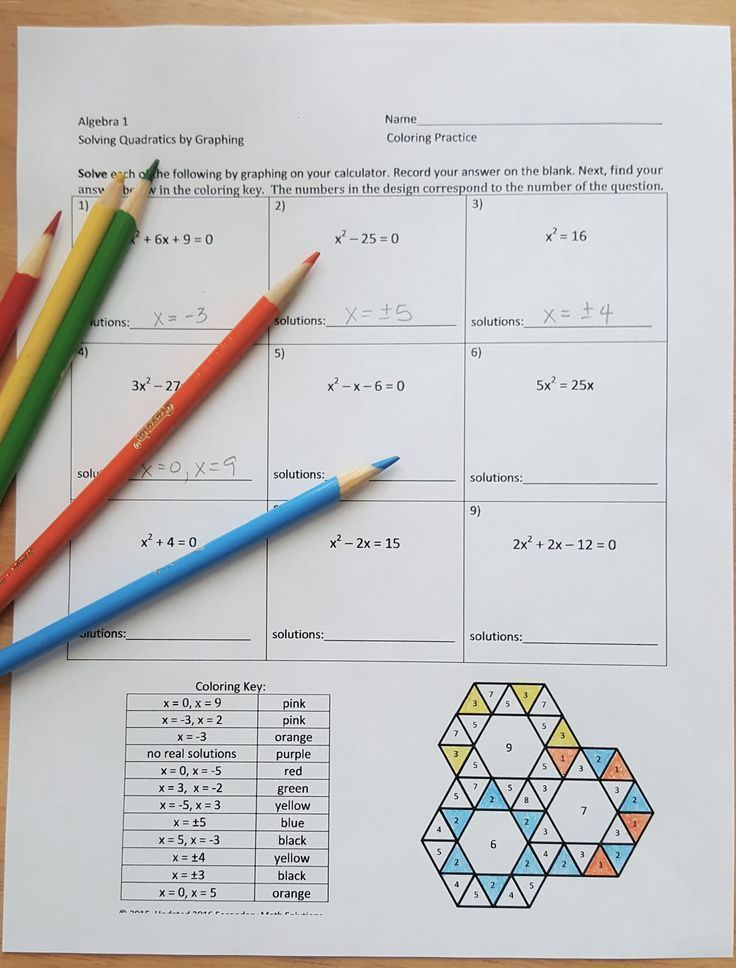
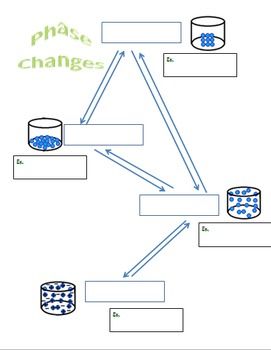
Phase Diagram Worksheet Answers Key

Understanding Phase Diagrams
Phase diagrams are graphical representations of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure. They are essential tools in chemistry, physics, and materials science, helping us understand the behavior of substances and predict their properties. In this post, we will explore the basics of phase diagrams, including the different types, how to read them, and their applications.
Types of Phase Diagrams
There are several types of phase diagrams, each with its own specific characteristics and applications.
- Simple Phase Diagram: This is the most basic type of phase diagram, showing the relationship between temperature and pressure for a single component system. It typically consists of three phases: solid, liquid, and gas.
- Binary Phase Diagram: This type of diagram shows the relationship between temperature and composition for a two-component system. It is commonly used to study the behavior of alloys and mixtures.
- Ternary Phase Diagram: This diagram shows the relationship between temperature and composition for a three-component system. It is used to study the behavior of complex mixtures and alloys.
Reading Phase Diagrams
Reading phase diagrams requires a basic understanding of the different phases and the transitions between them.
- Phase Boundaries: Phase boundaries are the lines that separate the different phases on a phase diagram. They represent the conditions under which a phase transition occurs.
- Triple Point: The triple point is the point on a phase diagram where the three phase boundaries meet. It represents the unique set of conditions under which all three phases coexist.
- Critical Point: The critical point is the point on a phase diagram where the liquid-vapor phase boundary terminates. It represents the conditions under which the liquid and vapor phases become indistinguishable.
Phase Diagram Worksheet Answers Key
Here are the answers to a sample phase diagram worksheet:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. What is the term for the line on a phase diagram that separates the solid and liquid phases? | Melting curve |
| 2. What is the term for the point on a phase diagram where the solid, liquid, and vapor phases meet? | Triple point |
| 3. What is the term for the point on a phase diagram where the liquid-vapor phase boundary terminates? | Critical point |
| 4. What type of phase diagram shows the relationship between temperature and composition for a two-component system? | Binary phase diagram |
| 5. What type of phase diagram shows the relationship between temperature and composition for a three-component system? | Ternary phase diagram |
📝 Note: The answers provided are for a sample worksheet and may not be applicable to all phase diagram worksheets.
Applications of Phase Diagrams
Phase diagrams have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Materials Science: Phase diagrams are used to study the behavior of materials and predict their properties.
- Chemical Engineering: Phase diagrams are used to design and optimize chemical processes.
- Geology: Phase diagrams are used to study the behavior of rocks and minerals.
- Biology: Phase diagrams are used to study the behavior of biomolecules and predict their properties.
Conclusion
In conclusion, phase diagrams are powerful tools that help us understand the behavior of substances under different conditions of temperature and pressure. By understanding how to read and interpret phase diagrams, we can gain valuable insights into the properties of materials and predict their behavior.
What is a phase diagram?
+A phase diagram is a graphical representation of the physical states of a substance under different conditions of temperature and pressure.
What are the different types of phase diagrams?
+There are several types of phase diagrams, including simple phase diagrams, binary phase diagrams, and ternary phase diagrams.
What is the triple point on a phase diagram?
+The triple point is the point on a phase diagram where the solid, liquid, and vapor phases meet.