5 Ways to Master Electron Configuration
Understanding Electron Configuration: A Key to Unlocking Chemistry
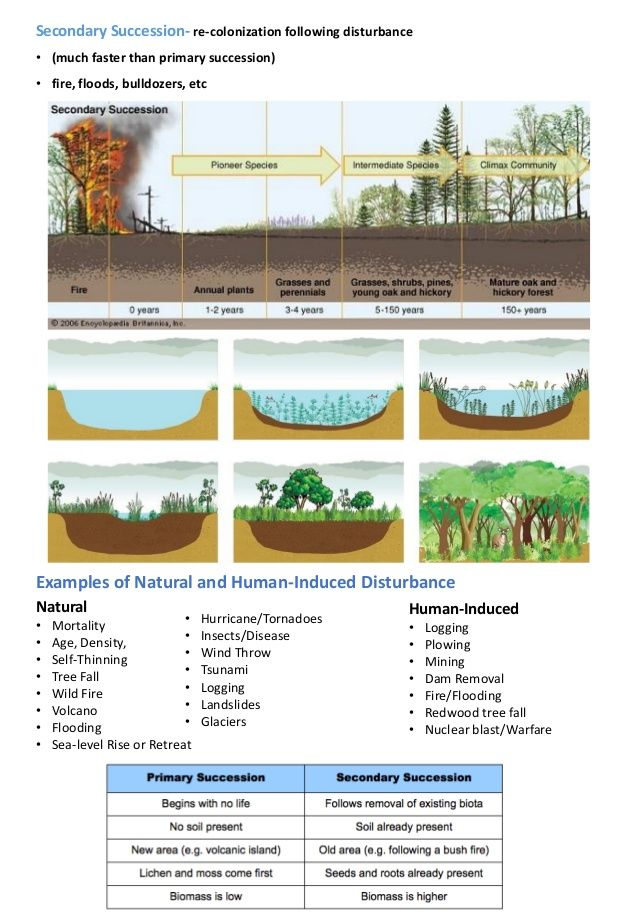
Electron configuration is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom. It is a crucial tool for understanding the properties and behavior of elements, and it is essential for students of chemistry to master. In this article, we will explore five ways to master electron configuration, including understanding the basics, using the Aufbau principle, applying the Pauli Exclusion Principle, using the Hund’s Rule, and practicing with examples.
1. Understanding the Basics of Electron Configuration
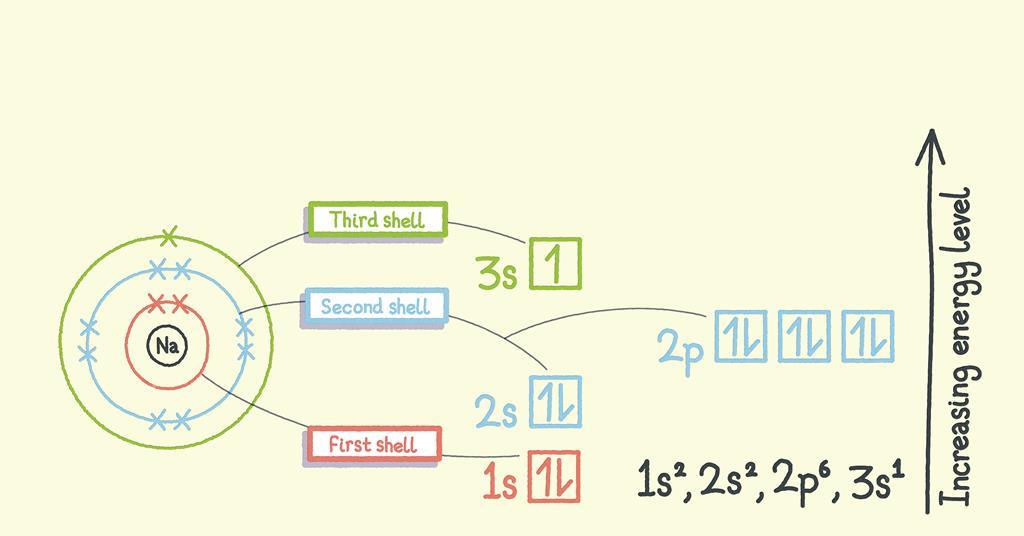
Before diving into the details of electron configuration, it is essential to understand the basics. Electron configuration describes the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which is determined by the energy levels or shells that the electrons occupy. The energy levels are designated by integers (1, 2, 3, etc.), and each energy level has a specific capacity for electrons. The electrons in an atom are arranged in a specific order, with the lowest energy electrons occupying the innermost energy level and the highest energy electrons occupying the outermost energy level.
