5 Easy Ways to Solve One Step Equations
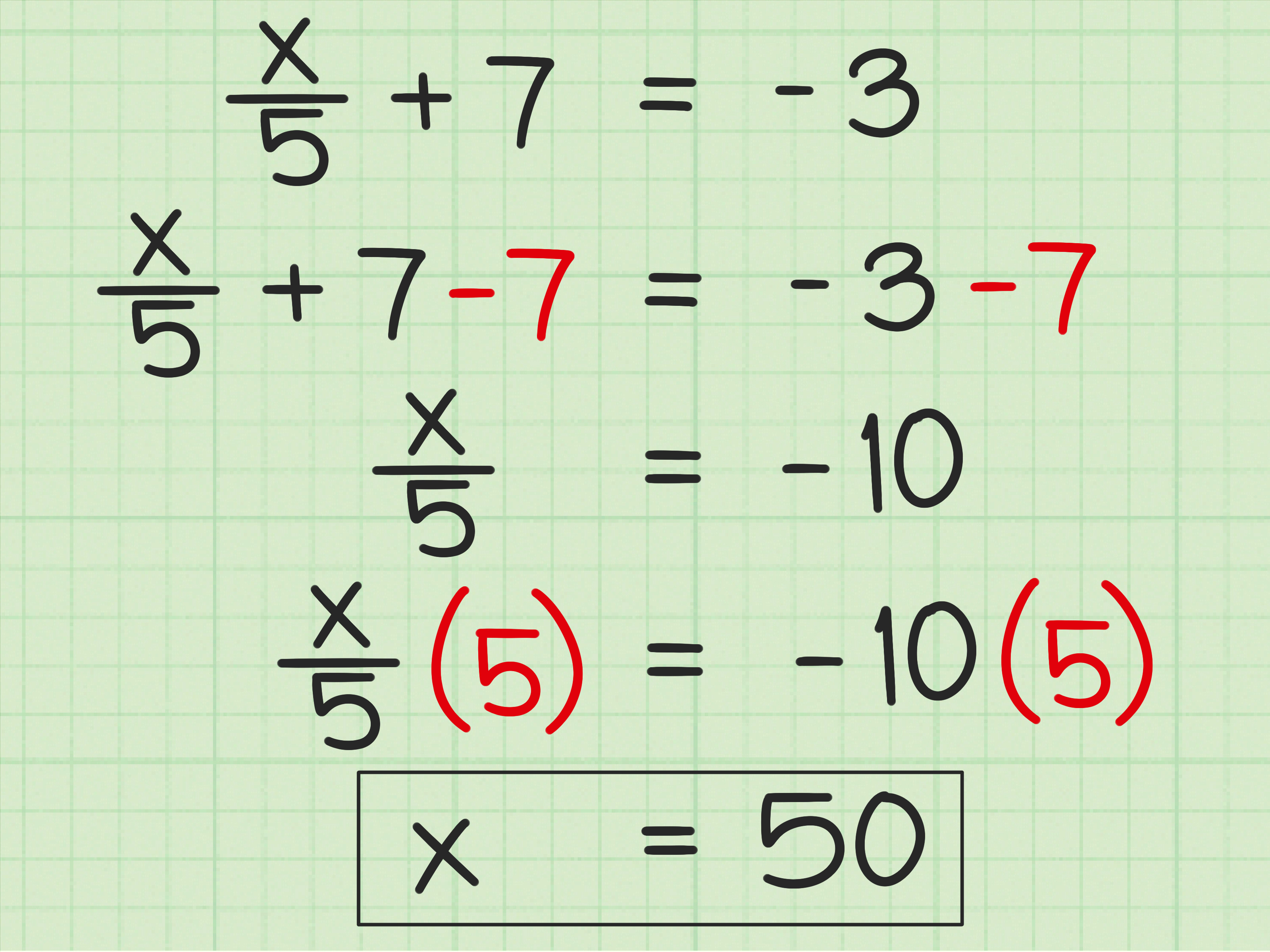
Introduction to One Step Equations
In mathematics, equations are statements that express the equality of two mathematical expressions. One step equations, also known as simple equations, are a fundamental concept in algebra that involve one variable and can be solved in a single step. These equations are a crucial building block for more complex mathematical problems and are used to solve a wide range of problems in science, engineering, economics, and everyday life.
What are One Step Equations?
One step equations are equations that can be solved by performing a single operation, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division, to isolate the variable. These equations typically have the form:
ax = b
Where a and b are constants and x is the variable.
