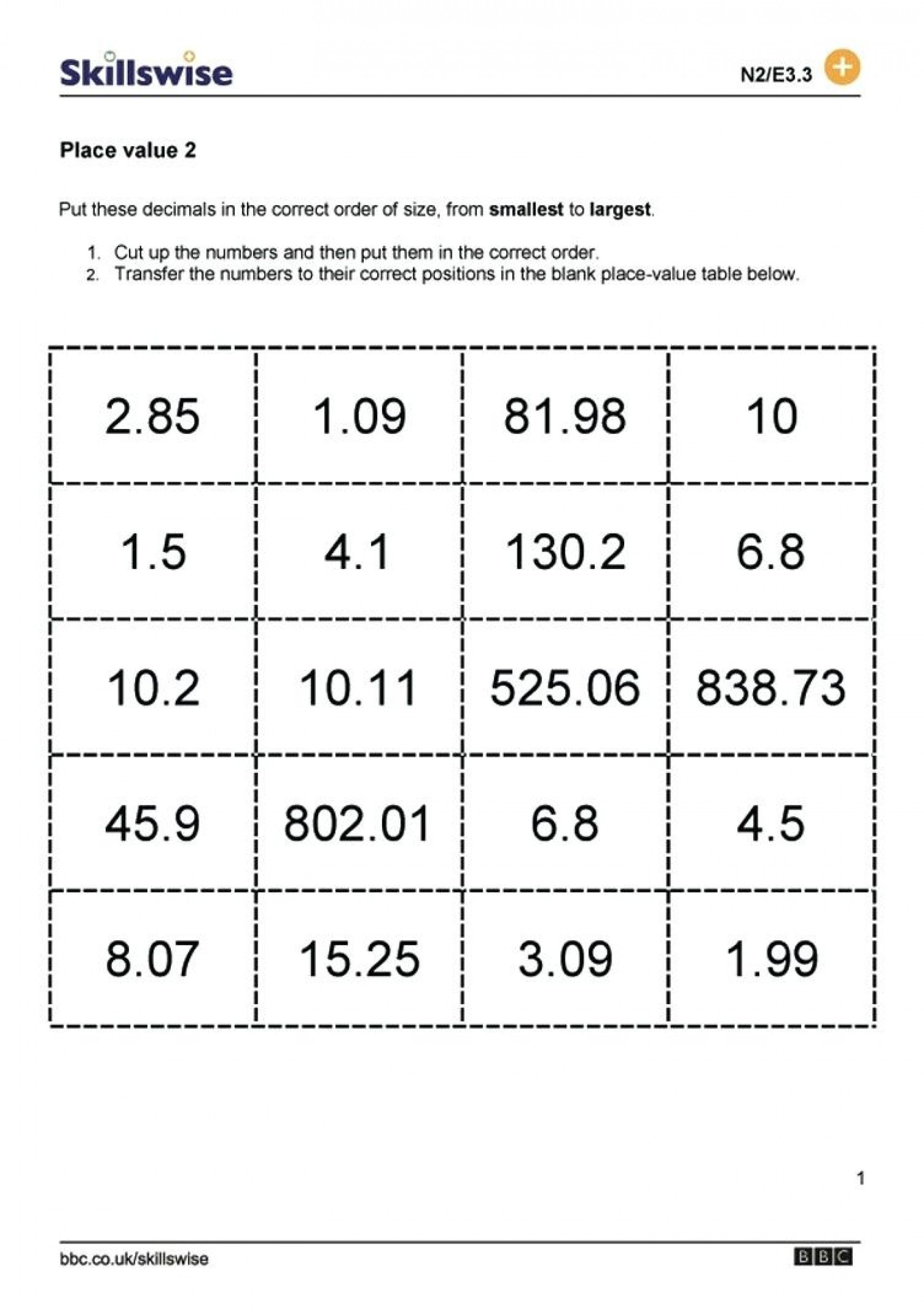
5 Ways to Master pH Calculations

Understanding pH and its Importance
The pH scale is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, while values below 7 are acidic and above 7 are basic. pH calculations are crucial in various fields, including chemistry, biology, medicine, and environmental science. Mastering pH calculations can help you understand and analyze complex chemical reactions, predict the behavior of ions in solution, and make informed decisions in various applications.
