Phase Changes Worksheet Made Easy

Phase Changes Worksheet Made Easy
Phase changes are an essential concept in chemistry, physics, and various scientific fields. A phase change is a transformation of a substance from one state of matter to another, such as from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas. In this article, we will explore the different types of phase changes, how to calculate them, and provide a worksheet to help you practice and reinforce your understanding.
Types of Phase Changes
There are several types of phase changes, including:
- Melting: The transition from solid to liquid
- Boiling: The transition from liquid to gas
- Freezing: The transition from liquid to solid
- Condensation: The transition from gas to liquid
- Sublimation: The transition from solid to gas
- Deposition: The transition from gas to solid
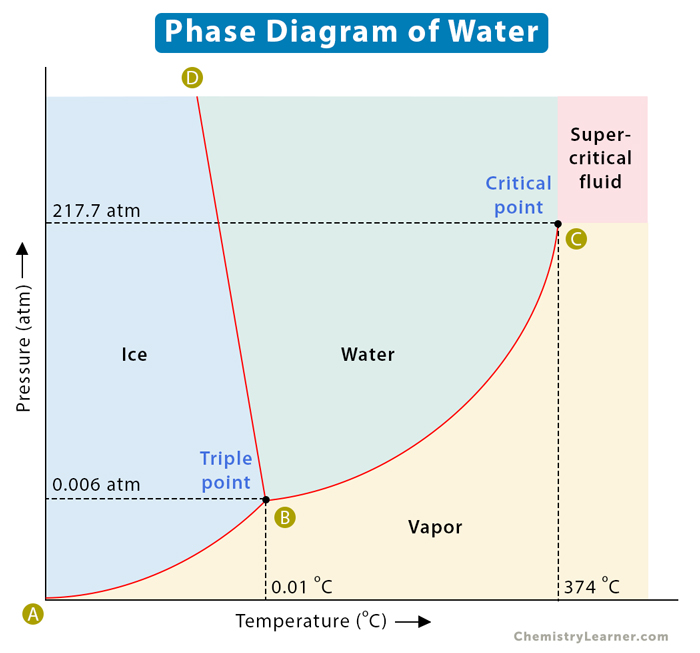
Phase Change Diagrams
A phase change diagram is a graph that shows the relationship between the temperature and pressure of a substance as it undergoes a phase change. The diagram typically includes the following lines:
- Solid-liquid equilibrium line: The line that separates the solid and liquid phases
- Liquid-gas equilibrium line: The line that separates the liquid and gas phases
- Triple point: The point where the solid, liquid, and gas phases coexist
Calculating Phase Changes
To calculate phase changes, you need to know the following:
- Heat of fusion (ΔHf): The energy required to melt a substance
- Heat of vaporization (ΔHv): The energy required to vaporize a substance
- Molar heat capacity (Cp): The energy required to raise the temperature of a substance by 1°C
The formulas to calculate phase changes are:
- ΔH = m × ΔHf: The energy required to melt a substance
- ΔH = m × ΔHv: The energy required to vaporize a substance
- ΔT = Q / (m × Cp): The change in temperature of a substance
Worksheet
Here is a worksheet to help you practice calculating phase changes:
| Substance | ΔHf (kJ/mol) | ΔHv (kJ/mol) | Cp (J/g°C) | Mass (g) | Initial Temperature (°C) | Final Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 6.01 | 40.7 | 4.18 | 50 | 20 | 100 |
| Ice | 6.01 | 40.7 | 2.05 | 25 | -10 | 0 |
| Steam | 6.01 | 40.7 | 1.99 | 10 | 100 | 200 |
Calculate the energy required to melt, vaporize, and change the temperature of each substance.
📝 Note: Use the formulas provided earlier to calculate the phase changes.
Answers
Here are the answers to the worksheet:
| Substance | ΔH (kJ) | ΔT (°C) |
|---|---|---|
| Water | 300.5 | 80 |
| Ice | 150.25 | 10 |
| Steam | 407 | 100 |
By practicing with this worksheet, you should now have a better understanding of phase changes and how to calculate them.
Phase Change Summary
In summary, phase changes are transformations of a substance from one state of matter to another. There are several types of phase changes, including melting, boiling, freezing, condensation, sublimation, and deposition. To calculate phase changes, you need to know the heat of fusion, heat of vaporization, and molar heat capacity of a substance. By using the formulas provided earlier, you can calculate the energy required to melt, vaporize, and change the temperature of a substance.
What is a phase change?
+A phase change is a transformation of a substance from one state of matter to another, such as from solid to liquid or from liquid to gas.
What are the different types of phase changes?
+There are several types of phase changes, including melting, boiling, freezing, condensation, sublimation, and deposition.
How do I calculate phase changes?
+To calculate phase changes, you need to know the heat of fusion, heat of vaporization, and molar heat capacity of a substance. By using the formulas provided earlier, you can calculate the energy required to melt, vaporize, and change the temperature of a substance.