🔍 Note: The energy levels are also referred to as electron shells or orbitals.
2. Using the Aufbau Principle to Build Electron Configurations
The Aufbau principle is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom. This principle is used to build electron configurations by adding electrons to the lowest available energy levels. The Aufbau principle is essential for understanding the arrangement of electrons in an atom and for predicting the properties of elements.
🔍 Note: The Aufbau principle is also known as the "building-up" principle.
Steps to Apply the Aufbau Principle:
- Identify the energy levels in an atom, starting from the lowest energy level (1s).
- Determine the number of electrons in the atom.
- Add electrons to the lowest available energy levels, starting from the 1s orbital.
- Continue adding electrons to the next available energy levels until all electrons are accounted for.
3. Applying the Pauli Exclusion Principle to Electron Configurations
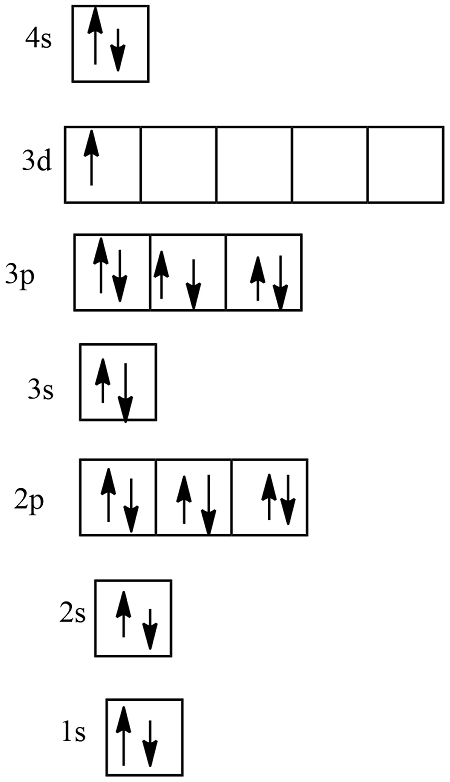
The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers. This principle is essential for understanding the arrangement of electrons in an atom and for predicting the properties of elements. The Pauli Exclusion Principle is used to determine the maximum number of electrons that can occupy a specific energy level.
Steps to Apply the Pauli Exclusion Principle:
- Identify the energy levels in an atom, starting from the lowest energy level (1s).
- Determine the number of electrons in the atom.
- Apply the Pauli Exclusion Principle to each energy level, ensuring that no two electrons have the same set of quantum numbers.
- Continue applying the principle to each energy level until all electrons are accounted for.
4. Using Hund's Rule to Determine Electron Configurations
Hund’s Rule states that when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, they occupy them singly and with parallel spins before pairing up. This rule is essential for understanding the arrangement of electrons in an atom and for predicting the properties of elements.
Steps to Apply Hund's Rule:
- Identify the energy levels in an atom, starting from the lowest energy level (1s).
- Determine the number of electrons in the atom.
- Apply Hund’s Rule to each energy level, ensuring that electrons occupy orbitals singly and with parallel spins before pairing up.
- Continue applying the rule to each energy level until all electrons are accounted for.
5. Practicing with Examples to Master Electron Configuration
Practicing with examples is essential for mastering electron configuration. By working through examples, students can apply the principles learned in this article to real-world problems.
Example 1: Electron Configuration of Oxygen
- Identify the energy levels in an oxygen atom, starting from the lowest energy level (1s).
- Determine the number of electrons in the atom (8).
- Apply the Aufbau principle to build the electron configuration: 1s² 2s² 2p⁴.
- Apply the Pauli Exclusion Principle to ensure that no two electrons have the same set of quantum numbers.
- Apply Hund’s Rule to determine the electron configuration: 1s² 2s² 2p⁴.
| Energy Level | Electron Configuration |
|---|---|
| 1s | 2 electrons |
| 2s | 2 electrons |
| 2p | 4 electrons |
Mastering electron configuration is essential for understanding the properties and behavior of elements. By following the five steps outlined in this article, students can develop a deep understanding of electron configuration and apply it to real-world problems. Remember to practice with examples to reinforce your understanding of electron configuration.
What is the Aufbau principle?
+The Aufbau principle is a fundamental principle in chemistry that states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom.
What is the Pauli Exclusion Principle?
+The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers.
What is Hund’s Rule?
+Hund’s Rule states that when electrons occupy orbitals of equal energy, they occupy them singly and with parallel spins before pairing up.
Related Terms:
- Electron configuration pdf
- Electron configuration worksheet Doc