Master Ohm's Law with Free Worksheets and Examples
Understanding the Fundamentals of Ohm's Law
Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electricity and electronics that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. In 1827, Georg Simon Ohm, a German physicist, formulated this law, which has since become a cornerstone of electrical engineering and electronics.
🔌 Note: Ohm's Law is a crucial concept to grasp for anyone working with electricity or electronics.
The Formula Behind Ohm's Law
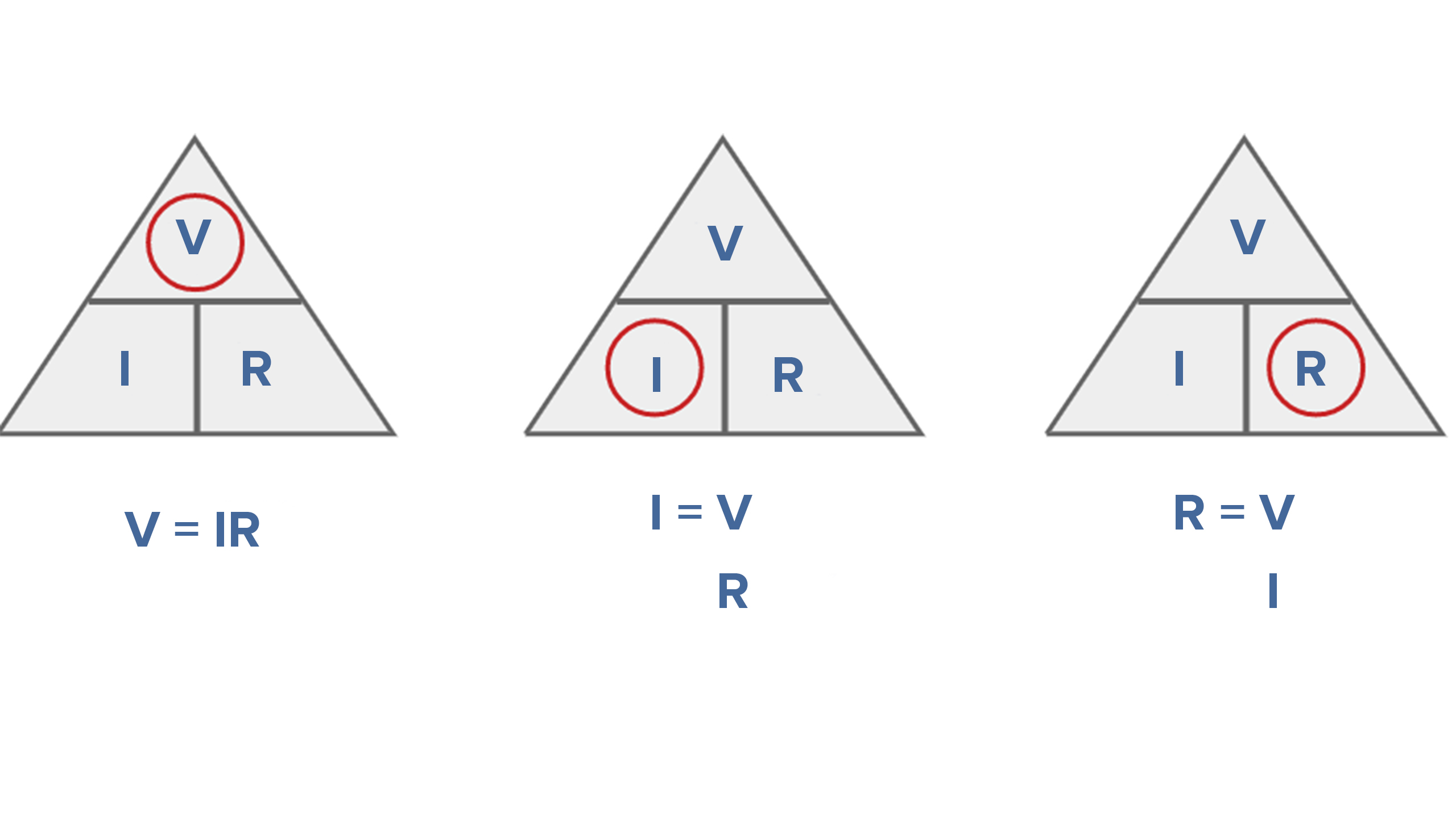
Ohm’s Law states that the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to the voltage applied across it, and inversely proportional to the resistance of the conductor. The formula is:
I = V/R
Where:
- I is the current in amperes (A)
- V is the voltage in volts (V)
- R is the resistance in ohms (Ω)
This formula can be rearranged to solve for voltage or resistance, given the other two values.
Solving for Voltage
V = I × R
Solving for Resistance
R = V/I
Free Worksheets and Examples
To help you master Ohm’s Law, we’ve created a set of free worksheets and examples. These resources will help you practice applying Ohm’s Law to different scenarios and reinforce your understanding of the concept.
Worksheet 1: Basic Ohm’s Law Problems
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| Find the current flowing through a 10 Ω resistor when a 12 V voltage is applied. | I = V/R = 12⁄10 = 1.2 A |
| A circuit has a resistance of 20 Ω and a current of 0.5 A. What is the voltage applied? | V = I × R = 0.5 × 20 = 10 V |
| A conductor has a voltage of 24 V and a current of 2 A. What is the resistance? | R = V/I = 24⁄2 = 12 Ω |
Worksheet 2: More Challenging Problems
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| A circuit has a resistance of 30 Ω and a voltage of 18 V. If the current is increased to 2 A, what is the new resistance? | R = V/I = 18⁄2 = 9 Ω |
| A wire has a resistance of 10 Ω and a current of 1 A. If the voltage is increased to 20 V, what is the new current? | I = V/R = 20⁄10 = 2 A |
| A circuit has a voltage of 12 V and a resistance of 8 Ω. If the current is 1.5 A, what is the power consumed? | P = V × I = 12 × 1.5 = 18 W |
Real-World Applications of Ohm's Law
Ohm’s Law has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Electrical Engineering: Ohm’s Law is used to design and analyze electrical circuits, including power distribution systems and electronic devices.
- Electronics: Ohm’s Law is used to calculate the current, voltage, and resistance of electronic components, such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors.
- Physics: Ohm’s Law is used to understand the behavior of electric currents and the properties of conductors.
💡 Note: Ohm's Law is a fundamental concept that has far-reaching applications in many fields.
Conclusion
Mastering Ohm’s Law is essential for anyone working with electricity or electronics. With practice and experience, you’ll become proficient in applying Ohm’s Law to solve problems and analyze circuits. Remember, the key to understanding Ohm’s Law is to practice, practice, practice!
What is Ohm’s Law?
+Ohm’s Law is a fundamental concept in electricity and electronics that describes the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit.
How do I calculate current using Ohm’s Law?
+Current (I) can be calculated using the formula: I = V/R, where V is the voltage and R is the resistance.
What are some real-world applications of Ohm’s Law?
+Ohm’s Law has numerous applications in various fields, including electrical engineering, electronics, and physics.



