Molar Conversion Made Easy Worksheet
Molar Conversion Made Easy: A Step-by-Step Guide
Molar conversion is a crucial concept in chemistry that involves converting between different units of measurement. It can be a daunting task, especially for students who are new to chemistry. However, with practice and the right tools, molar conversion can become second nature. In this guide, we will walk you through a step-by-step approach to molar conversion, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of the concept.
What is Molar Conversion?
Molar conversion is the process of converting between different units of measurement, such as grams to moles, moles to liters, or liters to grams. It is an essential skill in chemistry, as it allows you to work with different units and convert between them easily.
Why is Molar Conversion Important?
Molar conversion is important because it allows you to:
- Compare quantities: By converting between different units, you can compare quantities of different substances.
- Calculate amounts: Molar conversion enables you to calculate the amount of a substance needed for a reaction or experiment.
- Understand chemical reactions: Molar conversion helps you understand the stoichiometry of chemical reactions, which is crucial for predicting the products and yields of reactions.
Step-by-Step Approach to Molar Conversion
To perform molar conversion, follow these steps:
- Identify the given information: Start by identifying the given information, such as the mass of a substance, its molar mass, or the volume of a solution.
- Determine the conversion factor: Determine the conversion factor needed to convert between the given units. This can be a molar mass, a density, or a conversion factor between different units.
- Set up the conversion equation: Set up a conversion equation using the given information and the conversion factor.
- Solve for the unknown: Solve for the unknown quantity, using the conversion equation.
Examples of Molar Conversion
Here are some examples of molar conversion:
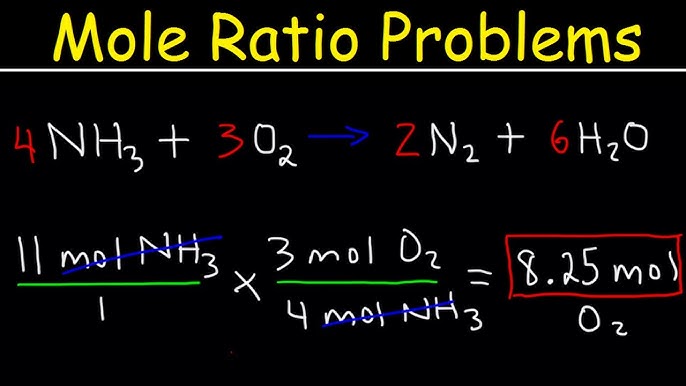
- Grams to moles: Convert 25 grams of sodium chloride (NaCl) to moles.
Given: 25 g NaCl
Molar mass of NaCl = 58.44 g/mol
Conversion equation: 25 g NaCl x (1 mol / 58.44 g) = 0.428 mol NaCl - Moles to liters: Convert 0.5 moles of a 2M solution of hydrochloric acid (HCl) to liters.
Given: 0.5 mol HCl, 2M solution
Conversion equation: 0.5 mol HCl x (1 L / 2 mol) = 0.25 L HCl
Common Conversion Factors
Here are some common conversion factors:

| Conversion Factor | Value |
|---|---|
| 1 mole | 6.022 x 10^23 particles |
| 1 liter | 1000 milliliters (mL) |
| 1 milliliter (mL) | 1 gram (g) |
| 1 kilogram (kg) | 1000 grams (g) |
| 1 molar (M) | 1 mole/liter |
📝 Note: It's essential to remember that these conversion factors are approximate and may vary slightly depending on the specific substance or solution.
Molar Conversion Worksheet
Practice your molar conversion skills with this worksheet:
Section 1: Grams to Moles
- Convert 50 grams of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) to moles. (Molar mass of CaCO3 = 100.09 g/mol)
- Convert 25 grams of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to moles. (Molar mass of NaOH = 40.00 g/mol)
Section 2: Moles to Liters
- Convert 0.25 moles of a 3M solution of sulfuric acid (H2SO4) to liters.
- Convert 1.5 moles of a 2M solution of potassium nitrate (KNO3) to liters.
Section 3: Mix-and-Match
- Convert 35 grams of magnesium oxide (MgO) to liters of a 2M solution.
- Convert 0.75 moles of a 1.5M solution of ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) to grams.
Answer Key
Section 1: Grams to Moles
- 0.5 mol CaCO3
- 0.625 mol NaOH
Section 2: Moles to Liters
- 0.083 L H2SO4
- 0.75 L KNO3
Section 3: Mix-and-Match
- 0.175 L MgO solution
- 23.63 g NH4Cl
In conclusion, molar conversion is a fundamental concept in chemistry that requires practice and patience to master. By following the step-by-step approach outlined in this guide, you’ll be able to convert between different units with ease. Remember to practice regularly and use the common conversion factors provided to become proficient in molar conversion.
What is the difference between molar mass and molecular weight?
+
Molar mass and molecular weight are often used interchangeably, but they have slightly different meanings. Molar mass refers to the mass of one mole of a substance, while molecular weight refers to the mass of a single molecule.
How do I convert between different units of measurement?
+
To convert between different units, use the conversion factors provided in this guide or look up the specific conversion factor needed for your calculation.
What is the significance of Avogadro’s number?
+
Avogadro’s number (6.022 x 10^23 particles) is a fundamental constant in chemistry that represents the number of particles in one mole of a substance.
Related Terms:
- Mole conversion Worksheet and answers
- Mole Conversion Worksheet Mixed Practice
- Multi step mole Conversions Worksheet
- Molar conversions