Molecular Polarity Worksheet Answer Key

Molecular Polarity Worksheet Answer Key
Molecular polarity is a crucial concept in chemistry, particularly in understanding the physical and chemical properties of molecules. It is essential to determine whether a molecule is polar or nonpolar, as this affects its behavior in various environments. In this answer key, we will guide you through the solutions to a molecular polarity worksheet, covering the key concepts and principles involved.
Understanding Molecular Polarity
Before diving into the answer key, let’s briefly review the concept of molecular polarity. Molecular polarity arises from the difference in electronegativity between atoms in a molecule, leading to a partial positive charge on one side and a partial negative charge on the other. This difference in electronegativity results in a dipole moment, making the molecule polar.
Factors Affecting Molecular Polarity
Several factors influence the polarity of a molecule, including:
- Electronegativity: The ability of an atom to attract electrons towards itself.
- Molecular shape: The arrangement of atoms in space affects the distribution of electron density.
- Bond polarity: The polarity of individual bonds contributes to the overall molecular polarity.
Answer Key
Now, let’s proceed to the answer key for the molecular polarity worksheet.
1. Determine the polarity of the following molecules:
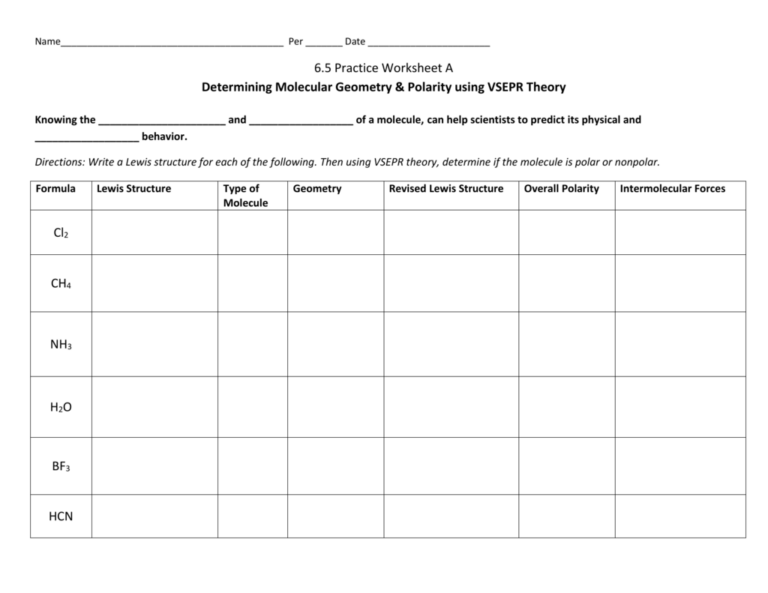
| Molecule | Polarity |
|---|---|
| CO2 | Nonpolar |
| H2O | Polar |
| CH4 | Nonpolar |
| NH3 | Polar |
Explanation:
- CO2: The molecule has a linear shape, and the electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen is not significant enough to create a dipole moment.
- H2O: The molecule has a bent shape, and the electronegativity difference between oxygen and hydrogen creates a dipole moment, making the molecule polar.
- CH4: The molecule has a tetrahedral shape, and the electronegativity difference between carbon and hydrogen is not significant enough to create a dipole moment.
- NH3: The molecule has a trigonal pyramidal shape, and the electronegativity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen creates a dipole moment, making the molecule polar.
2. Identify the polar molecules from the following list:
| Molecule | Polarity |
|---|---|
| HCl | Polar |
| CH3Cl | Polar |
| CO | Polar |
| N2 | Nonpolar |
Explanation:
- HCl: The molecule has a significant electronegativity difference between hydrogen and chlorine, creating a dipole moment.
- CH3Cl: The molecule has a tetrahedral shape, and the electronegativity difference between carbon and chlorine creates a dipole moment.
- CO: The molecule has a linear shape, but the electronegativity difference between carbon and oxygen creates a dipole moment.
- N2: The molecule has a linear shape, and the electronegativity difference between nitrogen atoms is not significant enough to create a dipole moment.
3. Determine the molecular polarity of the following molecules using their Lewis structures:
| Molecule | Lewis Structure | Polarity |
|---|---|---|
| BF3 | F:B:F | Nonpolar |
| CF4 | F:C:F:F | Nonpolar |
| SO2 | O:S:O | Polar |
Explanation:
- BF3: The molecule has a trigonal planar shape, and the electronegativity difference between boron and fluorine is not significant enough to create a dipole moment.
- CF4: The molecule has a tetrahedral shape, and the electronegativity difference between carbon and fluorine is not significant enough to create a dipole moment.
- SO2: The molecule has a bent shape, and the electronegativity difference between sulfur and oxygen creates a dipole moment, making the molecule polar.
Conclusion
In conclusion, determining the molecular polarity of a molecule involves analyzing the electronegativity difference between atoms, molecular shape, and bond polarity. By understanding these factors, you can predict the polarity of a molecule, which is essential in understanding its physical and chemical properties.
What is molecular polarity?
+Molecular polarity is the distribution of electric charge within a molecule, resulting from the difference in electronegativity between atoms.
What factors affect molecular polarity?
+Electronegativity, molecular shape, and bond polarity are the key factors that influence molecular polarity.
How do I determine the molecular polarity of a molecule?
+Determine the molecular polarity by analyzing the electronegativity difference between atoms, molecular shape, and bond polarity using Lewis structures.
Related Terms:
- Molecular Polarity Worksheet PDF
- Bond polarity Worksheet
- Polarity Practice Worksheet
- VSEPR worksheet with answers pdf