Osmosis and Diffusion Worksheet: Learn and Practice
Understanding Osmosis and Diffusion
Osmosis and diffusion are two fundamental biological processes that occur in living organisms. Both processes involve the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, but they differ in the type of molecules that move and the direction of movement.
What is Diffusion?
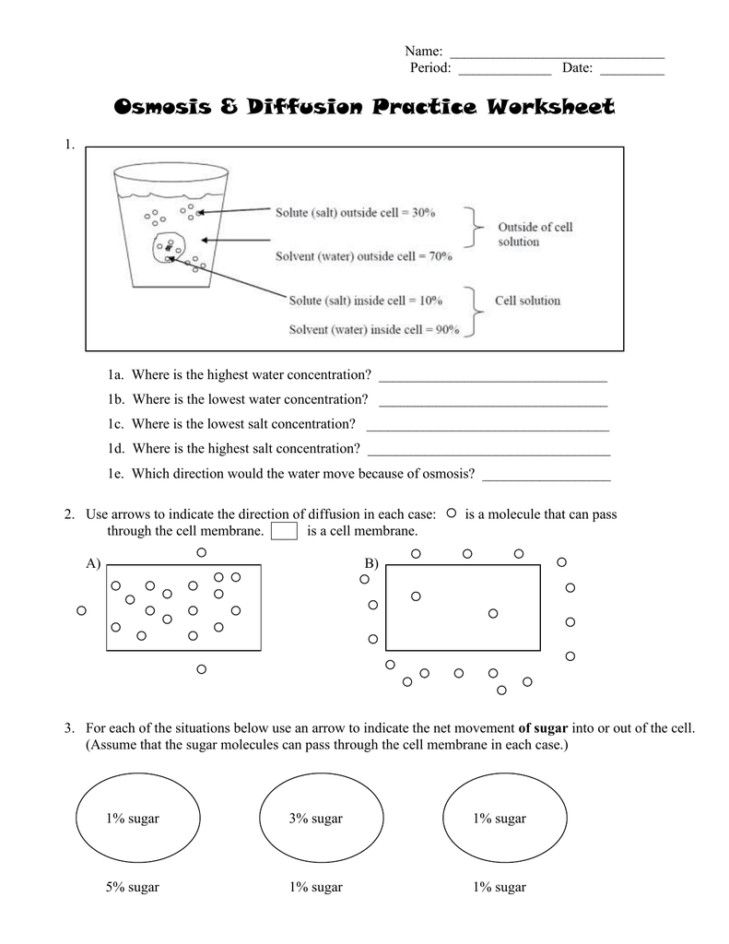
Diffusion is the random movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. This process occurs in gases, liquids, and solids and is an essential aspect of various biological processes, including respiration, photosynthesis, and nutrient uptake.
What is Osmosis?
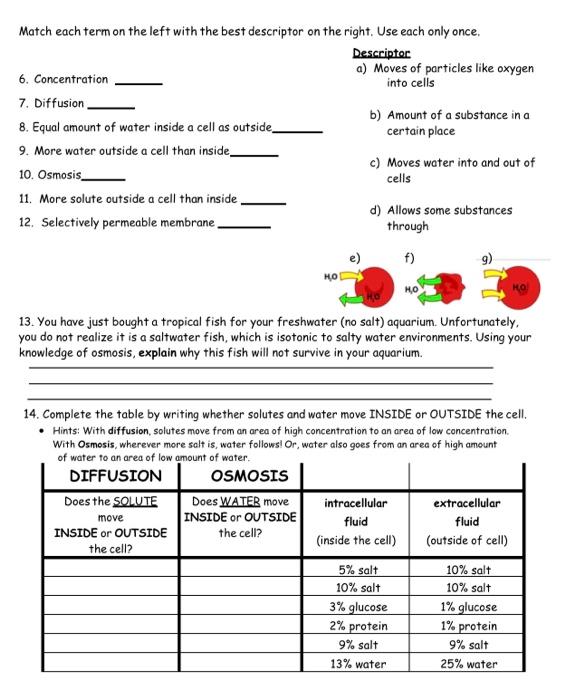
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane. This process is essential for maintaining cell shape, regulating cell volume, and facilitating nutrient and waste transport.
Key Differences between Osmosis and Diffusion
| Diffusion | Osmosis | |
|---|---|---|
| Type of Molecules | All types of molecules | Water molecules only |
| Direction of Movement | From higher concentration to lower concentration | From higher concentration to lower concentration through a selectively permeable membrane |
| Membrane Requirement | No membrane required | Selectively permeable membrane required |
| Examples | Gas exchange in lungs, nutrient uptake in gut | Cell shape maintenance, cell volume regulation |
📝 Note: Both osmosis and diffusion are passive transport processes, meaning they do not require energy input from the cell.
Osmosis in Cells
Osmosis plays a crucial role in maintaining cell shape and regulating cell volume. When a cell is placed in a hypotonic solution (lower solute concentration), water molecules enter the cell through osmosis, causing the cell to swell. In contrast, when a cell is placed in a hypertonic solution (higher solute concentration), water molecules leave the cell through osmosis, causing the cell to shrink.
Isotonic Solutions
An isotonic solution has the same solute concentration as the cell’s cytoplasm. In this case, there is no net movement of water molecules into or out of the cell, and the cell maintains its shape and volume.
Factors Affecting Osmosis and Diffusion
Several factors can influence the rate of osmosis and diffusion, including:
- Surface area: Increasing the surface area of a cell or membrane can increase the rate of osmosis and diffusion.
- Temperature: Increasing the temperature can increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to faster osmosis and diffusion rates.
- Concentration gradient: A steeper concentration gradient can increase the rate of osmosis and diffusion.
- Membrane permeability: Increasing the permeability of a membrane can increase the rate of osmosis and diffusion.
Practice Problems
- What is the primary difference between osmosis and diffusion?
- Describe the movement of molecules in a hypotonic solution.
- What is the effect of increasing the surface area on the rate of osmosis?
- Explain the concept of isotonic solutions.
Answer Key
- Osmosis involves the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, while diffusion involves the movement of all types of molecules.
- In a hypotonic solution, water molecules enter the cell through osmosis, causing the cell to swell.
- Increasing the surface area can increase the rate of osmosis by providing more sites for water molecules to enter or leave the cell.
- An isotonic solution has the same solute concentration as the cell’s cytoplasm, resulting in no net movement of water molecules into or out of the cell.
Now that you have completed this worksheet, you should have a better understanding of osmosis and diffusion. Remember to practice and review these concepts regularly to reinforce your knowledge.
What is the primary function of osmosis in cells?
+Osmosis helps maintain cell shape and regulate cell volume by controlling the movement of water molecules into and out of the cell.
What is the difference between a hypotonic and hypertonic solution?
+A hypotonic solution has a lower solute concentration than the cell’s cytoplasm, while a hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration than the cell’s cytoplasm.
What is the effect of increasing the temperature on the rate of osmosis?
+Increasing the temperature can increase the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to faster osmosis rates.



