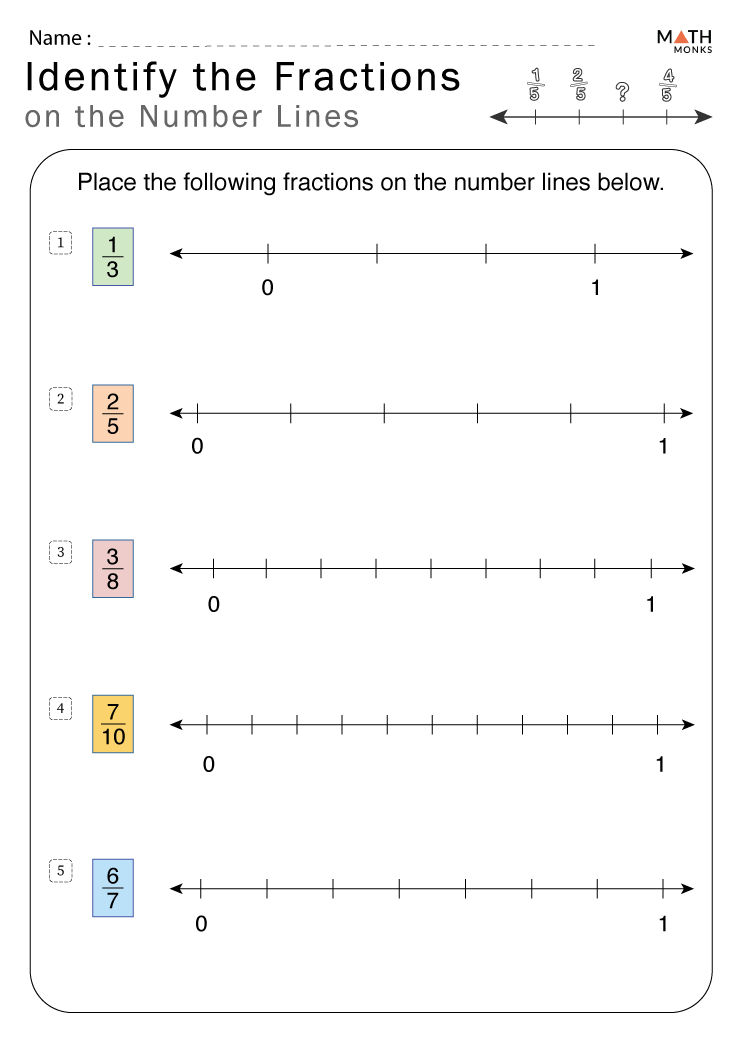
5 Essential Facts on Mutations Worksheet Answer Key Biology

Mutations: The Building Blocks of Genetic Variation
In the complex world of genetics, mutations play a crucial role in shaping the diversity of life on Earth. These changes in the DNA sequence can occur spontaneously or be induced by external factors, leading to a wide range of effects on organisms. Here, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of mutations and explore five essential facts that every biology enthusiast should know.
What are Mutations?
Mutations are changes in the DNA sequence of an organism. They can occur in either the coding or non-coding regions of the genome and can be caused by various factors, including errors during DNA replication, exposure to radiation, or viral infections.
Types of Mutations
There are several types of mutations, including:
- Point mutations: These occur when a single nucleotide is replaced by another.
- Frameshift mutations: These occur when one or more nucleotides are inserted or deleted, leading to a shift in the reading frame of the genetic code.
- Chromosomal mutations: These occur when there are changes in the number or structure of chromosomes.
Effects of Mutations
Mutations can have a range of effects on organisms, including:
- Neutral mutations: These have no significant effect on the organism.
- Beneficial mutations: These provide a selective advantage, increasing the organism’s chances of survival and reproduction.
- Deleterious mutations: These have a negative impact on the organism, reducing its fitness.
Examples of Mutations
Mutations are not just limited to the lab; they occur naturally in the world around us. Here are a few examples:
- Sickle cell anemia: This genetic disorder is caused by a point mutation in the hemoglobin gene, leading to the production of abnormal hemoglobin.
- Antibiotic resistance: Bacteria can develop resistance to antibiotics through mutations in their DNA, making them less susceptible to treatment.
Importance of Mutations in Evolution
Mutations are the raw material for evolution. They provide the genetic variation that allows populations to adapt to changing environments and evolve into new species.
🔬 Note: Mutations can occur spontaneously, but they can also be induced by external factors, such as radiation or chemicals.
Mutations Worksheet Answer Key
What is a mutation? Answer: A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence of an organism.
What are the different types of mutations? Answer: Point mutations, frameshift mutations, and chromosomal mutations.
What are the effects of mutations on organisms? Answer: Mutations can have neutral, beneficial, or deleterious effects on organisms.
Provide an example of a beneficial mutation. Answer: The lactase persistence mutation, which allows some humans to digest lactose into adulthood.
Why are mutations important in evolution? Answer: Mutations provide the genetic variation that allows populations to adapt to changing environments and evolve into new species.
What is the difference between a mutation and a genetic variation?
+A mutation is a change in the DNA sequence, while genetic variation refers to the differences in DNA sequences among individuals or populations.
Can mutations be inherited?
+Yes, mutations can be inherited from one generation to the next. This is known as hereditary mutation.
What is the relationship between mutations and cancer?
+Mutations can contribute to the development of cancer by disrupting normal cellular processes and leading to uncontrolled cell growth.
In conclusion, mutations are a vital aspect of genetics and play a significant role in shaping the diversity of life on Earth. Understanding the different types of mutations, their effects on organisms, and their importance in evolution can provide valuable insights into the complex world of genetics.