Monohybrid Cross Worksheet: Understanding Inheritance Patterns Easily
Introduction to Monohybrid Cross
In genetics, a monohybrid cross is a type of cross that involves the crossing of two parents that differ in only one trait. This type of cross is used to study the inheritance pattern of a single gene. By analyzing the results of a monohybrid cross, we can determine whether a trait is dominant or recessive, and how it is inherited from one generation to the next.
Understanding Monohybrid Cross Notation
To understand monohybrid cross, we need to understand the notation used to represent the genotype and phenotype of the parents and offspring. The following notation is commonly used:
- Uppercase letters represent dominant alleles (e.g., “R” represents the dominant allele for red flower color).
- Lowercase letters represent recessive alleles (e.g., “r” represents the recessive allele for white flower color).
- Homozygous genotypes are represented by two of the same letter (e.g., “RR” or “rr”).
- Heterozygous genotypes are represented by two different letters (e.g., “Rr”).
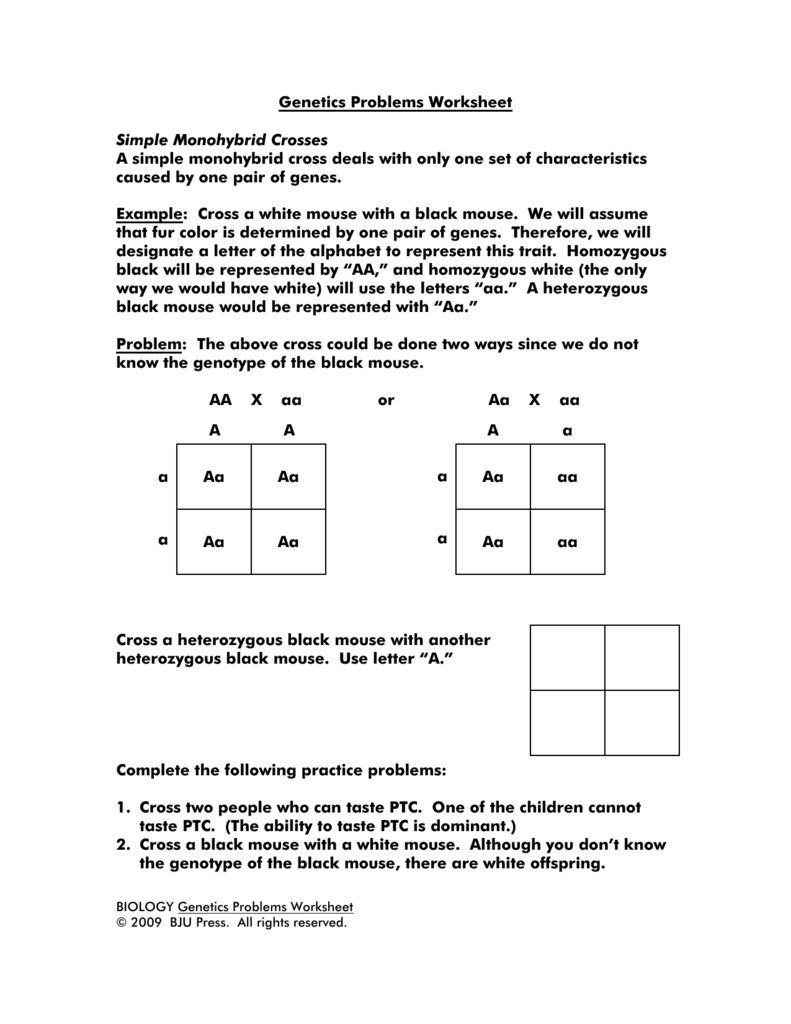
How to Solve a Monohybrid Cross Problem
To solve a monohybrid cross problem, we need to follow these steps:
- Determine the genotype of the parents: Identify the genotype of the two parents using the notation described above.
- Determine the possible gametes: Identify the possible gametes (sperm or egg cells) that each parent can produce.
- Predict the genotype of the offspring: Use a Punnett square to predict the genotype of the offspring.
- Determine the phenotype of the offspring: Use the genotype of the offspring to determine their phenotype.
📝 Note: A Punnett square is a diagram that shows all possible combinations of gametes from two parents.
