Mendelian Genetics Worksheet Answer Key
Understanding Mendelian Genetics
Mendelian genetics is the study of heredity using the scientific method. It is based on the principles of segregation and independent assortment, which describe how genes are inherited from one generation to the next. Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk, is considered the father of genetics due to his pioneering work in this field.
Key Concepts in Mendelian Genetics
- Genotype: The genetic makeup of an organism, consisting of the specific set of genes it possesses.
- Phenotype: The physical characteristics of an organism, resulting from the interaction of its genotype and the environment.
- Dominant and Recessive: Terms used to describe the relationship between different alleles (forms) of a gene. A dominant allele will be expressed if an individual has one or two copies of the allele, while a recessive allele will only be expressed if an individual has two copies.
- Punnett Square: A graphical representation of the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a cross between two parents.
Monohybrid Crosses
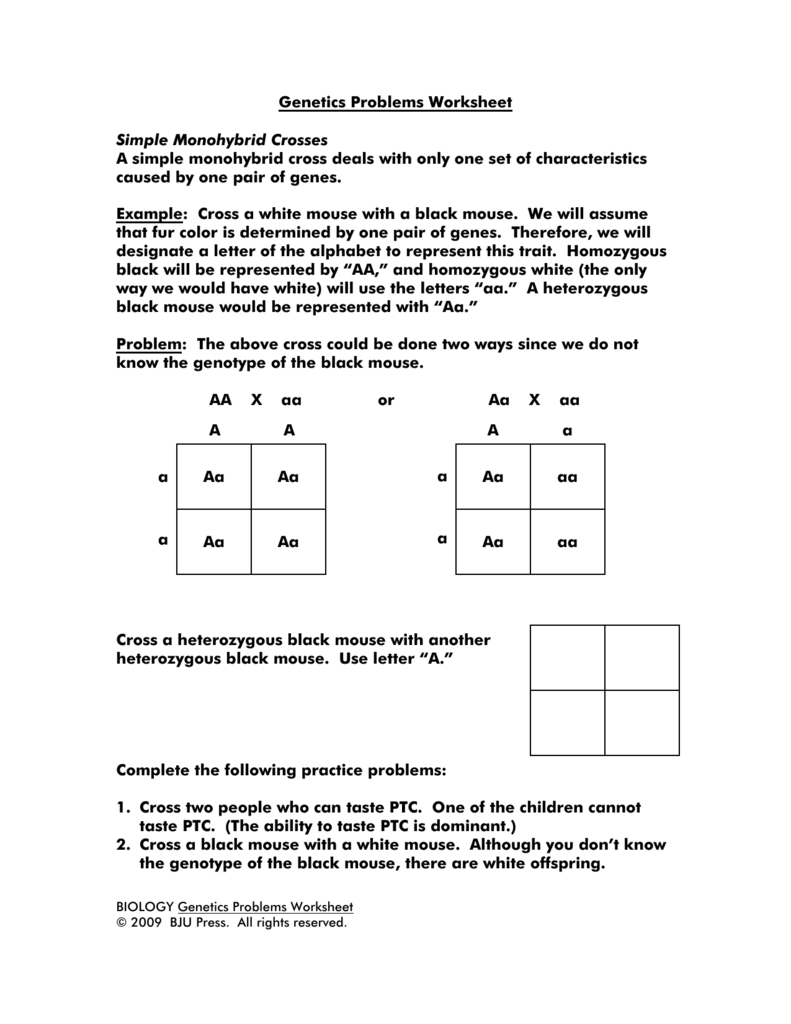
A monohybrid cross involves the crossing of two parents that differ in a single gene. The resulting offspring will have a combination of the alleles from each parent.
- Punnett Square for a Monohybrid Cross

| B | b | |
|---|---|---|
| B | BB | Bb |
| b | bB | bb |
In this example, the parents are Bb and bb. The offspring can have one of three genotypes: BB, Bb, or bb.
Dihybrid Crosses
A dihybrid cross involves the crossing of two parents that differ in two genes.
- Punnett Square for a Dihybrid Cross
| Rr | rr | |
|---|---|---|
| Rr | RR | Rr |
| rr | rr | rr |
In this example, the parents are Rr and rr. The offspring can have one of four genotypes: RR, Rr, rr, or rr.
Practice Problems
What is the genotype of an individual that is homozygous dominant for the B gene? Answer: BB
What is the phenotype of an individual that is heterozygous for the R gene? Answer: Rr (will express the dominant R phenotype)
What is the probability of an offspring inheriting the bb genotype from parents that are Bb and bb? Answer: 50% (1⁄2)
What is the genotype of an individual that is homozygous recessive for the r gene? Answer: rr
What is the phenotype of an individual that is heterozygous for the B gene? Answer: Bb (will express the dominant B phenotype)
💡 Note: The probability of an offspring inheriting a particular genotype can be calculated using a Punnett square.
Solving Genetics Problems
To solve genetics problems, follow these steps:
- Identify the parents’ genotypes: Determine the genotypes of the parents, including the alleles they possess.
- Determine the possible genotypes of the offspring: Use a Punnett square to determine the possible genotypes of the offspring.
- Calculate the probability of each genotype: Calculate the probability of each genotype by counting the number of times it appears in the Punnett square and dividing by the total number of possible genotypes.
- Determine the phenotype of each genotype: Determine the phenotype of each genotype based on the dominant and recessive relationships between the alleles.
Conclusion
Understanding Mendelian genetics is essential for understanding the principles of heredity. By applying the concepts of genotype, phenotype, dominant and recessive, and Punnett squares, you can solve genetics problems and predict the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
+The genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, while the phenotype refers to the physical characteristics of an organism.
What is a Punnett square?
+A Punnett square is a graphical representation of the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring from a cross between two parents.
How do you calculate the probability of an offspring inheriting a particular genotype?
+The probability of an offspring inheriting a particular genotype can be calculated by counting the number of times it appears in the Punnett square and dividing by the total number of possible genotypes.