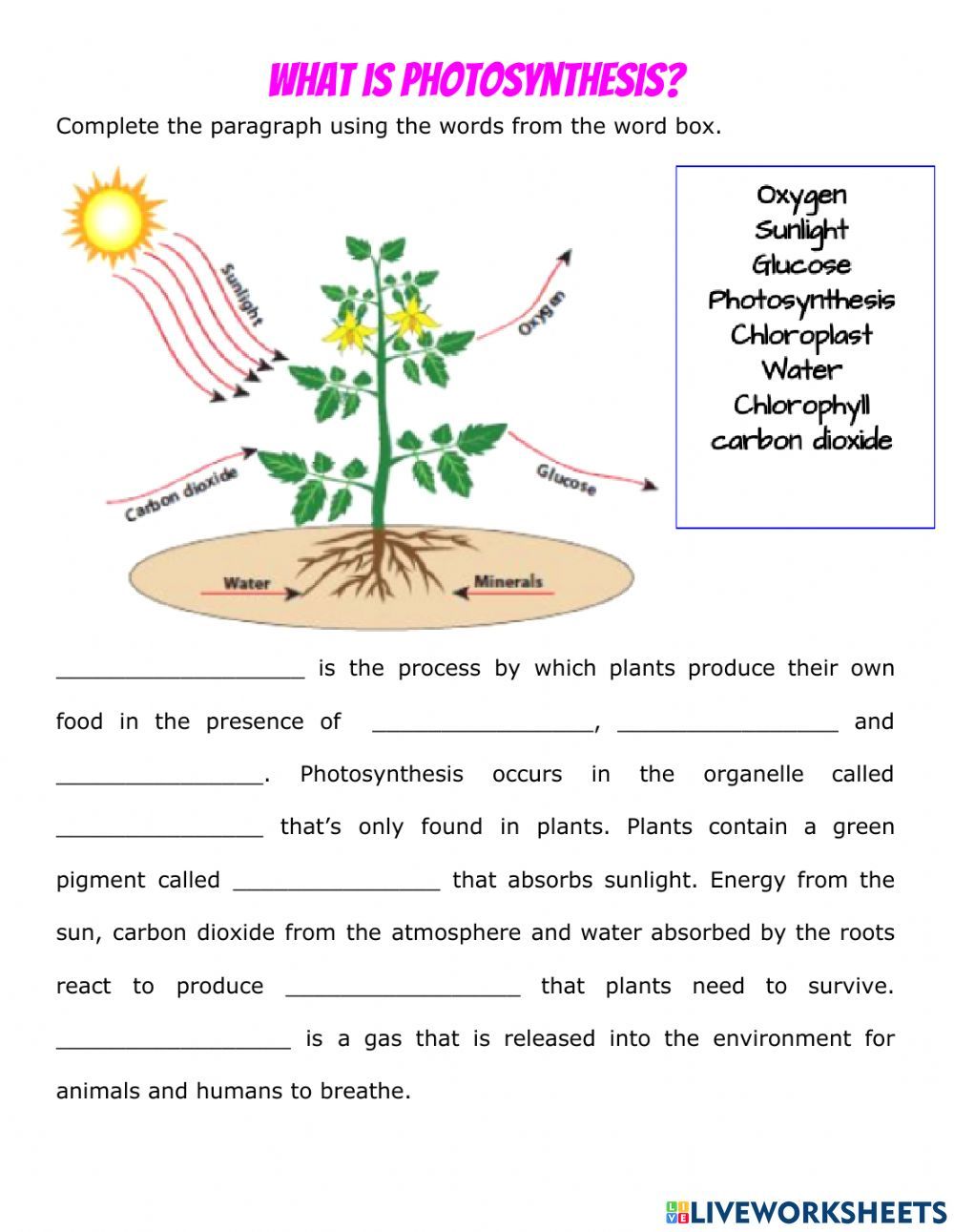
6 Ways to Solve One and Two Step Equations
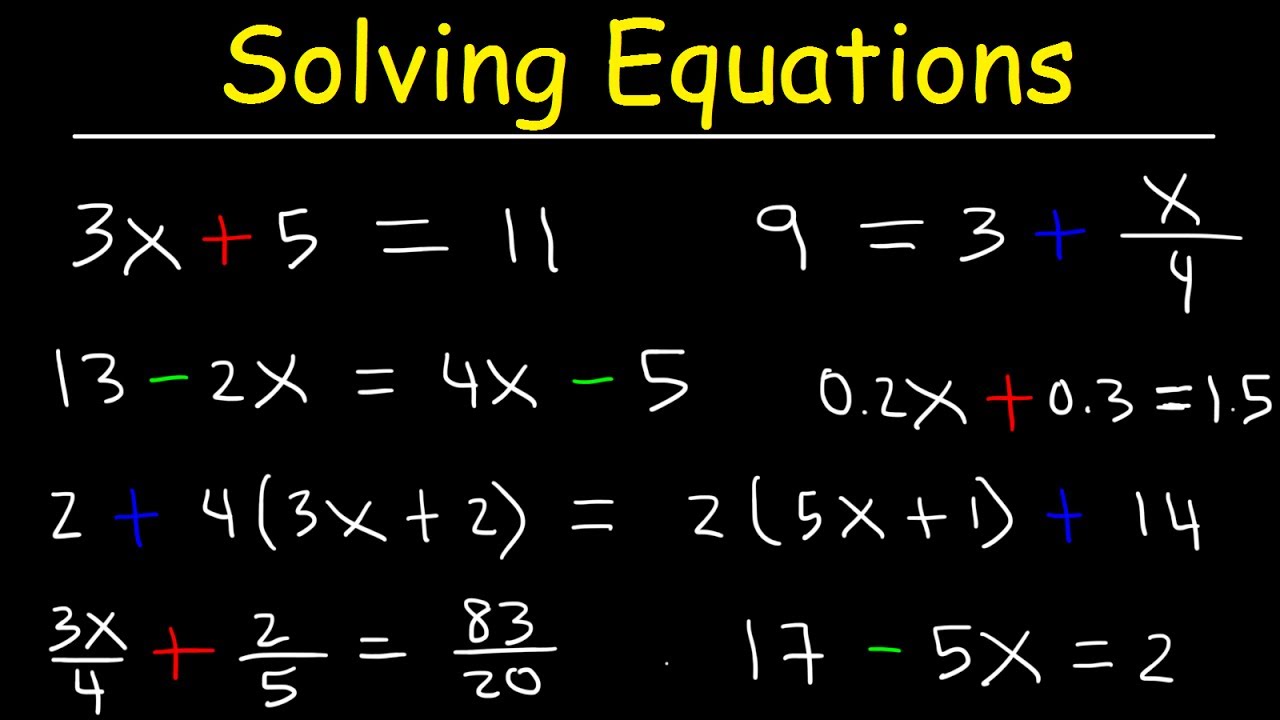
Understanding the Basics of One and Two Step Equations
Equations are a fundamental concept in mathematics, and solving them is a crucial skill that every student should master. In this article, we will focus on one and two step equations, which are the building blocks of more complex equations. We will explore six different ways to solve these types of equations, including addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
What are One and Two Step Equations?
One step equations are simple equations that can be solved in one step. They typically involve one operation, such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division. For example:
2x = 6
To solve this equation, we simply divide both sides by 2, which gives us x = 3.
Two step equations, on the other hand, require two steps to solve. They often involve a combination of operations, such as addition and multiplication, or subtraction and division. For example:
2x + 3 = 7
To solve this equation, we first subtract 3 from both sides, which gives us 2x = 4. Then, we divide both sides by 2, which gives us x = 2.
6 Ways to Solve One and Two Step Equations
Now that we have a basic understanding of one and two step equations, let’s explore six different ways to solve them.
Method 1: Addition
When solving equations with addition, we need to isolate the variable (the letter or symbol that we are trying to solve for) by getting rid of the constant (the number) on the same side of the equation. We can do this by subtracting the constant from both sides of the equation.
For example:
x + 2 = 5
To solve this equation, we subtract 2 from both sides, which gives us x = 3.
Method 2: Subtraction
When solving equations with subtraction, we need to isolate the variable by getting rid of the constant on the same side of the equation. We can do this by adding the constant to both sides of the equation.
For example:
x - 3 = 2
To solve this equation, we add 3 to both sides, which gives us x = 5.
Method 3: Multiplication
When solving equations with multiplication, we need to isolate the variable by getting rid of the coefficient (the number that is multiplied by the variable) on the same side of the equation. We can do this by dividing both sides of the equation by the coefficient.
For example:
2x = 6
To solve this equation, we divide both sides by 2, which gives us x = 3.
Method 4: Division
When solving equations with division, we need to isolate the variable by getting rid of the coefficient on the same side of the equation. We can do this by multiplying both sides of the equation by the coefficient.
