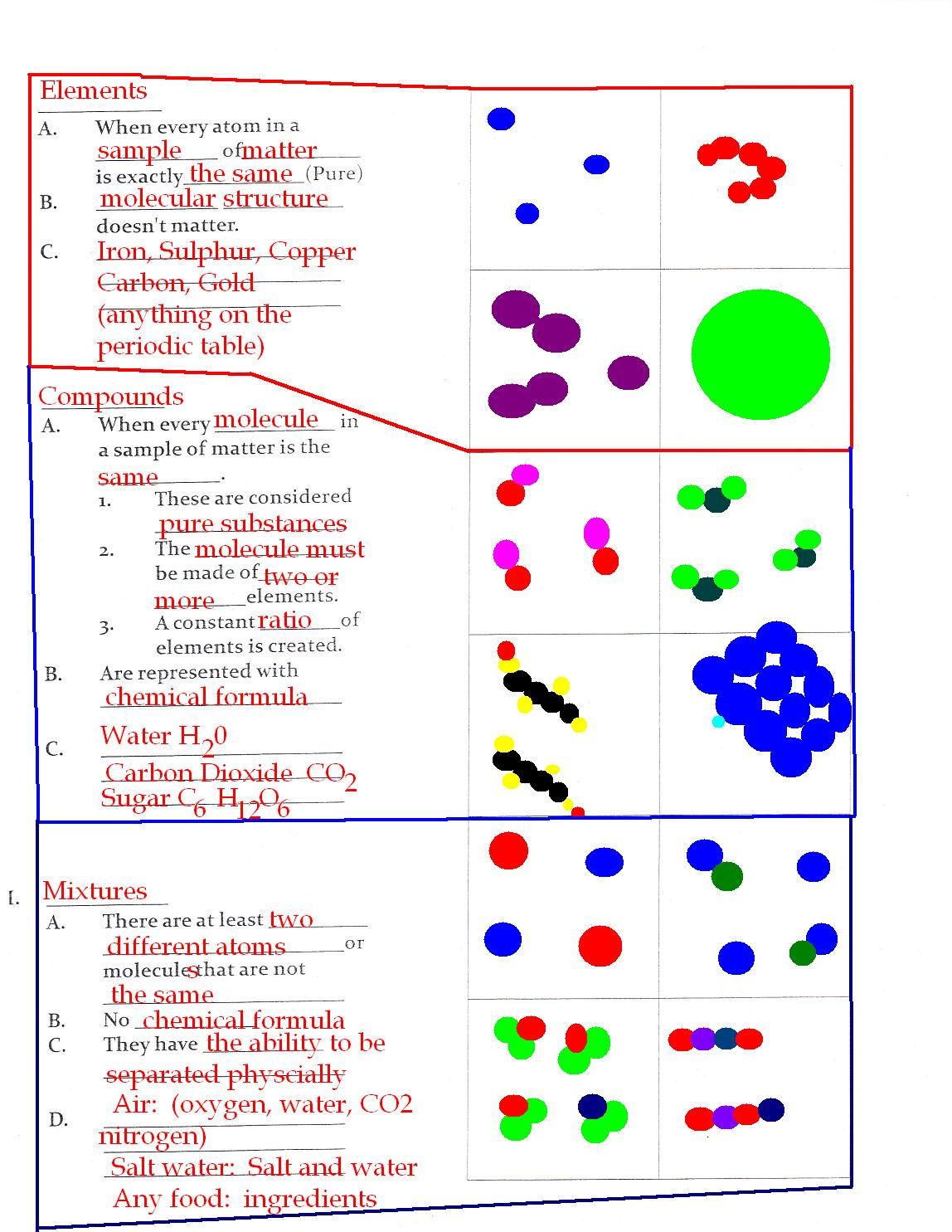
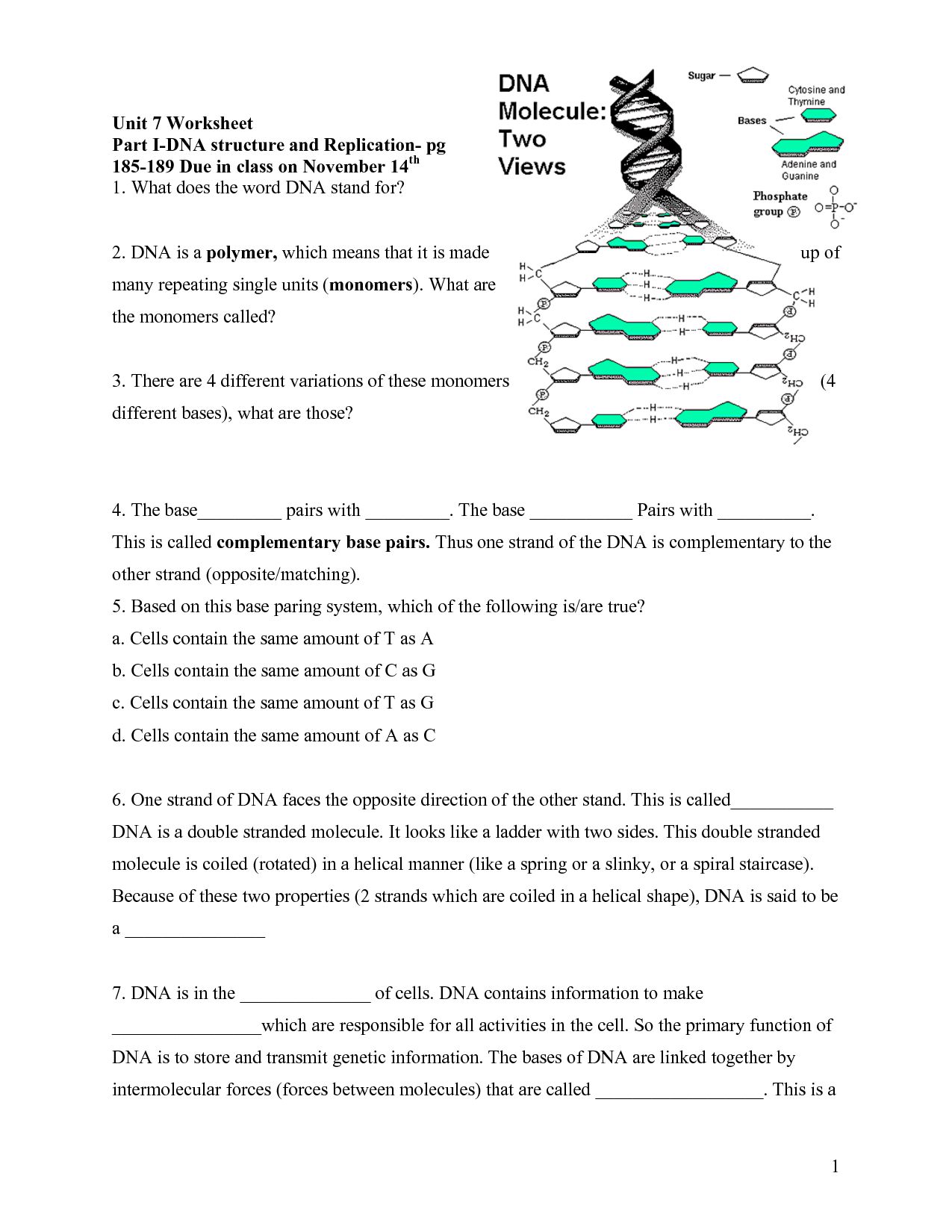
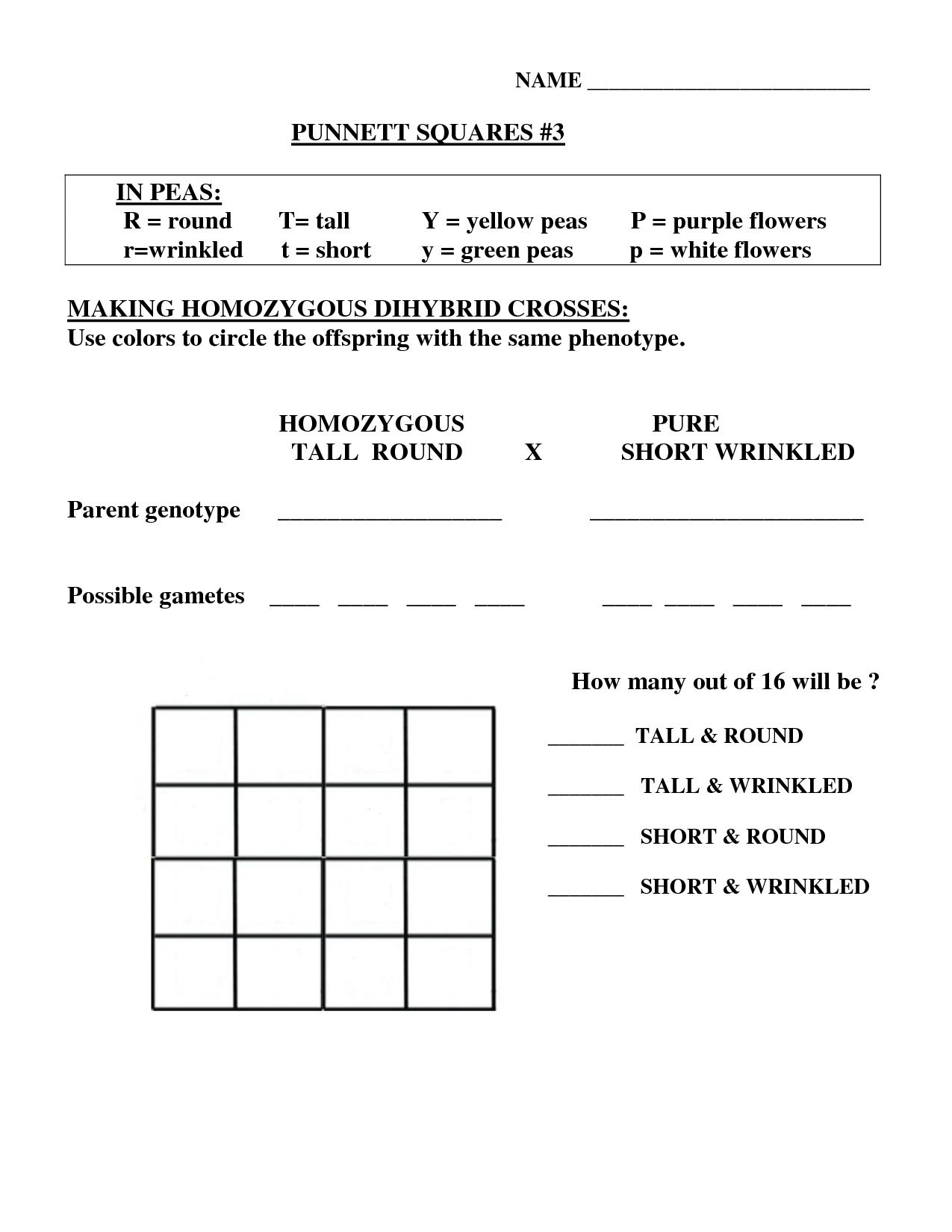
5 Easy Steps to Pea Plant Punnett Square Worksheet Answers

Understanding Pea Plant Genetics
Gregor Mendel’s experiments with pea plants revolutionized our understanding of genetics. By studying the inheritance of traits in pea plants, Mendel discovered the fundamental principles of genetics that govern the transmission of characteristics from one generation to the next. One of the essential tools for predicting the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring is the Punnett square. In this article, we will walk you through a step-by-step guide to creating a Punnett square for pea plants and provide answers to common worksheet questions.
Step 1: Determine the Genotype of the Parents
To create a Punnett square, you need to know the genotype of the two parent pea plants. The genotype is the genetic makeup of an individual, consisting of letters that represent different alleles (forms) of a gene. For example, the gene for flower color in pea plants has two alleles: “R” for red flowers and “r” for white flowers. A pea plant can be RR (homozygous dominant), Rr (heterozygous), or rr (homozygous recessive).
| Genotype | Phenotype |
|---|---|
| RR | Red flowers |
| Rr | Red flowers |
| rr | White flowers |
