7 Ways to Master Parallel Lines Cut by a Transversal
Understanding parallel lines cut by a transversal is a fundamental concept in geometry that can seem daunting at first, but with practice and the right strategies, it can become second nature. Here are 7 ways to master parallel lines cut by a transversal:
1. Visualize the Concept
Start by visualizing the concept of parallel lines cut by a transversal. Imagine two parallel lines, line A and line B, cut by a third line, line C, which is called the transversal. When the transversal intersects the parallel lines, it creates several angles. Remember, the key to mastering parallel lines cut by a transversal is to understand the relationships between these angles.
2. Learn the Basic Properties
Familiarize yourself with the basic properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal. These include:
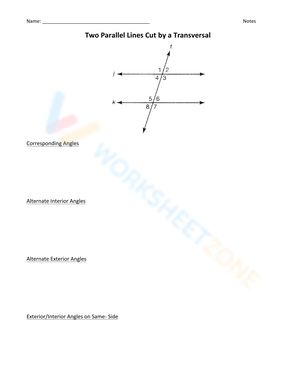
- Corresponding angles: angles that are in the same relative position in each intersection are equal.
- Alternate interior angles: angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and inside the parallel lines are equal.
- Alternate exterior angles: angles that are on opposite sides of the transversal and outside the parallel lines are equal.
- Interior angles on the same side of the transversal: angles that are on the same side of the transversal and inside the parallel lines are supplementary (add up to 180°).
3. Practice with Diagrams
Practice drawing diagrams of parallel lines cut by a transversal and labeling the angles. Start with simple diagrams and gradually move on to more complex ones. Use different colors to highlight the corresponding, alternate interior, and alternate exterior angles.
4. Use Real-World Examples
Use real-world examples to illustrate the concept of parallel lines cut by a transversal. For instance, consider a road intersecting two parallel railway tracks. The road is the transversal, and the railway tracks are the parallel lines. Identify the corresponding, alternate interior, and alternate exterior angles in this scenario.
5. Apply the Properties to Solve Problems
Practice applying the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal to solve problems. Start with simple problems and gradually move on to more complex ones. Use the properties to find missing angles and to determine whether two lines are parallel or not.
6. Watch Video Tutorials
Watch video tutorials to supplement your learning. Video tutorials can provide an alternative explanation of the concept and help you visualize the relationships between the angles. Take notes and pause the video to practice drawing diagrams and labeling angles.
7. Take Practice Tests
Take practice tests to assess your understanding of parallel lines cut by a transversal. Start with simple tests and gradually move on to more complex ones. Use online resources or worksheets to practice.
📝 Note: Practice consistently to master parallel lines cut by a transversal. Start with simple problems and gradually move on to more complex ones.
In conclusion, mastering parallel lines cut by a transversal requires practice, patience, and persistence. By visualizing the concept, learning the basic properties, practicing with diagrams, using real-world examples, applying the properties to solve problems, watching video tutorials, and taking practice tests, you can become proficient in this fundamental concept of geometry.
What are corresponding angles in parallel lines cut by a transversal?
+
Corresponding angles are angles that are in the same relative position in each intersection and are equal.
How can I determine whether two lines are parallel or not using a transversal?
+
You can use the properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal to determine whether two lines are parallel or not. If the corresponding angles are equal, then the lines are parallel.
What are some real-world examples of parallel lines cut by a transversal?
+
Some real-world examples of parallel lines cut by a transversal include a road intersecting two parallel railway tracks, a bridge crossing two parallel rivers, and a floor tile pattern.
Related Terms:
- teacher synergy llc
- Khan Academy
- IXL
- BrainPOP
- Udacity
- Duolingo