6 Ways to Multiply Mixed Numbers by Whole Numbers
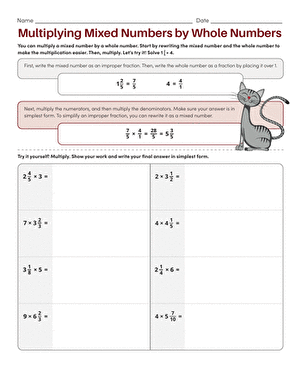
Introduction to Multiplying Mixed Numbers by Whole Numbers
Multiplying mixed numbers by whole numbers is a fundamental operation in mathematics that can seem daunting at first, but with the right approach, it can be simplified. A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a fraction, such as 3 1⁄2 or 2 3⁄4. In this article, we will explore six different methods to multiply mixed numbers by whole numbers, making it easier for you to understand and apply this mathematical operation.
Method 1: Converting Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions
One way to multiply mixed numbers by whole numbers is to convert the mixed number to an improper fraction first. An improper fraction is a fraction where the numerator is greater than the denominator, such as 5⁄4 or 7⁄3.
📝 Note: To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number by the denominator and add the numerator. Then, write the result over the denominator.
For example, let’s convert the mixed number 2 3⁄4 to an improper fraction:
2 × 4 = 8 8 + 3 = 11
So, 2 3⁄4 is equal to 11⁄4.
Method 2: Multiplying Mixed Numbers by Whole Numbers Using the Standard Algorithm
Another method is to use the standard algorithm for multiplying fractions and whole numbers. This involves multiplying the numerator of the fraction by the whole number and keeping the denominator the same.
📝 Note: Make sure to multiply the numerator by the whole number, not the denominator.
For example, let’s multiply 2 3⁄4 by 3:
2 × 3 = 6 3 × 3 = 9 So, 2 3⁄4 × 3 = 6 9⁄4
Method 3: Using Visual Models to Multiply Mixed Numbers by Whole Numbers
Visual models can be an effective way to multiply mixed numbers by whole numbers, especially for students who are visual learners. One way to do this is to use a number line or a hundreds chart to represent the mixed number and the whole number.
📝 Note: Visual models can help you understand the concept of multiplying mixed numbers by whole numbers, but they may not be practical for larger numbers.
For example, let’s use a number line to multiply 1 1⁄2 by 2:
[Visual model: Number line with 1 1⁄2 and 2]
The result is 3.
Method 4: Multiplying Mixed Numbers by Whole Numbers Using the FOIL Method
The FOIL method is a technique used to multiply two binomials, but it can also be applied to multiply mixed numbers by whole numbers. FOIL stands for First, Outer, Inner, Last, which refers to the order in which you multiply the terms.
📝 Note: The FOIL method can be a bit tricky, so make sure to practice it thoroughly.
For example, let’s multiply 2 3⁄4 by 3 using the FOIL method:
(2 × 3) + (3⁄4 × 3) = 6 + 9⁄4
So, 2 3⁄4 × 3 = 6 9⁄4
Method 5: Using Decimal Equivalents to Multiply Mixed Numbers by Whole Numbers
Another method is to convert the mixed number to a decimal and multiply it by the whole number.
📝 Note: To convert a mixed number to a decimal, divide the numerator by the denominator and add the whole number.
For example, let’s convert 2 3⁄4 to a decimal and multiply it by 3:
2 3⁄4 = 2.75 2.75 × 3 = 8.25
So, 2 3⁄4 × 3 = 8.25
Method 6: Multiplying Mixed Numbers by Whole Numbers Using the Distributive Property
The distributive property is a fundamental property of arithmetic that states that a single operation (such as multiplication) can be distributed over multiple operations (such as addition and subtraction).
📝 Note: The distributive property can be used to multiply mixed numbers by whole numbers, but it requires a good understanding of arithmetic operations.
For example, let’s multiply 2 3⁄4 by 3 using the distributive property:
(2 × 3) + (3⁄4 × 3) = 6 + 9⁄4
So, 2 3⁄4 × 3 = 6 9⁄4
In conclusion, multiplying mixed numbers by whole numbers can be simplified using different methods. Whether you prefer to convert mixed numbers to improper fractions, use the standard algorithm, or apply visual models, there’s a method that suits your learning style. By practicing these methods, you’ll become proficient in multiplying mixed numbers by whole numbers in no time.
What is a mixed number?
+
A mixed number is a combination of a whole number and a fraction, such as 3 1⁄2 or 2 3⁄4.
How do I convert a mixed number to an improper fraction?
+
To convert a mixed number to an improper fraction, multiply the whole number by the denominator and add the numerator. Then, write the result over the denominator.
What is the distributive property?
+
The distributive property is a fundamental property of arithmetic that states that a single operation (such as multiplication) can be distributed over multiple operations (such as addition and subtraction).
Related Terms:
- Multiplying mixed numbers Worksheet PDF
- Dividing Mixed Numbers Worksheet
- Multiplying Mixed Numbers math drills