Missing Angles Worksheet: Find the Hidden Degrees Easily
Missing Angles Worksheet: Find the Hidden Degrees Easily
Are you struggling to find the missing angles in a worksheet? Do you want to become proficient in solving angle problems with ease? Look no further! This comprehensive guide will walk you through the steps to find missing angles in a worksheet, making it easier for you to tackle complex geometry problems.
Understanding Angles and Their Types
Before diving into the worksheet, let’s quickly review the basics of angles. An angle is formed by two rays sharing a common endpoint, known as the vertex. Angles can be classified into different types, including:
- Acute angles: Less than 90 degrees
- Right angles: Exactly 90 degrees
- Obtuse angles: Greater than 90 degrees but less than 180 degrees
- Straight angles: Exactly 180 degrees
Key Concepts for Finding Missing Angles
To find missing angles, you need to understand the following key concepts:
- Angle sum property: The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Supplementary angles: Two angles whose sum is 180 degrees.
- Complementary angles: Two angles whose sum is 90 degrees.
Step-by-Step Guide to Finding Missing Angles
Now that you’ve brushed up on the basics, let’s move on to the step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Identify the Type of Angle
Look at the given angle and determine its type (acute, right, obtuse, or straight). This will help you decide the next steps.
Step 2: Use the Angle Sum Property
If you’re dealing with a triangle, use the angle sum property to find the missing angle. For example, if you know two angles of a triangle, you can find the third angle by subtracting the sum of the known angles from 180 degrees.
Step 3: Find Supplementary or Complementary Angles
If you’re given one angle and need to find its supplementary or complementary angle, simply subtract the given angle from 180 degrees (for supplementary angles) or 90 degrees (for complementary angles).
Step 4: Use Visual Aids
Draw a diagram to visualize the angles. This will help you identify relationships between angles and make it easier to find the missing angle.
Practice Time!
Let’s practice finding missing angles with some examples:
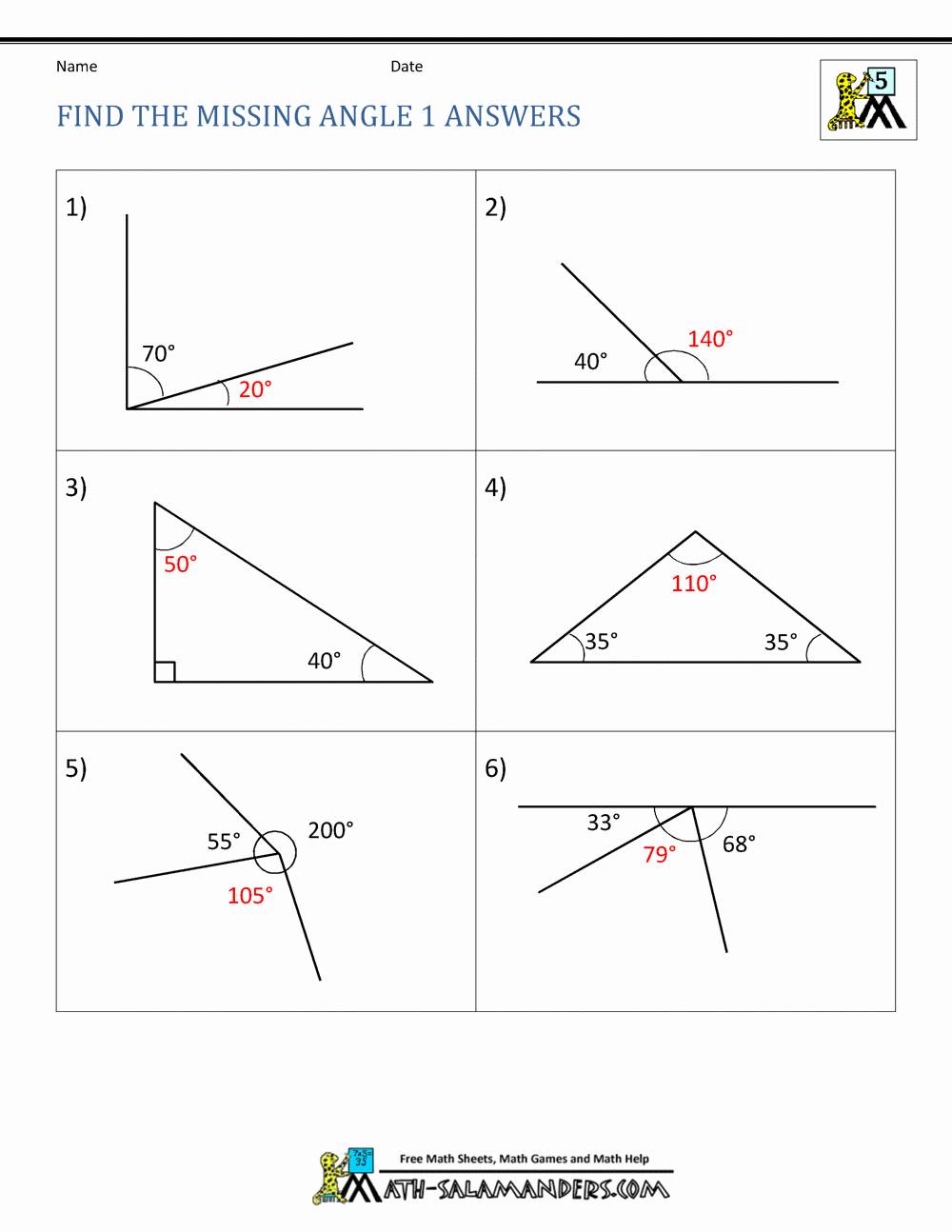
- Find the missing angle in the following triangle:
- Angle A = 30°
- Angle B = 60°
- Angle C =?
- Find the supplementary angle of 45°.
- Find the complementary angle of 75°.
Solutions
- Angle C = 180° - (30° + 60°) = 90°
- Supplementary angle of 45° = 180° - 45° = 135°
- Complementary angle of 75° = 90° - 75° = 15°
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When finding missing angles, watch out for these common mistakes:
- Forgetting to use the angle sum property for triangles
- Confusing supplementary and complementary angles
- Not drawing a diagram to visualize the angles
📝 Note: Always double-check your calculations and ensure you're using the correct formula for finding missing angles.
Conclusion
Finding missing angles in a worksheet can be a breeze if you understand the basics of angles and use the right strategies. Remember to use the angle sum property, find supplementary or complementary angles, and visualize the angles with a diagram. Practice makes perfect, so be sure to try out the examples and exercises to become more confident in your ability to find missing angles.
What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle?
+The sum of the interior angles of a triangle is always 180 degrees.
What is the difference between supplementary and complementary angles?
+Supplementary angles add up to 180 degrees, while complementary angles add up to 90 degrees.
How can I visualize angles to find missing angles?
+Draw a diagram to visualize the angles. This will help you identify relationships between angles and make it easier to find the missing angle.