Example of a Monohybrid Cross Problem
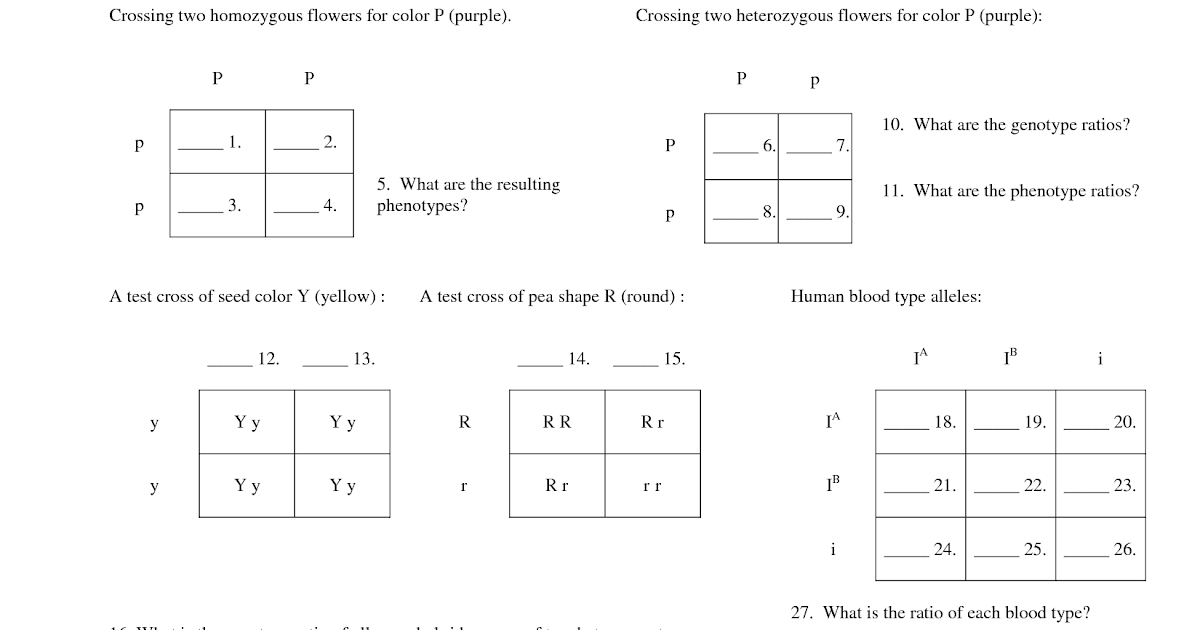
Let’s say we want to study the inheritance of flower color in pea plants. We have two parents: one with red flowers ® and one with white flowers ®.
Parent 1: RR (homozygous dominant) Parent 2: rr (homozygous recessive)
We want to determine the genotype and phenotype of the offspring.
Step 1: Determine the possible gametes
Parent 1 (RR) can produce only one type of gamete: R Parent 2 (rr) can produce only one type of gamete: r
Step 2: Predict the genotype of the offspring
Using a Punnett square, we can predict the genotype of the offspring:
| R | r | |
|---|---|---|
| R | RR | Rr |
| r | Rr | rr |
Step 3: Determine the phenotype of the offspring
Based on the genotype of the offspring, we can determine their phenotype:
- RR: Red flowers
- Rr: Red flowers (because R is dominant)
- rr: White flowers
Interpreting the Results
From the Punnett square, we can see that:
- 50% of the offspring will have the genotype RR or Rr (red flowers)
- 50% of the offspring will have the genotype rr (white flowers)
This means that the offspring will have a 50:50 ratio of red to white flowers.
Key Points to Remember
- Monohybrid cross involves the crossing of two parents that differ in only one trait.
- Use the notation R and r to represent dominant and recessive alleles, respectively.
- Use a Punnett square to predict the genotype of the offspring.
- Determine the phenotype of the offspring based on their genotype.
By following these steps and using the notation described above, we can easily solve monohybrid cross problems and understand the inheritance patterns of single genes.
What is a monohybrid cross?
+A monohybrid cross is a type of cross that involves the crossing of two parents that differ in only one trait.
How do you solve a monohybrid cross problem?
+To solve a monohybrid cross problem, you need to determine the genotype of the parents, determine the possible gametes, predict the genotype of the offspring using a Punnett square, and determine the phenotype of the offspring.
What is a Punnett square?
+A Punnett square is a diagram that shows all possible combinations of gametes from two parents.