5 Easy Ways to Solve One Step Equations
Solving one step equations is a straightforward process that involves isolating the variable by performing the inverse operation of the one that is being applied to it. Here are five easy ways to solve one step equations:
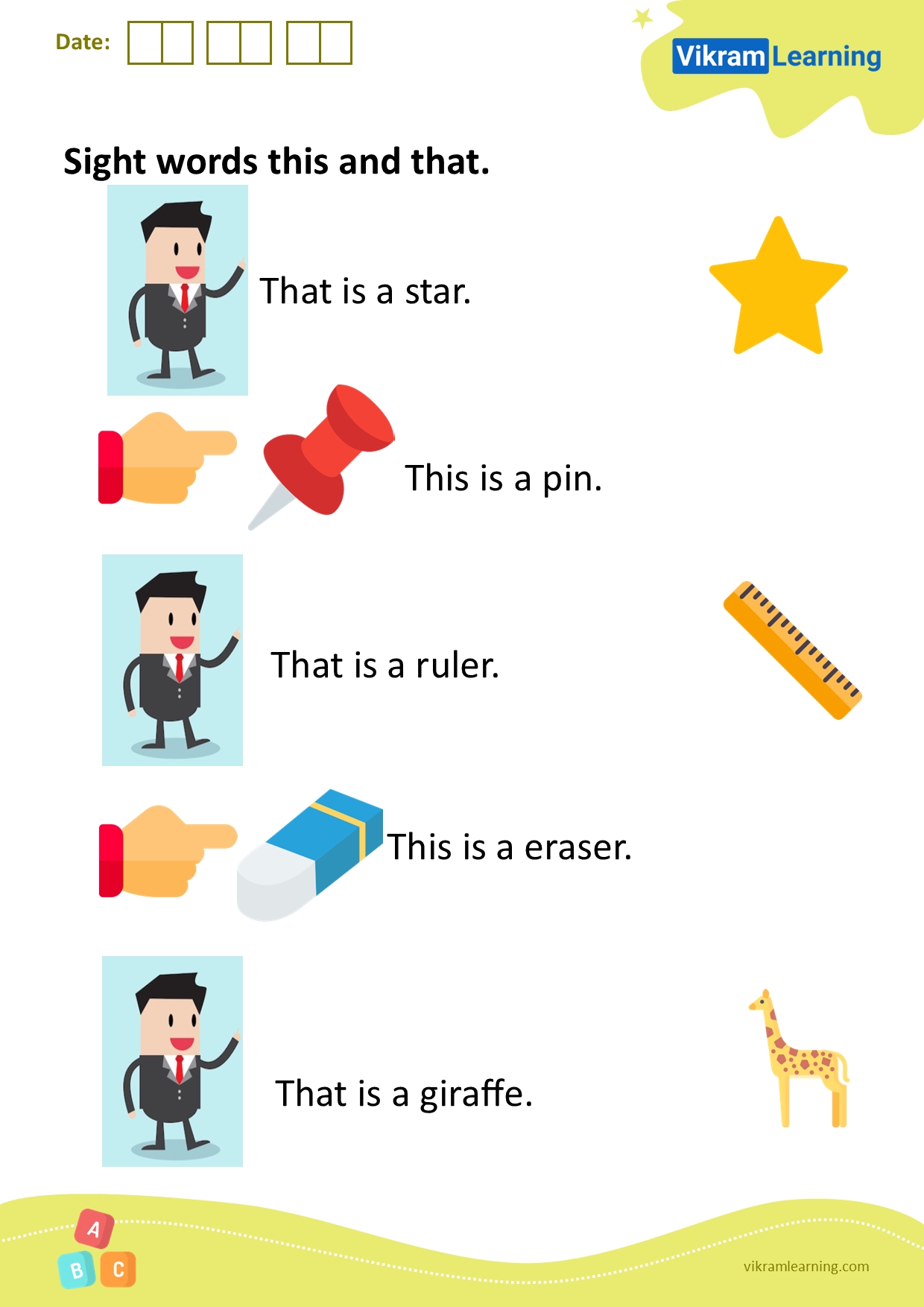
1. Addition and Subtraction Equations
To solve addition and subtraction equations, we need to isolate the variable by performing the inverse operation.
- Addition Equation: x + a = b
- Solution: x = b - a
Example: x + 2 = 5
Solution: x = 5 - 2 x = 3
- Subtraction Equation: x - a = b
- Solution: x = b + a
Example: x - 2 = 3
Solution: x = 3 + 2 x = 5
🤔 Note: To isolate the variable, we add or subtract the same value to both sides of the equation.
2. Multiplication and Division Equations
To solve multiplication and division equations, we need to isolate the variable by performing the inverse operation.
- Multiplication Equation: ax = b
- Solution: x = b/a
Example: 2x = 6
Solution: x = 6⁄2 x = 3
- Division Equation: x/a = b
- Solution: x = ab
Example: x/2 = 3
Solution: x = 3(2) x = 6
🤔 Note: To isolate the variable, we multiply or divide both sides of the equation by the same value.
3. Combining Addition and Multiplication Equations
Some one step equations may involve both addition and multiplication. To solve these equations, we need to perform the operations in the correct order.
- Equation: ax + b = c
- Solution: x = (c - b)/a
Example: 2x + 3 = 7
Solution: 2x = 7 - 3 2x = 4 x = 4⁄2 x = 2
🤔 Note: To isolate the variable, we need to subtract the constant term before dividing by the coefficient.
4. Combining Subtraction and Multiplication Equations
Some one step equations may involve both subtraction and multiplication. To solve these equations, we need to perform the operations in the correct order.
- Equation: ax - b = c
- Solution: x = (c + b)/a
Example: 2x - 3 = 4
Solution: 2x = 4 + 3 2x = 7 x = 7⁄2 x = 3.5
🤔 Note: To isolate the variable, we need to add the constant term before dividing by the coefficient.
5. Solving Equations with Negative Coefficients
Some one step equations may involve negative coefficients. To solve these equations, we need to remember that dividing by a negative number changes the sign of the result.
- Equation: -ax = b
- Solution: x = -b/a
Example: -2x = 6
Solution: x = -6⁄2 x = -3
🤔 Note: To isolate the variable, we need to divide by the negative coefficient and change the sign of the result.
Conclusion Summary
One step equations are a fundamental concept in algebra that can be solved in a single step. By following the inverse operations and performing the correct steps, we can solve a wide range of one step equations. Whether we’re dealing with addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division, the key is to isolate the variable and perform the operations in the correct order.
What is a one step equation?
+
A one step equation is an equation that can be solved in a single step by performing a single operation, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
How do I solve a one step equation?
+
To solve a one step equation, perform the inverse operation of the one that is being applied to the variable. For example, if the equation is x + 2 = 5, subtract 2 from both sides to get x = 3.
What is the inverse operation?
+
The inverse operation is the opposite operation of the one being applied to the variable. For example, the inverse operation of addition is subtraction, and the inverse operation of multiplication is division.