Mastering Econ Supply Curve Worksheet Chapter 5 Made Easy

Understanding the law of supply and the concept of a supply curve is essential for any student of economics. A supply curve is a graphical representation of the relationship between the price of a product and the quantity of the product that suppliers are willing and able to produce and sell at that price level, ceteris paribus (all other things being equal). This relationship is typically positive, meaning that as the price of the product increases, the quantity supplied also increases.
Law of Supply
The law of supply states that, ceteris paribus, as the price of a product increases, the quantity supplied of the product also increases. This makes sense because higher prices make production more profitable, encouraging suppliers to produce more. Conversely, lower prices make production less profitable, leading to a decrease in the quantity supplied.
Key Factors That Shift the Supply Curve
While the price of the product is the most direct determinant of the quantity supplied, several other factors can influence the position of the supply curve. These include:
- Production Costs: Changes in the cost of inputs (e.g., labor, raw materials) can affect the profitability of production and thus the quantity supplied.
- Technology: Improvements in technology can make production more efficient, reducing costs and increasing the quantity supplied at each price level.
- Expectations: Suppliers’ expectations about future market conditions can influence their current production decisions. If suppliers expect prices to rise in the future, they may increase current production to capitalize on anticipated higher prices.
- Number of Suppliers: An increase in the number of suppliers in a market can lead to an increase in the quantity supplied, as more firms are producing the product.
- Government Policies and Regulations: Taxes, subsidies, and regulations can all affect the profitability of production and thus the quantity supplied.
Supply Curve Worksheet Example
Below is a basic example of a supply curve worksheet. Let’s say we’re examining the market for wheat and have the following data:
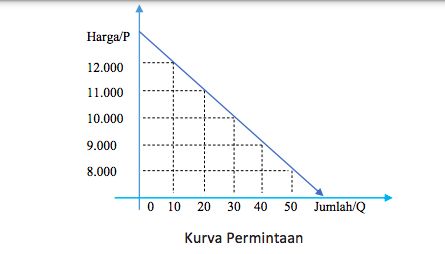
| Price per Bushel | Quantity Supplied (Bushels) |
|---|---|
| $2 | 100 |
| $3 | 150 |
| $4 | 200 |
| $5 | 250 |
| $6 | 300 |
From this data, we can plot the supply curve, which would show a positive relationship between the price per bushel and the quantity supplied. The exact shape and position of the supply curve can provide insights into the responsiveness of suppliers to price changes.
How to Plot a Supply Curve
Plotting a supply curve is relatively straightforward once you have the necessary data. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Gather Data: Collect data on the price of the product and the corresponding quantity supplied. This data can come from various sources, including market reports, surveys, or experiments.
- Organize Data: Arrange your data in a table with price levels in one column and quantities supplied in another. This will make it easier to visualize the relationship.
- Plot Points: Using your data, plot points on a graph where the x-axis represents the quantity supplied and the y-axis represents the price.
- Draw the Curve: Connect your plotted points with a smooth curve. The shape of this curve can provide insights into the supply relationship. A straight line indicates a linear relationship, while a curved line suggests a non-linear relationship.
📝 Note: In real-world scenarios, plotting a supply curve might involve more complex data and the use of statistical software to accurately depict the relationship between price and quantity supplied.
Conclusion
Mastering the supply curve worksheet chapter is about understanding the fundamental principles of supply and demand and how they interact in a market. By analyzing supply curves, you can gain insights into the behavior of suppliers and how they respond to changes in price and other market conditions. This knowledge is essential for making informed decisions in economics, business, and policy-making.
What is the main determinant of the quantity supplied of a product?
+The main determinant of the quantity supplied of a product is its price. As the price increases, the quantity supplied also increases, ceteris paribus.
How does an improvement in technology affect the supply curve?
+An improvement in technology makes production more efficient, reducing costs and increasing the quantity supplied at each price level. This would cause the supply curve to shift to the right.
What is the difference between a movement along the supply curve and a shift of the supply curve?
+A movement along the supply curve occurs when the price of the product changes, causing the quantity supplied to change along the existing supply curve. A shift of the supply curve occurs when any factor other than the price of the product changes, causing the entire supply curve to move.