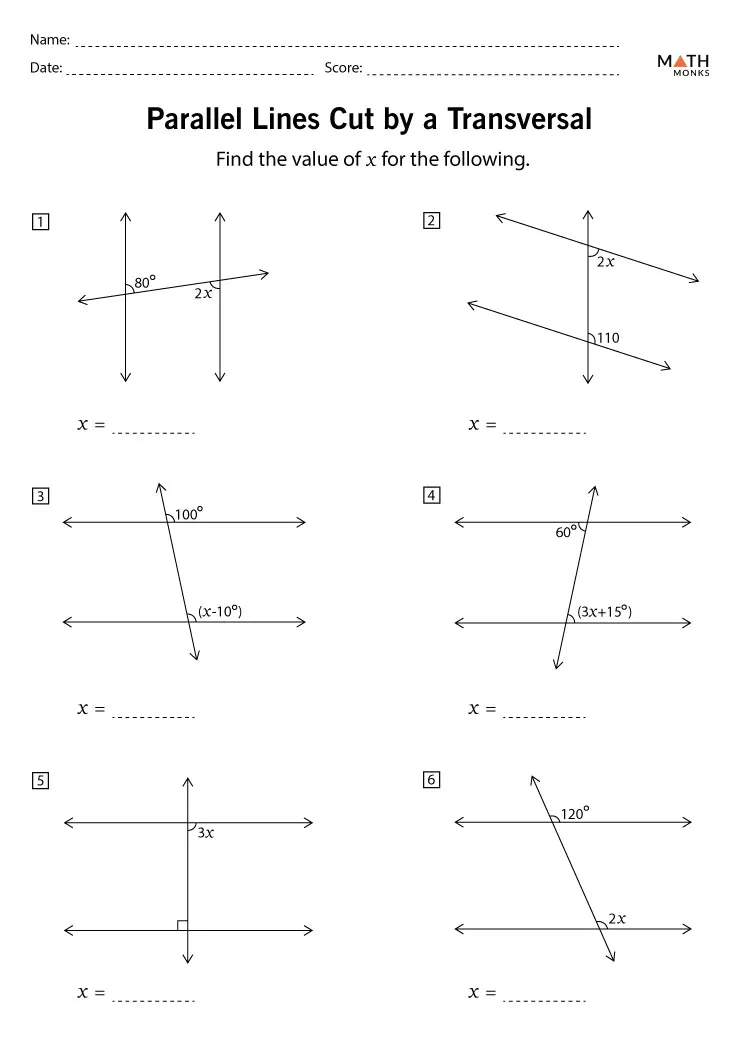
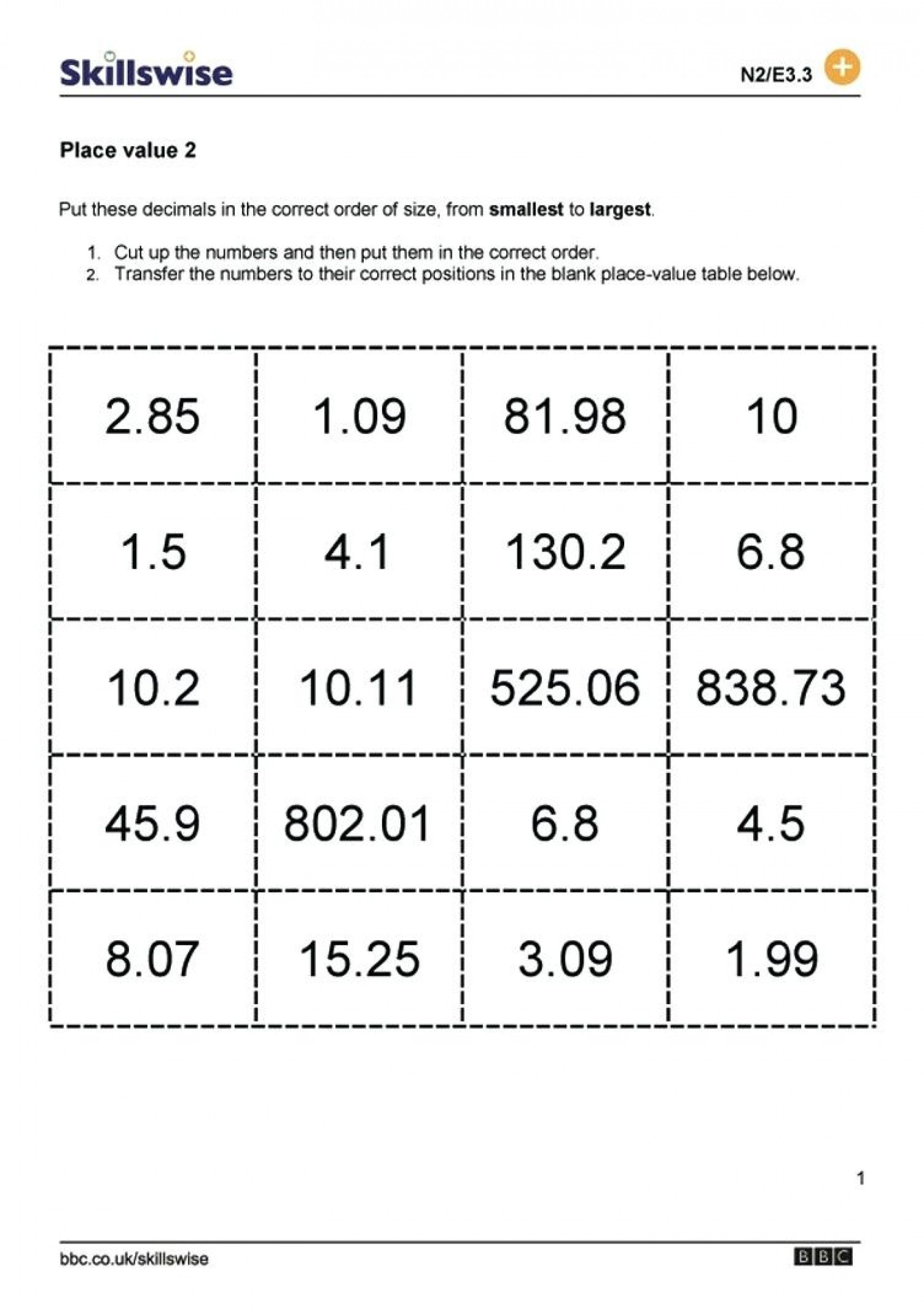
Naming Molecular Compounds Made Easy

Understanding Molecular Compounds
Molecular compounds are a type of chemical compound that is formed when two or more nonmetal atoms share electrons to form a covalent bond. Unlike ionic compounds, which are formed when one or more electrons are transferred between atoms, molecular compounds are formed through the sharing of electrons. This type of bonding is also known as covalent bonding.
Why Naming Molecular Compounds is Important
Naming molecular compounds is an essential skill for chemists, as it allows them to communicate effectively and accurately identify the compounds they are working with. The rules for naming molecular compounds are established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) and are used universally in the field of chemistry.
Prefixes, Roots, and Suffixes: The Building Blocks of Molecular Compound Names
Molecular compound names are composed of three main parts: prefixes, roots, and suffixes.
- Prefixes: Prefixes indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound. The prefixes are as follows:
- Mono- (1)
- Di- (2)
- Tri- (3)
- Tetra- (4)
- Penta- (5)
- Hexa- (6)
- Hepta- (7)
- Octa- (8)
- Nona- (9)
- Deca- (10)
- Roots: Roots are the main part of the name and indicate the type of element present. For example, the root for carbon is “carb-” and for nitrogen is “nit-”.
- Suffixes: Suffixes indicate the type of bond or the number of bonds between atoms. The suffixes are as follows:
- -ide (indicates a single bond)
- -ine (indicates a double bond)
- -yne (indicates a triple bond)
Steps for Naming Molecular Compounds
Here are the steps to follow when naming molecular compounds:
- Determine the elements present: Identify the elements present in the compound and their quantities.
- Determine the prefixes: Determine the prefixes for each element based on the number of atoms present.
- Determine the roots: Determine the roots for each element.
- Determine the suffixes: Determine the suffixes for each element based on the type of bond or number of bonds between atoms.
- Combine the prefixes, roots, and suffixes: Combine the prefixes, roots, and suffixes to form the full name of the compound.
