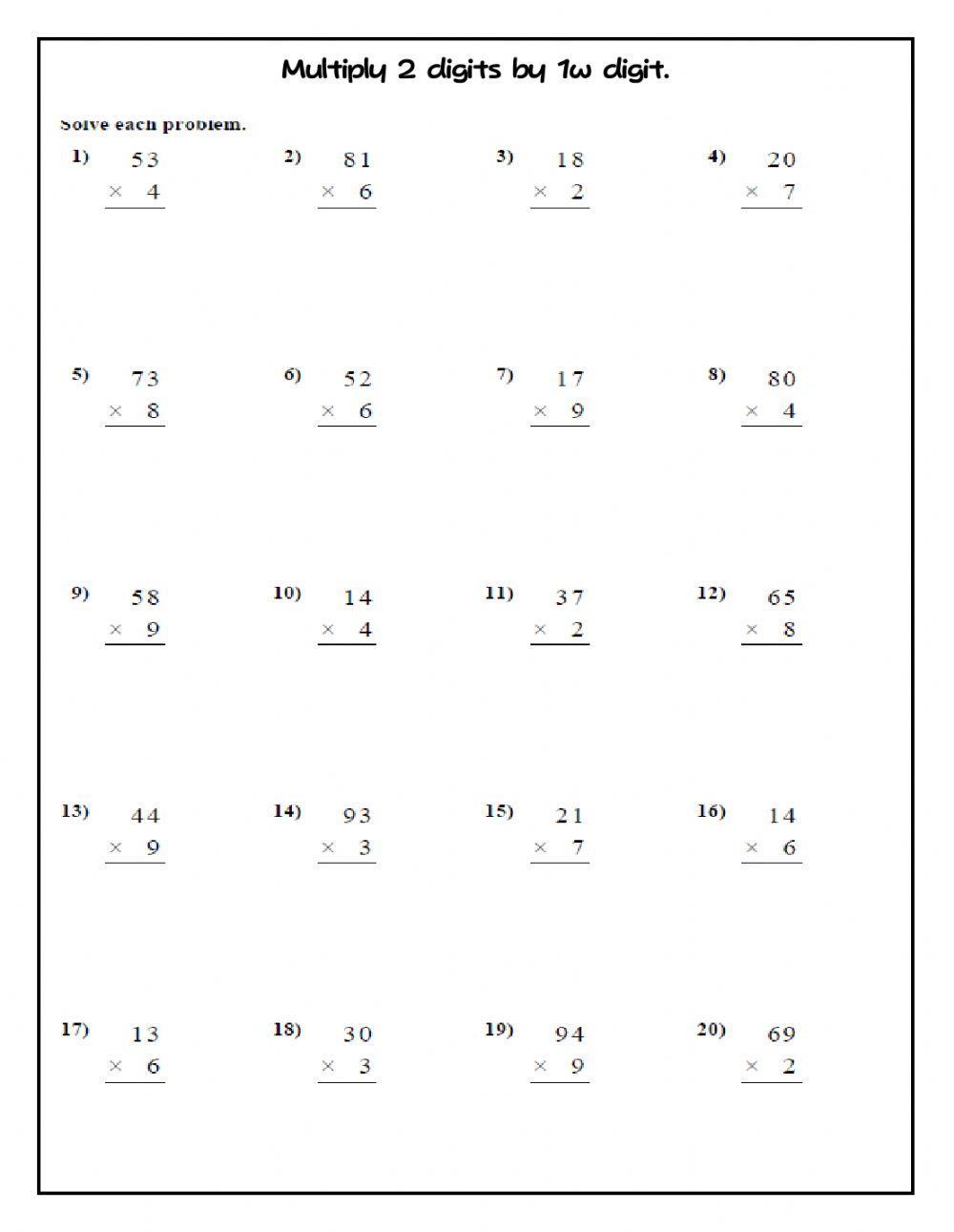
Arrays for Multiplication Mastery
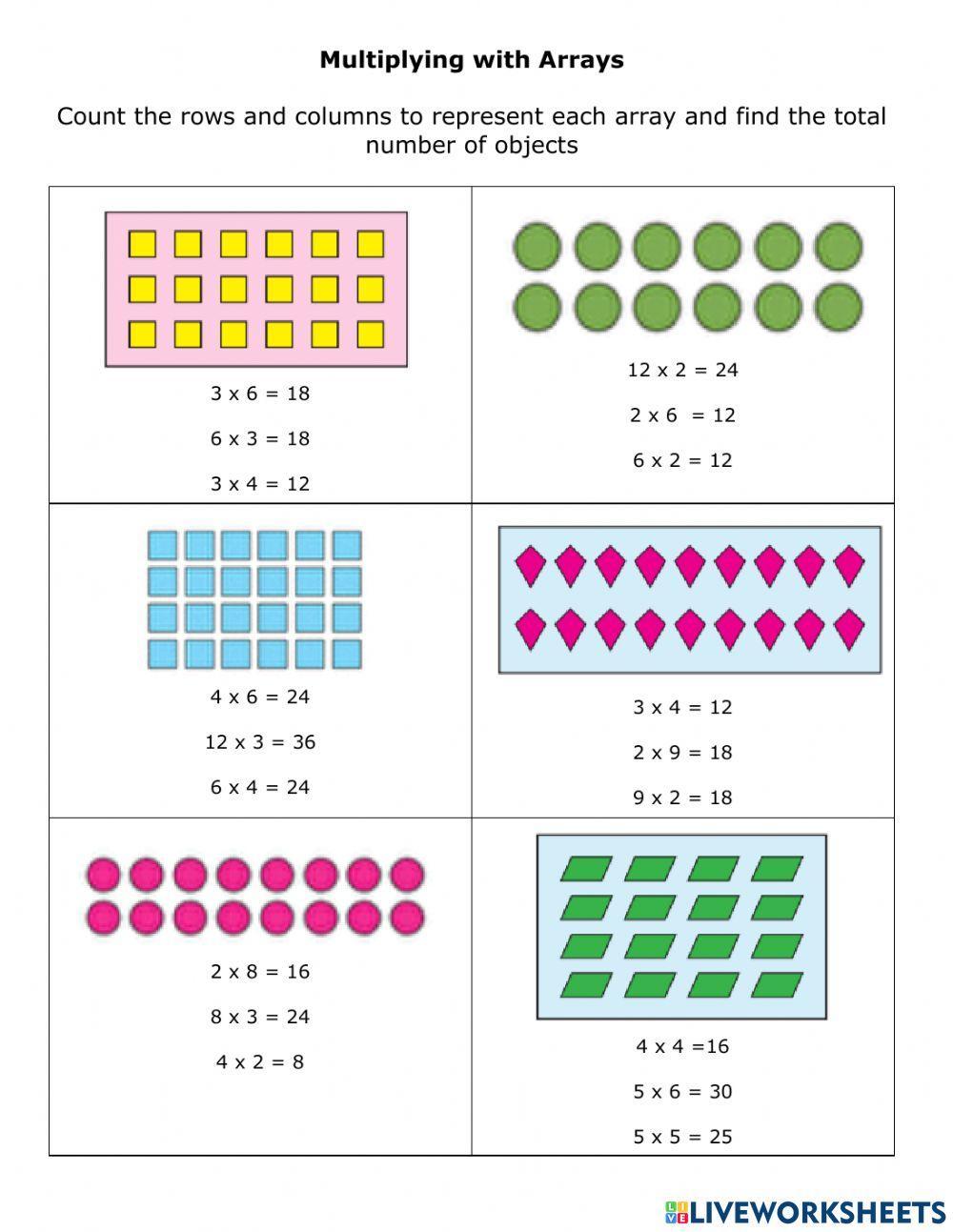
Understanding Arrays for Multiplication Mastery
When it comes to mastering multiplication, there are various techniques and tools that can help students grasp this fundamental concept. One such tool is the array, a simple yet powerful visual representation of multiplication. In this article, we will explore what arrays are, how they work, and how to use them to improve multiplication skills.
What are Arrays?
Arrays are rectangular arrangements of objects or symbols that represent the product of two numbers. They are often used to illustrate the concept of multiplication, making it easier for students to visualize and understand the process.
Imagine you have 3 groups of 4 pencils each. You can represent this situation using an array:
| • | • | • | • |
| • | • | • | • |
| • | • | • | • |
In this example, the array represents the multiplication problem 3 × 4 = 12. The number of rows (3) represents the multiplier, and the number of columns (4) represents the multiplicand. The total number of objects in the array (12) represents the product.
How to Use Arrays for Multiplication
Arrays can be used to solve multiplication problems in a variety of ways. Here are some steps to follow:
- Determine the multiplier and multiplicand: Identify the two numbers being multiplied.
- Draw the array: Create a rectangular array with the multiplier as the number of rows and the multiplicand as the number of columns.
- Fill in the array: Fill in the array with objects or symbols, making sure to leave no gaps.
- Count the total: Count the total number of objects in the array to find the product.
For example, let’s say you want to solve the multiplication problem 5 × 6. You would draw an array with 5 rows and 6 columns, fill it in with objects or symbols, and then count the total number of objects to find the product.
💡 Note: Arrays can also be used to solve division problems by finding the missing factor. For example, if you have an array with 12 objects and you want to find the missing factor of 4, you would divide the total number of objects (12) by 4 to find the quotient (3).
