6 Periodic Trends to Master for Chemistry Success
Understanding Periodic Trends: A Key to Unlocking Chemistry Success
Chemistry, a subject that can be both fascinating and intimidating, requires a strong grasp of various concepts to achieve success. Among these concepts, periodic trends stand out as a crucial aspect of mastering chemistry. Periodic trends refer to the patterns and relationships that exist between elements and their properties, as presented in the periodic table. In this blog post, we will delve into six essential periodic trends that every chemistry student should understand to excel in their studies.
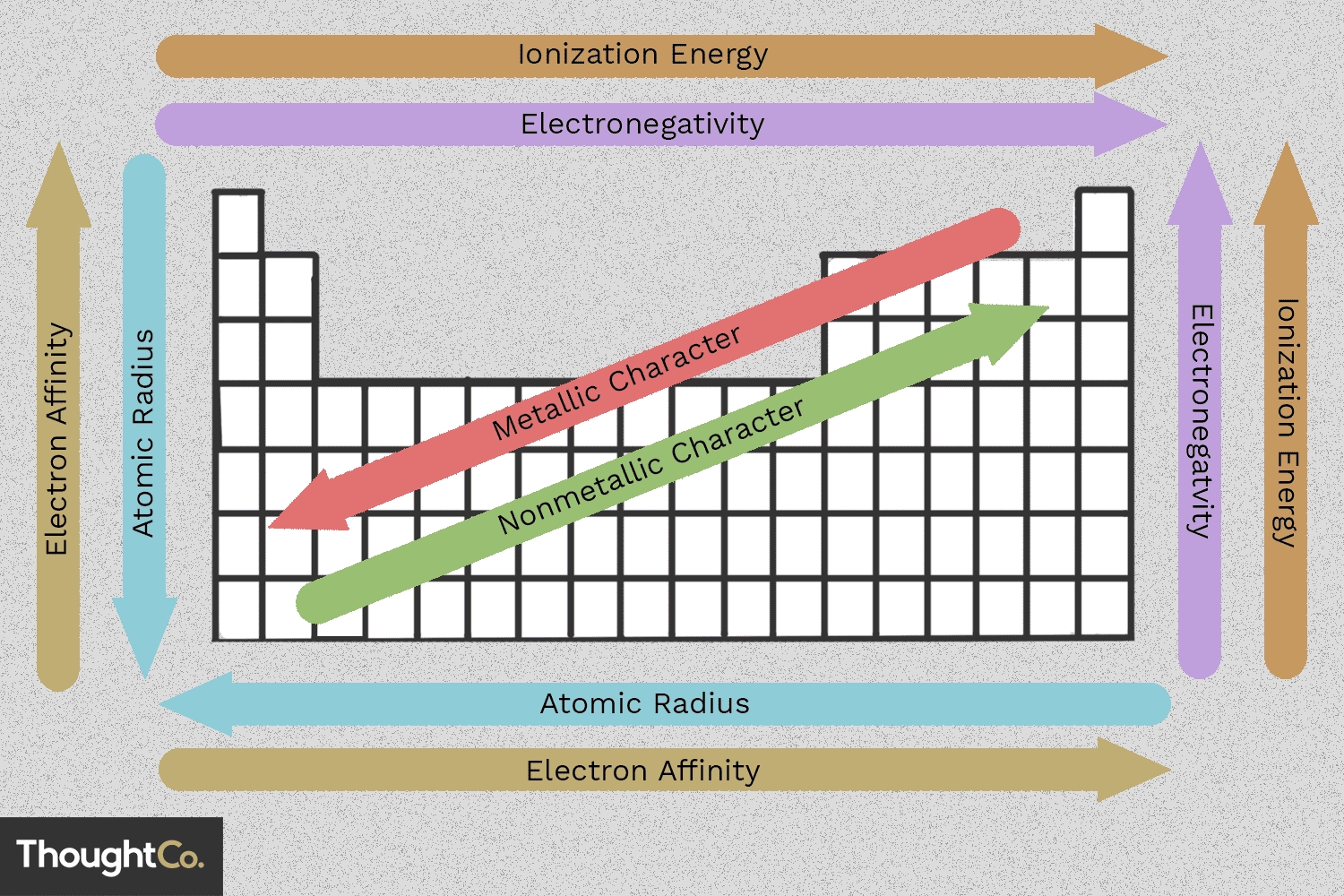
1. Atomic Radius Trend
One of the most fundamental periodic trends is the atomic radius trend. The atomic radius of an element is the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron. As you move from left to right across a period, the atomic radius decreases. This decrease in atomic radius is due to the increase in the number of protons in the nucleus, which pulls the electrons closer to the nucleus.
