Mastering Newton's Laws Worksheet: Physics Essentials
Understanding Newton's Laws: A Comprehensive Guide
Sir Isaac Newton’s laws of motion are fundamental principles in physics that describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it. These laws, which were first presented in the late 17th century, are still widely used today to predict and explain the motion of objects. In this article, we will delve into the details of each law, provide examples, and offer a worksheet to help you master Newton’s laws.
Newton's First Law: The Law of Inertia
Newton’s first law, also known as the law of inertia, states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue to move with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force. This law is often expressed as:
“An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue to move with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force.”
For example, imagine you are sitting in a car that is traveling at a constant speed. If the car suddenly stops, you will be thrown forward because your body tends to maintain its state of motion. This is a demonstration of Newton’s first law in action.
Newton's Second Law: The Law of Acceleration
Newton’s second law relates the motion of an object to the force acting upon it. It states that the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the force applied and inversely proportional to its mass. The law is often expressed as:
F = ma
Where:
- F is the net force acting on the object
- m is the mass of the object
- a is the acceleration of the object
For example, imagine you are pushing a box across the floor. If you push the box with a greater force, it will accelerate faster. However, if the box is heavier, it will require more force to achieve the same acceleration.
Newton's Third Law: The Law of Action and Reaction
Newton’s third law states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This law applies to all interactions between objects. When object A exerts a force on object B, object B always exerts an equal and opposite force on object A.
“For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.”
For example, imagine you are standing on the ground and pushing against a wall. The wall exerts an equal and opposite force on you, keeping you in place.
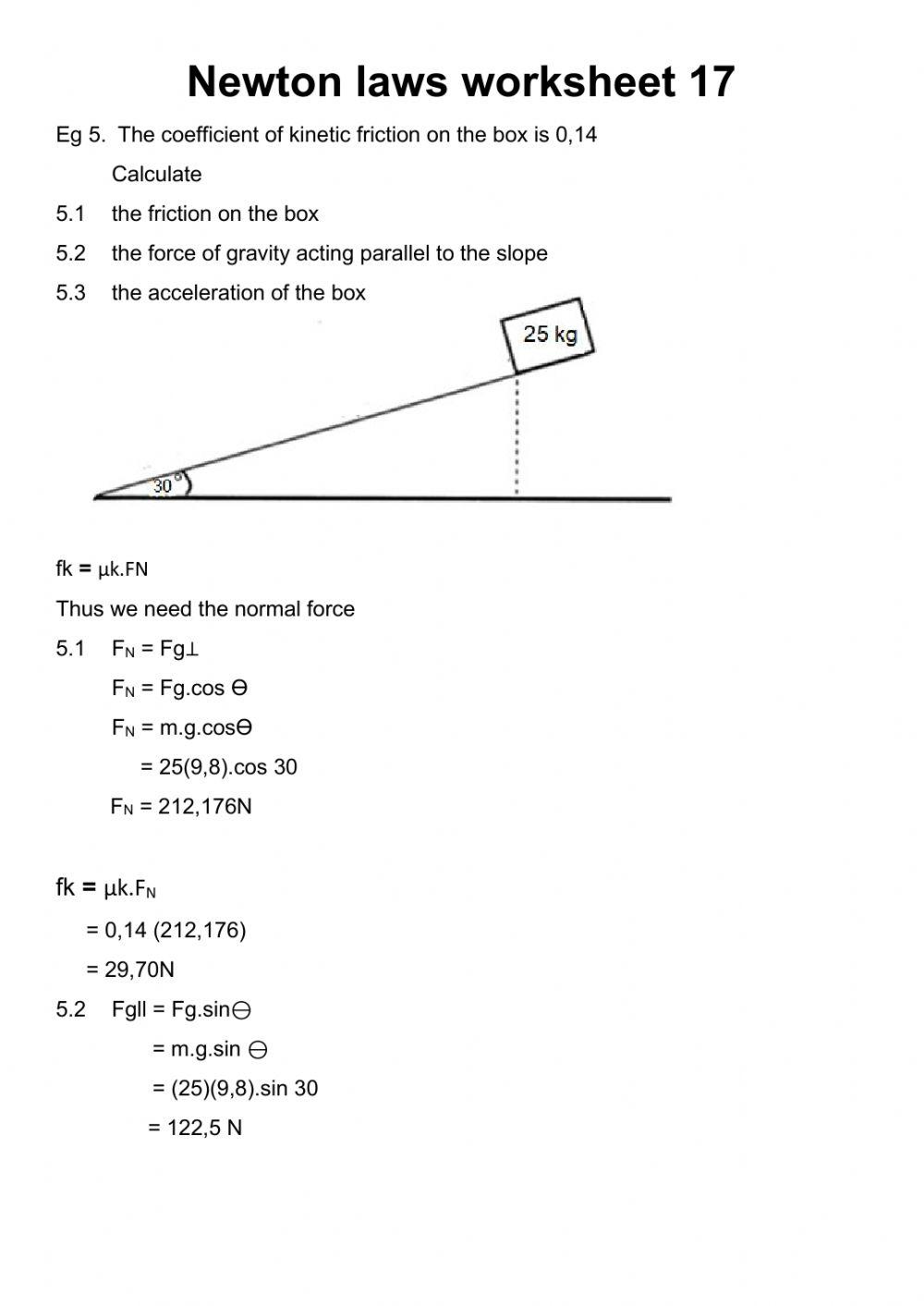
Mastering Newton's Laws: A Worksheet
To help you master Newton’s laws, we have created a worksheet with a series of questions and problems. Work through the worksheet and check your answers to ensure you have a solid understanding of the laws.
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| 1. What is Newton's first law? | An object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue to move with a constant velocity, unless acted upon by an external force. |
| 2. What is the relationship between force and acceleration according to Newton's second law? | F = ma |
| 3. What is Newton's third law? | For every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. |
| 4. A car is traveling at a constant speed of 60 km/h. What will happen if the brakes are applied? | The car will slow down due to the external force of the brakes. |
| 5. A box is pushed across the floor with a force of 10 N. If the box has a mass of 5 kg, what is its acceleration? | a = F / m = 10 N / 5 kg = 2 m/s^2 |
📝 Note: The worksheet is designed to help you understand and apply Newton's laws. Take your time to work through the questions and problems, and check your answers to ensure you have a solid grasp of the concepts.
In conclusion, Newton’s laws are fundamental principles that describe the relationship between a body and the forces acting upon it. By understanding and applying these laws, you can predict and explain the motion of objects in a wide range of situations. Remember to practice and reinforce your understanding with the worksheet provided.
What is the main difference between Newton’s first and second laws?
+Newton’s first law describes the tendency of an object to resist changes in its motion, while Newton’s second law relates the motion of an object to the force acting upon it.
Can you provide an example of Newton’s third law in action?
+When you throw a ball, the ball exerts an equal and opposite force on your hand, causing it to move backward.
How can I apply Newton’s laws in real-life situations?
+Newton’s laws can be applied to a wide range of situations, from predicting the motion of objects to designing safety systems. By understanding and applying these laws, you can make informed decisions and solve problems in fields such as physics, engineering, and architecture.