Benefits of Using Arrays for Multiplication
Using arrays to solve multiplication problems has several benefits, including:
- Improved visualization: Arrays help students visualize the multiplication process, making it easier to understand and remember.
- Increased accuracy: Arrays reduce the likelihood of errors, as students can see the actual number of objects being multiplied.
- Enhanced problem-solving skills: Arrays promote critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as students learn to apply the concept of multiplication to real-world situations.
- Develops spatial reasoning: Arrays help students develop their spatial reasoning skills, as they learn to arrange objects in a logical and systematic way.
Common Multiplication Arrays
Here are some common multiplication arrays that students should be familiar with:
- 2 × 3: An array with 2 rows and 3 columns, representing the multiplication problem 2 × 3 = 6.
- 4 × 5: An array with 4 rows and 5 columns, representing the multiplication problem 4 × 5 = 20.
- 6 × 7: An array with 6 rows and 7 columns, representing the multiplication problem 6 × 7 = 42.
Conclusion
Arrays are a powerful tool for mastering multiplication. By understanding how to create and use arrays, students can improve their visualization, accuracy, and problem-solving skills. Whether you’re a teacher or a parent, incorporating arrays into your multiplication lessons can make a significant difference in your students’ understanding and confidence.
What is an array in multiplication?
+An array is a rectangular arrangement of objects or symbols that represents the product of two numbers.
How do I use arrays to solve multiplication problems?
+Draw an array with the multiplier as the number of rows and the multiplicand as the number of columns, fill it in with objects or symbols, and then count the total number of objects to find the product.
What are the benefits of using arrays for multiplication?
+Arrays improve visualization, increase accuracy, enhance problem-solving skills, and develop spatial reasoning.
Related Terms:
- Perkalian
- Bilangan bulat
- Akar kuadrat
- Akar bilangan
- Penambahan
- Pembagian