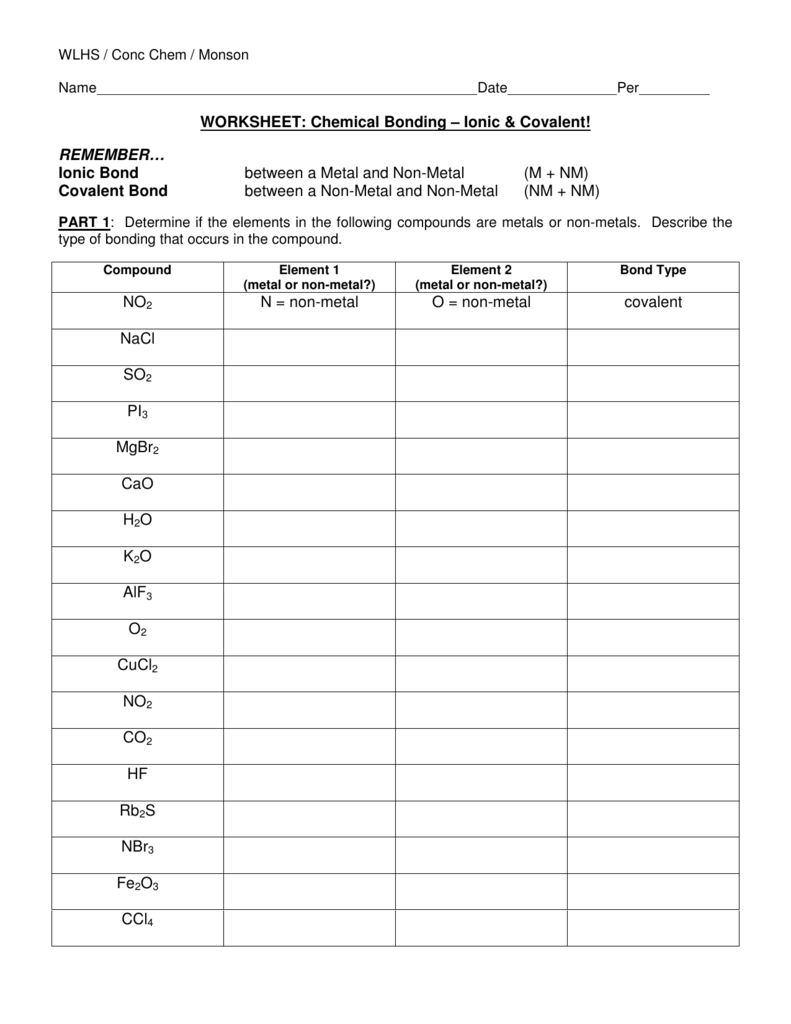
Ionic bonds are a fundamental concept in chemistry, and mastering them is crucial for understanding the structure and properties of molecules. In this article, we will delve into the world of ionic bonds, exploring what they are, how they form, and providing you with 7 ways to master them.
What are Ionic Bonds?
Ionic bonds are a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms with significantly different electronegativities. This difference in electronegativity leads to the transfer of one or more electrons from the less electronegative atom (typically a metal) to the more electronegative atom (typically a nonmetal). The resulting ions are electrostatically attracted to each other, forming a strong chemical bond.
How Do Ionic Bonds Form?
The formation of ionic bonds involves the following steps:
- Electron transfer: The less electronegative atom (metal) loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion (cation).
- Electron gain: The more electronegative atom (nonmetal) gains one or more electrons to form a negatively charged ion (anion).
- Electrostatic attraction: The positively charged cation is electrostatically attracted to the negatively charged anion, forming a strong chemical bond.
7 Ways to Master Ionic Bonds
Mastering ionic bonds requires a deep understanding of their formation, properties, and applications. Here are 7 ways to help you master ionic bonds:
1. Understand the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a powerful tool for understanding ionic bonds. By analyzing the periodic table, you can identify the electronegativity of different elements and predict which elements are likely to form ionic bonds.
- Metals: Tend to lose electrons to form cations.
- Nonmetals: Tend to gain electrons to form anions.
🔍 Note: Familiarize yourself with the periodic table to quickly identify the electronegativity of elements.
2. Learn to Identify Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are formed when a metal and a nonmetal combine. To identify ionic compounds, look for the following characteristics:
- Metal and nonmetal: Ionic compounds typically consist of a metal and a nonmetal.
- High melting point: Ionic compounds have high melting points due to the strong electrostatic attraction between ions.
- High boiling point: Ionic compounds have high boiling points due to the strong electrostatic attraction between ions.
3. Understand the Octet Rule
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain or lose electrons to achieve a full outer energy level, typically consisting of eight electrons. This rule is crucial for understanding the formation of ionic bonds.
- Cations: Typically have a full outer energy level with eight electrons.
- Anions: Typically have a full outer energy level with eight electrons.
4. Practice Writing Ionic Formulas
Writing ionic formulas requires a deep understanding of the charges on ions. To write an ionic formula, follow these steps:
- Determine the charges: Identify the charges on the cation and anion.
- Balance the charges: Balance the charges to form a neutral compound.
| Cation | Anion | Ionic Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Na+ | Cl- | NaCl |
| Ca2+ | O2- | CaO |
| Al3+ | N3- | AlN |
5. Learn to Name Ionic Compounds
Naming ionic compounds requires a deep understanding of the charges on ions. To name an ionic compound, follow these steps:
Name the cation: Name the cation first, using the suffix “-ium” for metals.
Name the anion: Name the anion second, using the suffix “-ide” for nonmetals.
NaCl: Sodium chloride
CaO: Calcium oxide
AlN: Aluminum nitride
6. Understand the Properties of Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds have distinct properties, including:
- High melting and boiling points: Ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points due to the strong electrostatic attraction between ions.
- Solubility: Ionic compounds are typically soluble in water.
- Conductivity: Ionic compounds are typically good conductors of electricity.
7. Apply Ionic Bonds to Real-World Situations
Ionic bonds have numerous applications in real-world situations, including:
- Batteries: Ionic bonds are used in batteries to store electrical energy.
- Medicine: Ionic bonds are used in medicine to develop new treatments for diseases.
- Materials science: Ionic bonds are used in materials science to develop new materials with unique properties.
In summary, mastering ionic bonds requires a deep understanding of their formation, properties, and applications. By following these 7 ways, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a master of ionic bonds.
What is the difference between an ionic bond and a covalent bond?
+
An ionic bond is a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms with significantly different electronegativities, resulting in the transfer of one or more electrons. A covalent bond, on the other hand, is a type of chemical bond that forms between two atoms that share one or more pairs of electrons.
What is the octet rule, and how does it relate to ionic bonds?
+
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain or lose electrons to achieve a full outer energy level, typically consisting of eight electrons. This rule is crucial for understanding the formation of ionic bonds, as atoms tend to form ions with full outer energy levels.
What are some common applications of ionic bonds?
+
Ionic bonds have numerous applications in real-world situations, including batteries, medicine, and materials science. They are used to store electrical energy, develop new treatments for diseases, and develop new materials with unique properties.
Related Terms:
- Metallic bonding GCSE questions pdf
- Covalent bond Worksheet pdf
- Identifying CHEMICAL BONDS Worksheet
- Ionic and covalent bonds worksheet
- Ionic and covalent bonds PDF
- Molecular Bonding Worksheet



