5 Ways to Master Monetary Policy

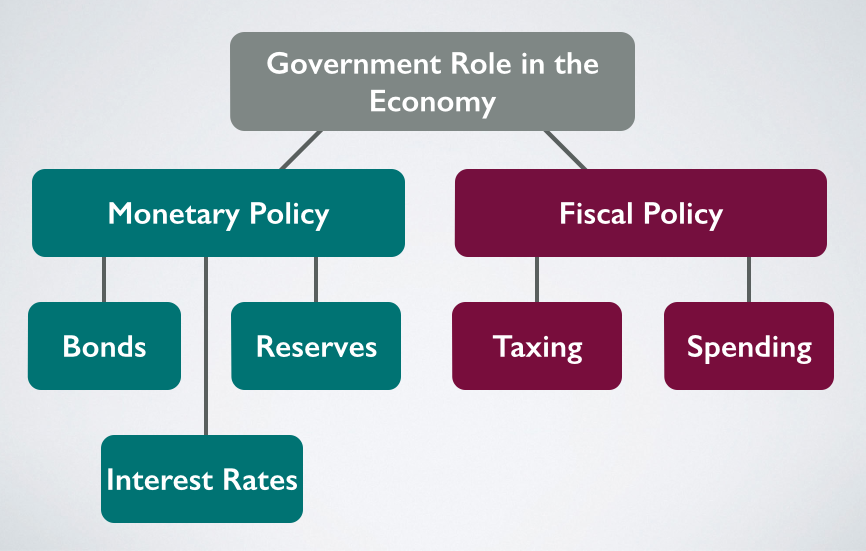
Understanding the Basics of Monetary Policy
Monetary policy is a crucial tool used by central banks to manage a country’s economy. It involves the use of interest rates, money supply, and other measures to control inflation, promote economic growth, and maintain financial stability. Mastering monetary policy requires a deep understanding of its instruments, objectives, and transmission mechanisms. In this article, we will discuss five ways to master monetary policy, including understanding the basics, analyzing economic indicators, using monetary policy tools, managing expectations, and coordinating with fiscal policy.
1. Understanding the Basics of Monetary Policy
To master monetary policy, it is essential to understand its basics. This includes knowing the objectives of monetary policy, which typically include price stability, maximum employment, and moderate long-term interest rates. It is also crucial to understand the transmission mechanisms of monetary policy, which include the interest rate channel, credit channel, and exchange rate channel. Additionally, one should be familiar with the various monetary policy tools, such as open market operations, reserve requirements, and forward guidance.
📝 Note: Understanding the basics of monetary policy is essential for making informed decisions about monetary policy.
2. Analyzing Economic Indicators
Analyzing economic indicators is critical for mastering monetary policy. This involves monitoring a range of indicators, including inflation rates, unemployment rates, GDP growth rates, and interest rates. By analyzing these indicators, policymakers can assess the state of the economy and make informed decisions about monetary policy. For example, if inflation is rising, policymakers may need to increase interest rates to control inflation. On the other hand, if unemployment is high, policymakers may need to lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth.
- Key economic indicators to monitor:
- Inflation rate
- Unemployment rate
- GDP growth rate
- Interest rates
- Exchange rates
3. Using Monetary Policy Tools
Monetary policy tools are the instruments used by central banks to implement monetary policy. The most common monetary policy tools include:
- Open market operations: buying or selling government securities to increase or decrease the money supply
- Reserve requirements: setting the minimum amount of reserves that commercial banks must hold against deposits
- Forward guidance: communicating future policy intentions to influence market expectations
- Interest rates: setting the interest rate at which banks borrow from the central bank
| Monetary Policy Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Open Market Operations | Buying or selling government securities to increase or decrease the money supply |
| Reserve Requirements | Setting the minimum amount of reserves that commercial banks must hold against deposits |
| Forward Guidance | Communicating future policy intentions to influence market expectations |
| Interest Rates | Setting the interest rate at which banks borrow from the central bank |
4. Managing Expectations
Managing expectations is critical for mastering monetary policy. This involves communicating clearly and transparently with financial markets and the public about monetary policy intentions and decisions. By managing expectations, policymakers can influence market expectations and shape the behavior of economic agents. For example, if policymakers communicate a clear intention to keep interest rates low, market participants may adjust their expectations and behavior accordingly.
💬 Note: Clear communication is essential for managing expectations and influencing market behavior.
5. Coordinating with Fiscal Policy
Coordinating with fiscal policy is essential for mastering monetary policy. Fiscal policy and monetary policy are both macroeconomic policies used to manage the economy. Fiscal policy involves the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy, while monetary policy involves the use of interest rates and money supply to influence the economy. By coordinating with fiscal policy, policymakers can achieve a more effective and sustainable economic outcome.
- Benefits of coordinating with fiscal policy:
- Achieving a more effective and sustainable economic outcome
- Avoiding conflicting policy objectives
- Enhancing policy credibility and transparency
In conclusion, mastering monetary policy requires a deep understanding of its instruments, objectives, and transmission mechanisms. By analyzing economic indicators, using monetary policy tools, managing expectations, and coordinating with fiscal policy, policymakers can achieve a more effective and sustainable economic outcome.
What is the primary objective of monetary policy?
+The primary objective of monetary policy is to achieve price stability, maximum employment, and moderate long-term interest rates.
What is the difference between monetary policy and fiscal policy?
+Monetary policy involves the use of interest rates and money supply to influence the economy, while fiscal policy involves the use of government spending and taxation to influence the economy.
Why is clear communication essential for monetary policy?
+Clear communication is essential for managing expectations and influencing market behavior.
Related Terms:
- Monetary and fiscal policy scenarios
- Fiscal policy worksheet Answer Key
- Monetary policy simple definition
- Role of monetary policy