5 Tips to Master Pedigrees for Human Genetic Disorders
Understanding Pedigrees for Human Genetic Disorders
Studying pedigrees is a crucial aspect of understanding human genetic disorders. A pedigree is a chart that represents the family relationships and medical history of a particular individual or family. It is an essential tool for geneticists, researchers, and healthcare professionals to identify patterns of inheritance, diagnose genetic disorders, and provide genetic counseling. Mastering pedigrees requires a combination of knowledge, skills, and practice. In this article, we will provide five tips to help you improve your skills in reading and interpreting pedigrees for human genetic disorders.
Tip 1: Understand the Symbols and Notations
To start, it is essential to understand the standard symbols and notations used in pedigree charts. The most common symbols include:
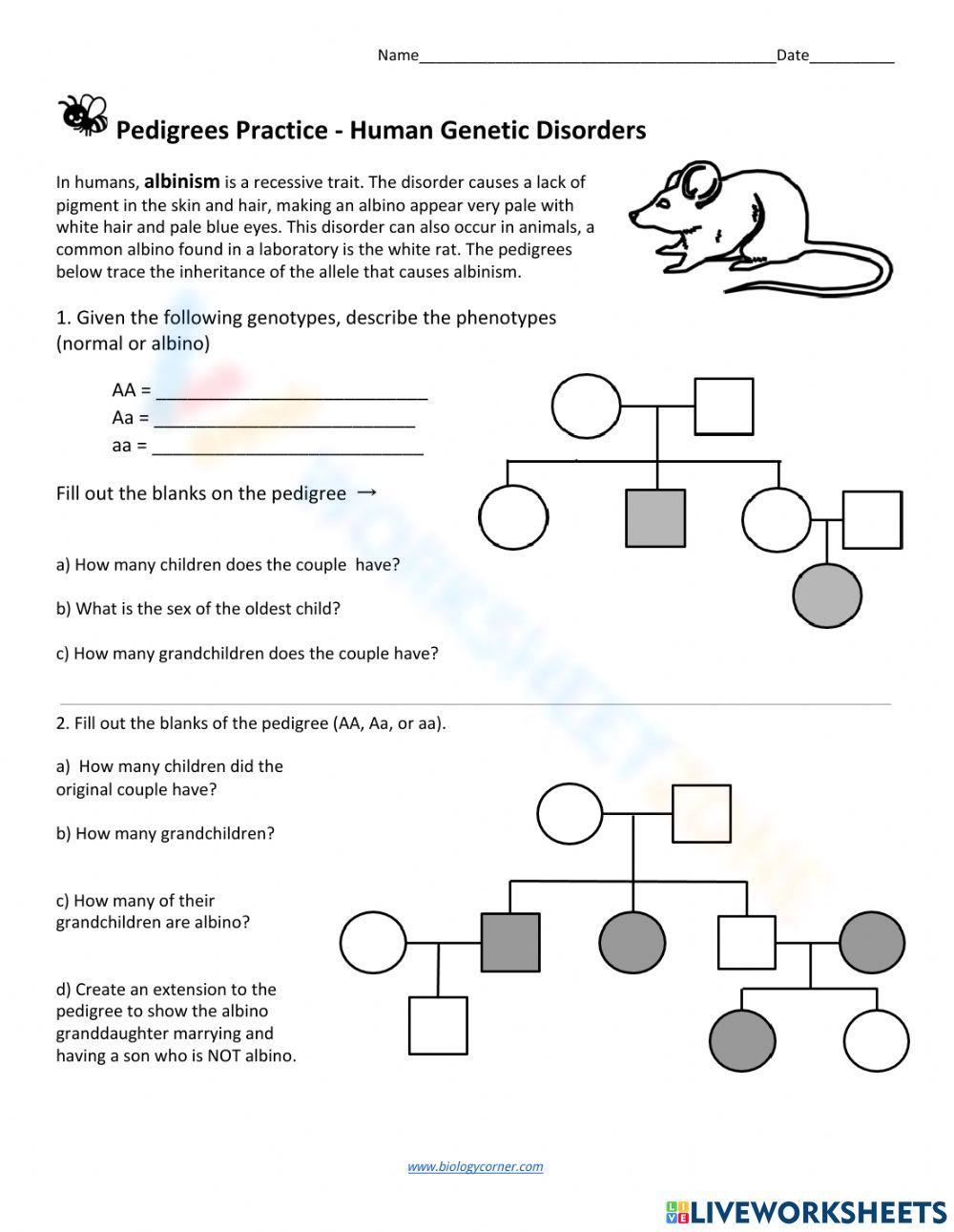
- Squares: Represent males
- Circles: Represent females
- Horizontal lines: Connect parents to offspring
- Vertical lines: Connect generations
- Diagonal lines: Indicate a deceased individual
- Shaded symbols: Indicate an affected individual
- Open symbols: Indicate an unaffected individual
Familiarize yourself with these symbols and notations to ensure you can accurately interpret and create pedigree charts.
