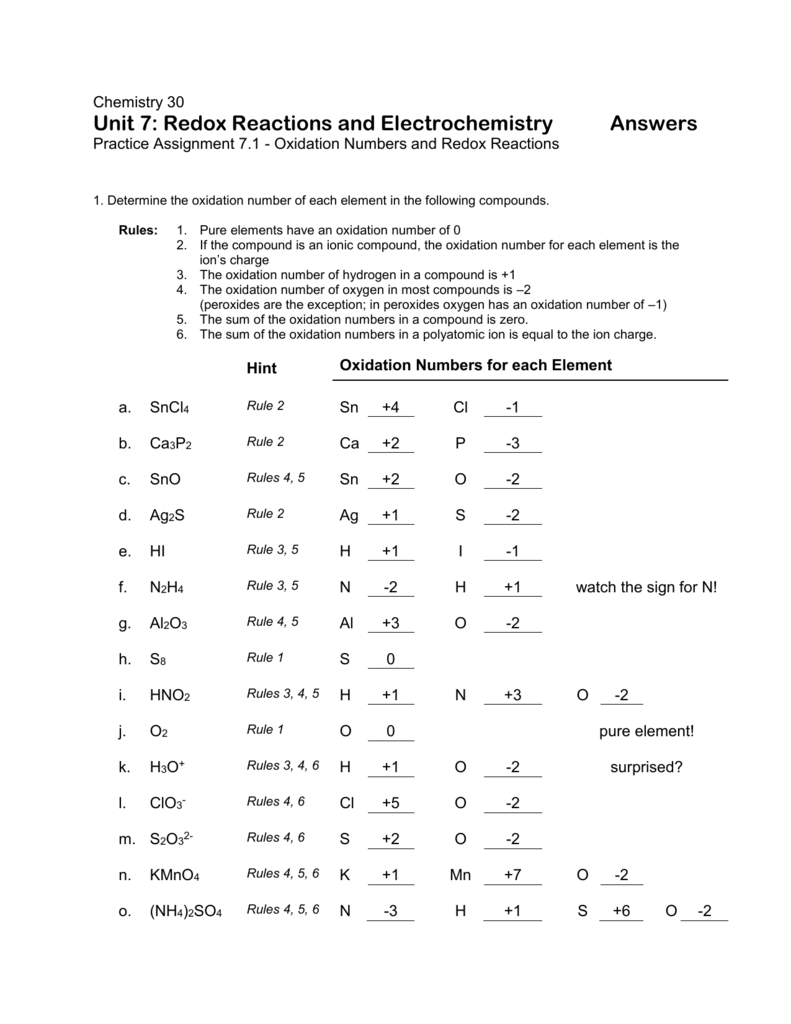
5 Tips to Master Oxidation Numbers Worksheet

Mastering oxidation numbers is a crucial skill for any chemistry student. It can be a challenging concept to grasp, but with practice and the right strategies, you can become proficient in assigning oxidation numbers. Here are five tips to help you master oxidation numbers worksheet:
Tip 1: Understand the Rules
To assign oxidation numbers, you need to know the basic rules. These rules are:
- Free elements have an oxidation number of 0.
- Monatomic ions have an oxidation number equal to their charge.
- Oxygen has an oxidation number of -2, except in peroxides where it is -1.
- Hydrogen has an oxidation number of +1, except in hydrides where it is -1.
- The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound is 0.
- The sum of the oxidation numbers of all atoms in a polyatomic ion is equal to the charge of the ion.
Make sure you understand these rules and can apply them to different situations.
Tip 2: Practice, Practice, Practice
Practice is key to mastering oxidation numbers. Start with simple compounds and gradually move on to more complex ones. Practice assigning oxidation numbers to different elements and compounds.
Some examples of compounds to practice with include:
- NaCl (sodium chloride)
- H2O (water)
- CO2 (carbon dioxide)
- NH3 (ammonia)
- CH4 (methane)
You can find many online resources that provide practice worksheets and exercises.
Tip 3: Use the Periodic Table
The periodic table can be a useful tool when assigning oxidation numbers. By looking at the periodic table, you can determine the common oxidation states of different elements.
For example, elements in group 1 (alkali metals) typically have an oxidation number of +1, while elements in group 2 (alkaline earth metals) typically have an oxidation number of +2.
| Group | Common Oxidation States |
|---|---|
| 1 (Alkali metals) | +1 |
| 2 (Alkaline earth metals) | +2 |
| 17 (Halogens) | -1 |
| 18 (Noble gases) | 0 |
Tip 4: Break Down Complex Compounds
When dealing with complex compounds, break them down into smaller parts. Assign oxidation numbers to each element separately, and then combine them to get the overall oxidation number.
For example, consider the compound K2Cr2O7 (potassium dichromate). To assign oxidation numbers, break it down as follows:
- Potassium (K) has an oxidation number of +1.
- Chromium (Cr) has an oxidation number of +6.
- Oxygen (O) has an oxidation number of -2.
Combine these oxidation numbers to get the overall oxidation number of the compound.
Tip 5: Check Your Work
Finally, check your work to make sure you have assigned oxidation numbers correctly. Go back and review the rules and make sure you have applied them correctly.
You can also use online tools and calculators to check your answers.
👍 Note: Mastering oxidation numbers takes time and practice. Don't get discouraged if you don't get it right away. Keep practicing, and you will eventually become proficient.
By following these five tips, you can master oxidation numbers and become more confident in your ability to assign them. Remember to practice regularly and check your work to ensure accuracy.
When you feel confident in your ability to assign oxidation numbers, try tackling more complex compounds and reactions. With time and practice, you will become proficient in this important chemistry skill.
Mastering oxidation numbers is a valuable skill that will help you succeed in chemistry and other related fields. By following these tips and practicing regularly, you can become proficient in this important skill and achieve your academic and professional goals.
And that’s it! With these five tips, you can master oxidation numbers and become more confident in your ability to assign them. Remember to practice regularly and check your work to ensure accuracy.
What is the oxidation number of oxygen in a peroxide?
+The oxidation number of oxygen in a peroxide is -1.
How do I assign oxidation numbers to a polyatomic ion?
+To assign oxidation numbers to a polyatomic ion, sum the oxidation numbers of all atoms in the ion. The sum should equal the charge of the ion.
What is the common oxidation state of elements in group 1?
+The common oxidation state of elements in group 1 is +1.