📝 Note: When combining prefixes, roots, and suffixes, the prefix for the first element is always used, followed by the root for the first element, and then the suffix. The prefix for the second element is then used, followed by the root for the second element, and then the suffix.
Examples of Naming Molecular Compounds
Here are some examples of naming molecular compounds:
- CO2: This compound consists of one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. The prefix for carbon is “mono-” and the prefix for oxygen is “di-”. The root for carbon is “carb-” and the root for oxygen is “ox-”. The suffix for the compound is “-ide”. Therefore, the full name of the compound is carbon dioxide.
- CH4: This compound consists of one carbon atom and four hydrogen atoms. The prefix for carbon is “mono-” and the prefix for hydrogen is “tetra-”. The root for carbon is “carb-” and the root for hydrogen is “hyd-”. The suffix for the compound is “-ide”. Therefore, the full name of the compound is methane.
Naming Molecular Compounds with Multiple Bonds
When naming molecular compounds with multiple bonds, the suffixes are modified to indicate the type of bond. For example:
- C2H4: This compound consists of two carbon atoms and four hydrogen atoms, with a double bond between the carbon atoms. The prefix for carbon is “di-” and the prefix for hydrogen is “tetra-”. The root for carbon is “carb-” and the root for hydrogen is “hyd-”. The suffix for the compound is “-ene”. Therefore, the full name of the compound is ethene.
Conclusion
Naming molecular compounds is a straightforward process that involves combining prefixes, roots, and suffixes to form the full name of the compound. By following the steps outlined above, you can easily name molecular compounds and communicate effectively with other chemists.
What is the purpose of prefixes in molecular compound names?
+Prefixes indicate the number of atoms of each element present in the compound.
What is the difference between -ide, -ine, and -yne suffixes?
+-ide indicates a single bond, -ine indicates a double bond, and -yne indicates a triple bond.
How do I name a molecular compound with multiple bonds?
+When naming molecular compounds with multiple bonds, the suffixes are modified to indicate the type of bond. For example, -ene indicates a double bond and -yne indicates a triple bond.