Tip 2: Identify Patterns of Inheritance
Pedigrees can reveal patterns of inheritance, such as autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, X-linked dominant, and X-linked recessive. To identify these patterns, look for the following:
- Autosomal dominant: Affected individuals are heterozygous (Aa), and the disorder is inherited from one affected parent. The pedigree will show a vertical line connecting affected individuals.
- Autosomal recessive: Affected individuals are homozygous (aa), and the disorder is inherited from two unaffected carrier parents. The pedigree will show two unaffected parents with affected offspring.
- X-linked dominant: Affected individuals are heterozygous (Aa), and the disorder is inherited from an affected mother or father. The pedigree will show a higher frequency of affected females than males.
- X-linked recessive: Affected individuals are hemizygous (aY), and the disorder is inherited from an affected father or an unaffected carrier mother. The pedigree will show affected males and unaffected carrier females.
Identifying patterns of inheritance is crucial for diagnosing genetic disorders and providing genetic counseling.
Tip 3: Look for Consanguinity
Consanguinity, or the practice of marrying within the family, can increase the risk of genetic disorders. When reviewing a pedigree, look for:
- First cousins: Married to each other, indicating a high risk of autosomal recessive disorders.
- Uncle-niece or aunt-nephew marriages: Indicating a higher risk of genetic disorders due to shared ancestry.
Recognizing consanguinity can help you identify potential genetic risks and provide accurate genetic counseling.
Tip 4: Identify Multiple Generations
Pedigrees that show multiple generations can provide valuable information about the inheritance pattern of a genetic disorder. Look for:
- Three or more generations: Showing the disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant or X-linked dominant pattern.
- Two or more generations: Showing the disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive or X-linked recessive pattern.
Identifying multiple generations can help you determine the likelihood of inheritance and provide accurate genetic counseling.
Tip 5: Consider Multiple Factors
When interpreting a pedigree, consider multiple factors, such as:
- Family history: Look for a history of genetic disorders, birth defects, or unexplained illnesses.
- Medical history: Consider the medical history of the individual and their family members.
- Genetic testing: Look for genetic testing results, such as DNA sequencing or chromosome analysis.
Considering multiple factors can help you provide accurate genetic counseling and identify potential genetic risks.
📝 Note: Practice reading and interpreting pedigrees regularly to improve your skills and become proficient in identifying patterns of inheritance and genetic risks.
In conclusion, mastering pedigrees requires a combination of knowledge, skills, and practice. By understanding the symbols and notations, identifying patterns of inheritance, looking for consanguinity, identifying multiple generations, and considering multiple factors, you can improve your skills in reading and interpreting pedigrees for human genetic disorders. With practice and experience, you will become proficient in using pedigrees to diagnose genetic disorders and provide accurate genetic counseling.
What is a pedigree chart?
+A pedigree chart is a diagram that represents the family relationships and medical history of an individual or family. It is used to identify patterns of inheritance and diagnose genetic disorders.
What is the difference between autosomal dominant and autosomal recessive inheritance?
+Autosomal dominant inheritance occurs when a single copy of the mutated gene is enough to cause the disorder, whereas autosomal recessive inheritance occurs when an individual inherits two copies of the mutated gene, one from each parent.
How can I identify consanguinity in a pedigree?
+Look for married couples who are first cousins, uncle-niece, or aunt-nephew, indicating a high risk of genetic disorders due to shared ancestry.
Related Terms:
- Practice pedigree charts answer Key
- Pedigree worksheet
- Pedigree questions and answers PDF
- Practice analyzing pedigrees answers