On the other hand, as you move down a group, the atomic radius increases. This increase is due to the addition of new energy levels, which increases the distance between the nucleus and the outermost electron.
Key Points:
- Atomic radius decreases across a period (left to right)
- Atomic radius increases down a group (top to bottom)
2. Electronegativity Trend
Electronegativity is the measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. The electronegativity trend is closely related to the atomic radius trend. As you move across a period, electronegativity increases due to the decrease in atomic radius. This increase in electronegativity means that atoms have a greater tendency to attract electrons.
On the other hand, as you move down a group, electronegativity decreases due to the increase in atomic radius. This decrease in electronegativity means that atoms have a lower tendency to attract electrons.
Key Points:
- Electronegativity increases across a period (left to right)
- Electronegativity decreases down a group (top to bottom)
3. Ionization Energy Trend
Ionization energy is the energy required to remove an electron from an atom. The ionization energy trend is closely related to the atomic radius trend. As you move across a period, ionization energy increases due to the decrease in atomic radius. This increase in ionization energy means that it becomes more difficult to remove an electron from an atom.
On the other hand, as you move down a group, ionization energy decreases due to the increase in atomic radius. This decrease in ionization energy means that it becomes easier to remove an electron from an atom.
Key Points:
- Ionization energy increases across a period (left to right)
- Ionization energy decreases down a group (top to bottom)
4. Electron Affinity Trend
Electron affinity is the energy released when an electron is added to an atom. The electron affinity trend is closely related to the atomic radius trend. As you move across a period, electron affinity becomes more negative due to the decrease in atomic radius. This increase in negative electron affinity means that atoms have a greater tendency to attract electrons.
On the other hand, as you move down a group, electron affinity becomes less negative due to the increase in atomic radius. This decrease in negative electron affinity means that atoms have a lower tendency to attract electrons.
Key Points:
- Electron affinity becomes more negative across a period (left to right)
- Electron affinity becomes less negative down a group (top to bottom)
5. Metallic Character Trend
Metallic character refers to the properties of metals, such as malleability, ductility, and conductivity. The metallic character trend is closely related to the atomic radius trend. As you move across a period, metallic character decreases due to the decrease in atomic radius. This decrease in metallic character means that elements have fewer metallic properties.
On the other hand, as you move down a group, metallic character increases due to the increase in atomic radius. This increase in metallic character means that elements have more metallic properties.
Key Points:
- Metallic character decreases across a period (left to right)
- Metallic character increases down a group (top to bottom)
6. Valence Electrons Trend
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom. The valence electrons trend is closely related to the atomic radius trend. As you move across a period, the number of valence electrons increases due to the decrease in atomic radius. This increase in valence electrons means that atoms have more electrons available for bonding.
On the other hand, as you move down a group, the number of valence electrons remains the same due to the increase in atomic radius. This means that atoms have the same number of electrons available for bonding.
Key Points:
- Number of valence electrons increases across a period (left to right)
- Number of valence electrons remains the same down a group (top to bottom)
🔍 Note: Understanding periodic trends is crucial for mastering chemistry. By recognizing these trends, you can predict the properties and behavior of elements and their compounds.
As we conclude our discussion on periodic trends, it is essential to remember that these trends are not absolute and may have exceptions. However, understanding these trends will provide you with a solid foundation in chemistry and enable you to make predictions and connections between elements and their properties.
What is the most important periodic trend in chemistry?
+
The atomic radius trend is often considered the most important periodic trend in chemistry, as it affects many other properties, such as electronegativity, ionization energy, and metallic character.
How do periodic trends help in predicting the properties of elements?
+
Periodic trends help in predicting the properties of elements by recognizing patterns and relationships between elements and their properties. By understanding these trends, you can make predictions about the behavior and properties of elements and their compounds.
Are there any exceptions to periodic trends?
+
Yes, there are exceptions to periodic trends. While these trends are generally true, there may be exceptions due to various factors, such as the presence of lone pairs or the influence of other elements.