Step 2: Identify the Trait and Alleles
Choose a specific trait, such as flower color, and identify the alleles involved. In this case, we will use the “R” and “r” alleles for red and white flowers, respectively.
Step 3: Draw the Punnett Square
Create a grid with the alleles of one parent on the top and the alleles of the other parent on the side. Each box in the grid represents a possible combination of alleles.
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | rR | rr |
Step 4: Fill in the Punnett Square
Fill in each box with the genotype of the offspring that would result from the combination of alleles from the two parents. For example, if the top parent contributes an “R” allele and the side parent contributes an “r” allele, the genotype of the offspring would be “Rr”.
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | rR | rr |
Step 5: Determine the Probability of Each Genotype
To determine the probability of each genotype, count the number of boxes with each genotype and divide by the total number of boxes.
| Genotype | Number of Boxes | Probability |
|---|---|---|
| RR | 1 | 25% |
| Rr | 2 | 50% |
| rr | 1 | 25% |
Answers to Common Worksheet Questions
- What is the probability of a pea plant with the genotype “RR” producing offspring with red flowers?
Answer: 100% (since RR is homozygous dominant)
- What is the probability of a pea plant with the genotype “Rr” producing offspring with white flowers?
Answer: 25% (since Rr is heterozygous and can produce rr offspring)
- If two pea plants with the genotype “Rr” are crossed, what is the probability of their offspring having the genotype “RR”?
Answer: 25% (since Rr x Rr can produce RR, Rr, and rr offspring)
👍 Note: These answers assume that the trait is determined by a single gene with two alleles. In reality, many traits are influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors.
**In conclusion, creating a Punnett square is a powerful tool for predicting the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring. By following these easy steps, you can determine the probability of specific traits being passed down from one generation to the next.
What is the purpose of a Punnett square?
+
A Punnett square is used to predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in offspring.
What are the alleles for flower color in pea plants?
+
The alleles for flower color in pea plants are “R” for red flowers and “r” for white flowers.
What is the probability of a pea plant with the genotype “Rr” producing offspring with white flowers?
+
25%
Related Terms:
- Punnett square worksheet answer key
- Punnett squares Worksheet PDF
- Punnett Square Worksheet-Human characteristics
- Punnett Square worksheet Printable