For example:
x/2 = 3
To solve this equation, we multiply both sides by 2, which gives us x = 6.
Method 5: Combining Addition and Multiplication
When solving two step equations, we often need to combine addition and multiplication. We can do this by first isolating the variable using addition or subtraction, and then using multiplication or division to solve for the variable.
For example:
2x + 3 = 7
To solve this equation, we first subtract 3 from both sides, which gives us 2x = 4. Then, we divide both sides by 2, which gives us x = 2.
Method 6: Combining Subtraction and Division
When solving two step equations, we often need to combine subtraction and division. We can do this by first isolating the variable using subtraction or addition, and then using division or multiplication to solve for the variable.
For example:
x - 2 = 3⁄2
To solve this equation, we first add 2 to both sides, which gives us x = 3⁄2 + 2. Then, we simplify the right-hand side of the equation by converting the fraction to a decimal or a mixed number, which gives us x = 3.5 or x = 3 1⁄2.
💡 Note: When combining operations, it's essential to follow the order of operations (PEMDAS) to ensure that we are solving the equation correctly.
Conclusion
Solving one and two step equations is a fundamental skill that every student should master. By using the six methods outlined in this article, students can develop a strong foundation in algebra and problem-solving. Remember to always follow the order of operations and to combine operations carefully to ensure accurate solutions.
What is the difference between one step and two step equations?
+One step equations can be solved in one step, while two step equations require two steps to solve. Two step equations often involve a combination of operations, such as addition and multiplication, or subtraction and division.
How do I know which method to use to solve an equation?
+The method you use to solve an equation depends on the type of equation and the operations involved. If the equation involves addition or subtraction, you can use the addition or subtraction method. If the equation involves multiplication or division, you can use the multiplication or division method. If the equation involves a combination of operations, you may need to use a combination of methods.
What is the order of operations, and why is it important?
+The order of operations is a set of rules that tells us which operations to perform first when solving an equation. The order of operations is parentheses, exponents, multiplication and division, and addition and subtraction. Following the order of operations is essential to ensure that we are solving equations accurately and avoiding errors.