Method 1: pH Calculation using the Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is a simple and widely used method for calculating the pH of a buffer solution. The equation is:
pH = pKa + log10([A-]/[HA])
Where: pH = the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration pKa = the acid dissociation constant [A-] = the concentration of the conjugate base [HA] = the concentration of the weak acid
To use this equation, you need to know the pKa value of the acid and the concentrations of the acid and its conjugate base.
📝 Note: The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is only applicable to buffer solutions, where the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base are equal.
Method 2: pH Calculation using the Arrhenius Equation
The Arrhenius equation is a more general method for calculating the pH of a solution. The equation is:
pH = -log10[H+]
Where: pH = the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration [H+] = the concentration of hydrogen ions
To use this equation, you need to know the concentration of hydrogen ions in the solution.
💡 Note: The Arrhenius equation is applicable to any solution, not just buffer solutions.
Method 3: pH Calculation using the Strong Acid-Strong Base Titration Curve
A strong acid-strong base titration curve is a graphical representation of the pH of a solution as a function of the volume of strong acid or base added. By analyzing the curve, you can determine the pH of the solution at different points during the titration.
To use this method, you need to:
- Plot the pH of the solution against the volume of strong acid or base added.
- Identify the equivalence point, where the pH is maximum or minimum.
- Read the pH value from the curve at the desired point.
📊 Note: This method requires experimental data and is typically used in laboratory settings.
Method 4: pH Calculation using the Weak Acid-Weak Base Titration Curve
A weak acid-weak base titration curve is similar to the strong acid-strong base titration curve, but it is more complex due to the presence of weak acids and bases.
To use this method, you need to:
- Plot the pH of the solution against the volume of weak acid or base added.
- Identify the equivalence point, where the pH is maximum or minimum.
- Read the pH value from the curve at the desired point.
📊 Note: This method requires experimental data and is typically used in laboratory settings.
Method 5: pH Calculation using Software and Online Tools
There are many software programs and online tools available that can calculate pH values quickly and accurately. These tools often use complex algorithms and databases to determine the pH of a solution based on the concentrations of various ions and compounds.
To use these tools, you simply need to input the relevant data, such as the concentrations of ions and compounds, and the software will calculate the pH value for you.

| Method | Description | Applicability |
|---|---|---|
| Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation | pH = pKa + log10([A-]/[HA]) | Buffer solutions |
| Arrhenius Equation | pH = -log10[H+] | All solutions |
| Strong Acid-Strong Base Titration Curve | Plot pH vs. volume of strong acid or base added | Laboratory settings |
| Weak Acid-Weak Base Titration Curve | Plot pH vs. volume of weak acid or base added | Laboratory settings |
| Software and Online Tools | Use software or online tools to calculate pH | All solutions |
In conclusion, mastering pH calculations is crucial for understanding and analyzing complex chemical reactions and predicting the behavior of ions in solution. By using one or more of the five methods outlined above, you can accurately calculate pH values and make informed decisions in various applications.
What is the difference between pH and pKa?
+pH is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration, while pKa is the acid dissociation constant. pKa is a measure of the strength of an acid, while pH is a measure of the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution.
Can I use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for all types of solutions?
+No, the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation is only applicable to buffer solutions, where the concentration of the acid and its conjugate base are equal.
What is the advantage of using software and online tools for pH calculations?
+The advantage of using software and online tools is that they can quickly and accurately calculate pH values based on complex algorithms and databases, saving time and effort.
Related Terms:
- How to calculate ph
- pH Worksheet pdf
- Worksheet pH Calculations
- pH Calculations PDF