Mastering Circuits: Series and Parallel Circuits Worksheet
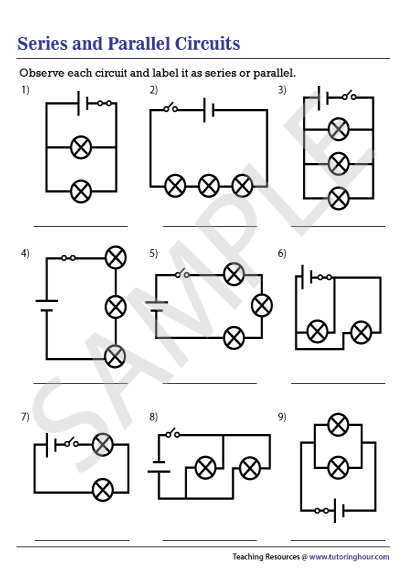
Understanding the Basics of Electric Circuits
Electric circuits are a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, and they play a crucial role in our daily lives. From the simplest devices to complex systems, electric circuits are the backbone of modern technology. In this article, we will delve into the world of series and parallel circuits, exploring their characteristics, advantages, and applications.
Series Circuits: What You Need to Know
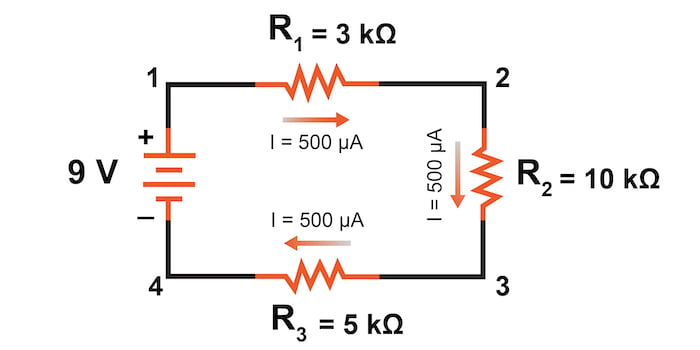
A series circuit is a type of electric circuit where components are connected one after the other, and there is only one path for the electric current to flow. In a series circuit, the current flows through each component in sequence, and the voltage is divided among the components.
Key Characteristics of Series Circuits:
- Single Path: There is only one path for the electric current to flow.
- Voltage Division: The voltage is divided among the components.
- Current is the Same: The current is the same throughout the circuit.
Advantages of Series Circuits:
- Simple Design: Series circuits are easy to design and build.
- Low Cost: They require fewer components, making them a cost-effective option.
- Easy to Analyze: Series circuits are straightforward to analyze and troubleshoot.
Disadvantages of Series Circuits:
- Single Point of Failure: If one component fails, the entire circuit is affected.
- Limited Flexibility: Series circuits are not suitable for complex systems.
Parallel Circuits: What You Need to Know
A parallel circuit is a type of electric circuit where components are connected between the same two points, and there are multiple paths for the electric current to flow. In a parallel circuit, the voltage is the same across each component, and the current is divided among the components.
Key Characteristics of Parallel Circuits:
- Multiple Paths: There are multiple paths for the electric current to flow.
- Voltage is the Same: The voltage is the same across each component.
- Current Division: The current is divided among the components.
Advantages of Parallel Circuits:
- Increased Reliability: Parallel circuits are less prone to single-point failures.
- Improved Flexibility: They are suitable for complex systems and can be easily expanded.
- Higher Current Capacity: Parallel circuits can handle higher currents.
Disadvantages of Parallel Circuits:
- Complex Design: Parallel circuits are more complex to design and build.
- Higher Cost: They require more components, making them more expensive.
- Difficult to Analyze: Parallel circuits can be challenging to analyze and troubleshoot.
Comparison of Series and Parallel Circuits
| Series Circuits | Parallel Circuits | |
|---|---|---|
| Path | Single path | Multiple paths |
| Voltage | Divided among components | Same across components |
| Current | Same throughout | Divided among components |
| Reliability | Single point of failure | Increased reliability |
| Flexibility | Limited flexibility | Improved flexibility |
| Cost | Low cost | Higher cost |
| Complexity | Simple design | Complex design |
🔍 Note: The table above summarizes the key differences between series and parallel circuits. It's essential to understand these differences to design and analyze electric circuits effectively.
Applications of Series and Parallel Circuits
Both series and parallel circuits have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Electronics: Series circuits are used in simple devices like calculators, while parallel circuits are used in complex systems like computers.
- Power Distribution: Parallel circuits are used in power distribution systems to provide reliable and efficient power supply.
- Automotive: Series circuits are used in automotive systems, such as lighting and accessory circuits, while parallel circuits are used in complex systems like engine control units.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding series and parallel circuits is crucial for designing and analyzing electric circuits. While series circuits are simple and cost-effective, parallel circuits offer increased reliability and flexibility. By recognizing the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of each type of circuit, you can make informed decisions when designing and building electric circuits.
What is the main difference between series and parallel circuits?
+The main difference between series and parallel circuits is the way components are connected. In a series circuit, components are connected one after the other, while in a parallel circuit, components are connected between the same two points.
Which type of circuit is more reliable?
+Parallel circuits are generally more reliable than series circuits because they are less prone to single-point failures.
What are some common applications of series and parallel circuits?
+Series circuits are used in simple devices like calculators, while parallel circuits are used in complex systems like computers and power distribution systems.
Related Terms:
- Series circuit worksheet
- Electrical circuit pdf
- Parallel circuit questions