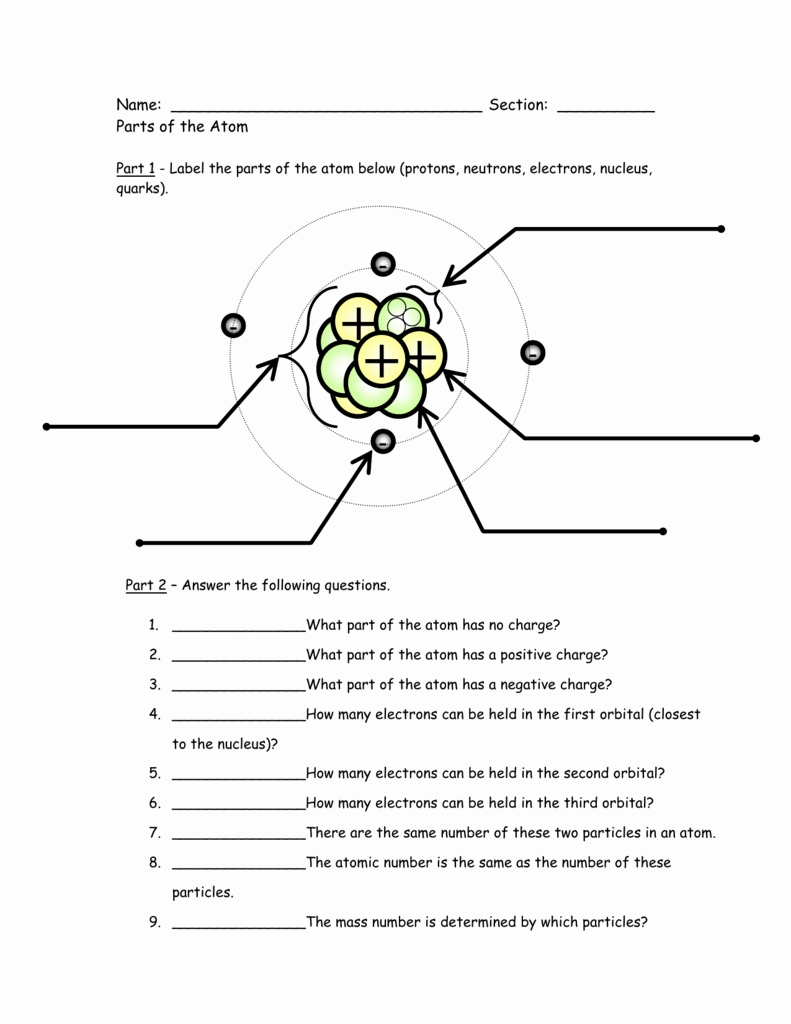
5 Essential Parts of the Atom Explained

Understanding the Building Blocks of Matter: The Atom
The atom is the fundamental unit of matter, and it’s composed of several essential parts that work together to form the basis of everything around us. From the air we breathe to the stars in the sky, atoms are the building blocks of our universe. In this article, we’ll delve into the five essential parts of the atom, exploring their functions, properties, and relationships.
The Nucleus: The Central Hub of the Atom
The nucleus is the central part of the atom, containing the majority of its mass. It’s made up of two main particles: protons and neutrons. Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
🔍 Note: The number of protons in an atom's nucleus is also known as the atomic number.
Protons: The Positive Players
Protons are positively charged particles that reside in the nucleus. They have a mass of approximately 1 atomic mass unit (amu) and a charge of +1 elementary charge. The number of protons in an atom’s nucleus determines the element of an atom, and each element has a unique number of protons in its atoms.
- Properties of protons:
- Positive charge
- Mass of approximately 1 amu
- Reside in the nucleus
Neutrons: The Neutral Supporting Actors
Neutrons are particles that have no charge and reside in the nucleus along with protons. They have a mass of approximately 1 amu, slightly larger than that of protons. Neutrons play a crucial role in determining the mass of an atom, as they contribute to the overall mass of the nucleus.
- Properties of neutrons:
- No charge
- Mass of approximately 1 amu
- Reside in the nucleus
Electrons: The Negative Orbiters
Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. They have a mass of approximately 1⁄1836 that of a proton and a charge of -1 elementary charge. Electrons are arranged in energy levels or shells around the nucleus, and their arrangement determines the chemical properties of an element.
- Properties of electrons:
- Negative charge
- Mass of approximately 1⁄1836 that of a proton
- Orbit the nucleus in energy levels or shells
The Electron Cloud: The Probabilistic Region
The electron cloud is the region around the nucleus where electrons are likely to be found. It’s a probabilistic region, meaning that we can’t determine the exact location of an electron at a given time. Instead, we can predict the likelihood of finding an electron within a particular region.
- Properties of the electron cloud:
- Probabilistic region
- Determines the chemical properties of an element
- Shaped by the arrangement of electrons in energy levels or shells
Table: Comparison of Atomic Particles
| Particle | Charge | Mass (amu) | Location |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | Positive (+1) | 1 | Nucleus |
| Neutron | No charge (0) | 1 | Nucleus |
| Electron | Negative (-1) | 1/1836 | Orbits nucleus |
In conclusion, the five essential parts of the atom – the nucleus, protons, neutrons, electrons, and the electron cloud – work together to form the basis of matter. Understanding the properties and relationships of these particles is crucial for grasping the fundamental principles of chemistry and physics.
What is the nucleus of an atom?
+The nucleus is the central part of the atom, containing the majority of its mass. It’s made up of two main particles: protons and neutrons.
What is the function of electrons in an atom?
+Electrons are negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. They determine the chemical properties of an element and are arranged in energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
What is the difference between protons and neutrons?
+Protons have a positive charge, while neutrons have no charge. Protons reside in the nucleus and determine the element of an atom, while neutrons contribute to the overall mass of the nucleus.
Related Terms:
- Parts of an atom pdf