7 Essential Steps for Series Circuit Calculations
Understanding Series Circuits
Series circuits are a fundamental concept in electronics, where components are connected one after the other, and there is only one path for current to flow. Calculating the total resistance, voltage, and current in a series circuit is crucial for designing and analyzing electronic circuits. In this article, we will break down the 7 essential steps for series circuit calculations, making it easier for you to understand and apply these concepts.
Step 1: Identify the Components and Their Values
Before starting any calculation, it is essential to identify the components in the series circuit, including their values. This includes resistors, capacitors, inductors, and any other components that may be present. Make sure to note the units of measurement for each component, such as ohms (Ω) for resistors, farads (F) for capacitors, and henries (H) for inductors.
💡 Note: Ensure that you have a clear diagram or schematic of the circuit to visualize the components and their connections.
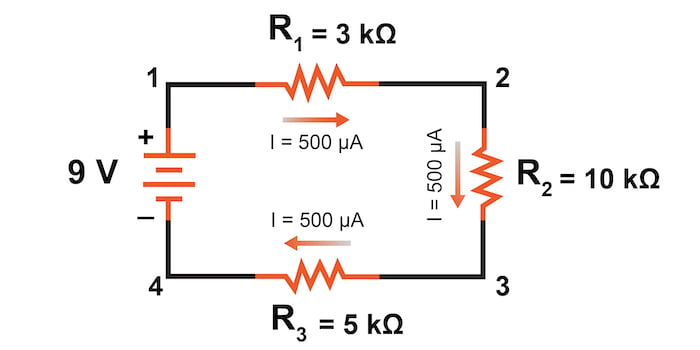
Step 2: Determine the Total Resistance (RT)
To calculate the total resistance in a series circuit, you can use the following formula:
RT = R1 + R2 +… + Rn
Where R1, R2,…, Rn are the individual resistances in the circuit.
| Component | Resistance (Ω) |
|---|---|
| R1 | 10 Ω |
| R2 | 20 Ω |
| R3 | 30 Ω |
Using the formula, we can calculate the total resistance:
RT = 10 Ω + 20 Ω + 30 Ω = 60 Ω
Step 3: Calculate the Total Voltage (VT)
The total voltage in a series circuit is the sum of the individual voltages across each component. You can use the following formula:
VT = V1 + V2 +… + Vn
Where V1, V2,…, Vn are the individual voltages across each component.
Step 4: Calculate the Total Current (IT)
The total current in a series circuit is the same as the current through each individual component. You can use Ohm’s Law to calculate the total current:
IT = VT / RT
Using the values from previous steps, we can calculate the total current:
IT = 60 V / 60 Ω = 1 A
Step 5: Calculate the Power (P) Dissipated in Each Component
The power dissipated in each component can be calculated using the following formula:
P = V x I
Where V is the voltage across the component, and I is the current through the component.
| Component | Voltage (V) | Current (A) | Power (W) |
|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | 10 V | 1 A | 10 W |
| R2 | 20 V | 1 A | 20 W |
| R3 | 30 V | 1 A | 30 W |
Step 6: Verify the Calculations
Once you have completed the calculations, it is essential to verify the results to ensure accuracy. You can use the following checks:
- The total resistance should be equal to the sum of the individual resistances.
- The total voltage should be equal to the sum of the individual voltages.
- The total current should be the same as the current through each individual component.
- The power dissipated in each component should be calculated correctly.
Step 7: Analyze the Results
Finally, analyze the results to understand the behavior of the series circuit. You can use the calculations to:
- Determine the total resistance and its effect on the circuit.
- Identify the component with the highest voltage drop.
- Determine the power dissipated in each component and its effect on the circuit.
In conclusion, by following these 7 essential steps, you can accurately calculate the total resistance, voltage, and current in a series circuit. Remember to verify the calculations and analyze the results to ensure a deep understanding of the circuit’s behavior.
What is the difference between series and parallel circuits?
+In a series circuit, components are connected one after the other, and there is only one path for current to flow. In a parallel circuit, components are connected between the same two points, and there are multiple paths for current to flow.
How do I calculate the total resistance in a series circuit?
+The total resistance in a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistances. You can use the formula: RT = R1 + R2 +… + Rn
What is the total current in a series circuit?
+The total current in a series circuit is the same as the current through each individual component. You can use Ohm’s Law to calculate the total current: IT = VT / RT