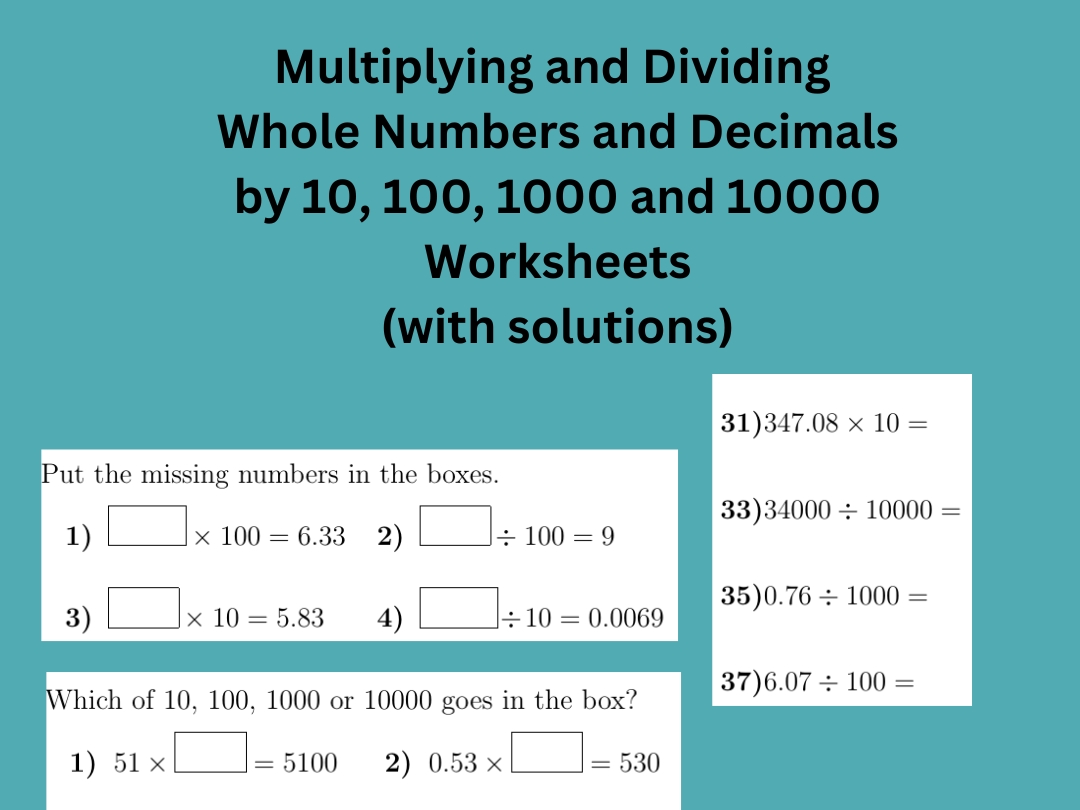
Linear Equations with One Variable Worksheet Solutions

Linear Equations with One Variable: A Comprehensive Guide
Linear equations with one variable are a fundamental concept in algebra, and understanding how to solve them is crucial for success in mathematics and science. In this article, we will provide a detailed explanation of linear equations with one variable, including the definition, types, and step-by-step solutions.
What is a Linear Equation with One Variable?
A linear equation with one variable is an equation in which the highest power of the variable is 1. It is a simple equation that can be written in the form:
ax = b
where ‘a’ and ‘b’ are constants, and ‘x’ is the variable.
Types of Linear Equations with One Variable
There are several types of linear equations with one variable, including:
- Simple Linear Equations: These are equations in which the variable is not multiplied by a constant, e.g., x = 5.
- Linear Equations with Constants: These are equations in which the variable is multiplied by a constant, e.g., 2x = 10.
- Linear Equations with Fractions: These are equations in which the variable is multiplied by a fraction, e.g., (1⁄2)x = 3.
- Linear Equations with Decimals: These are equations in which the variable is multiplied by a decimal, e.g., 0.5x = 2.
Step-by-Step Solutions to Linear Equations with One Variable
Solving linear equations with one variable involves isolating the variable on one side of the equation. Here are the step-by-step solutions:
Step 1: Add or Subtract the Same Value to Both Sides
If the equation has a constant term on the same side as the variable, add or subtract the same value to both sides to isolate the variable.
Example: x + 3 = 7
Subtract 3 from both sides:
x = 7 - 3 x = 4
Step 2: Multiply or Divide Both Sides by the Same Value
If the equation has a coefficient (a constant multiplied by the variable), multiply or divide both sides by the same value to isolate the variable.
Example: 2x = 12
Divide both sides by 2:
x = 12 ÷ 2 x = 6
Step 3: Simplify the Equation
Once the variable is isolated, simplify the equation by combining like terms.
Example: x/2 + 2 = 5
Subtract 2 from both sides:
x/2 = 5 - 2 x/2 = 3
Multiply both sides by 2:
x = 3 × 2 x = 6
Linear Equations with One Variable Worksheet Solutions
Here are some examples of linear equations with one variable, along with their solutions:
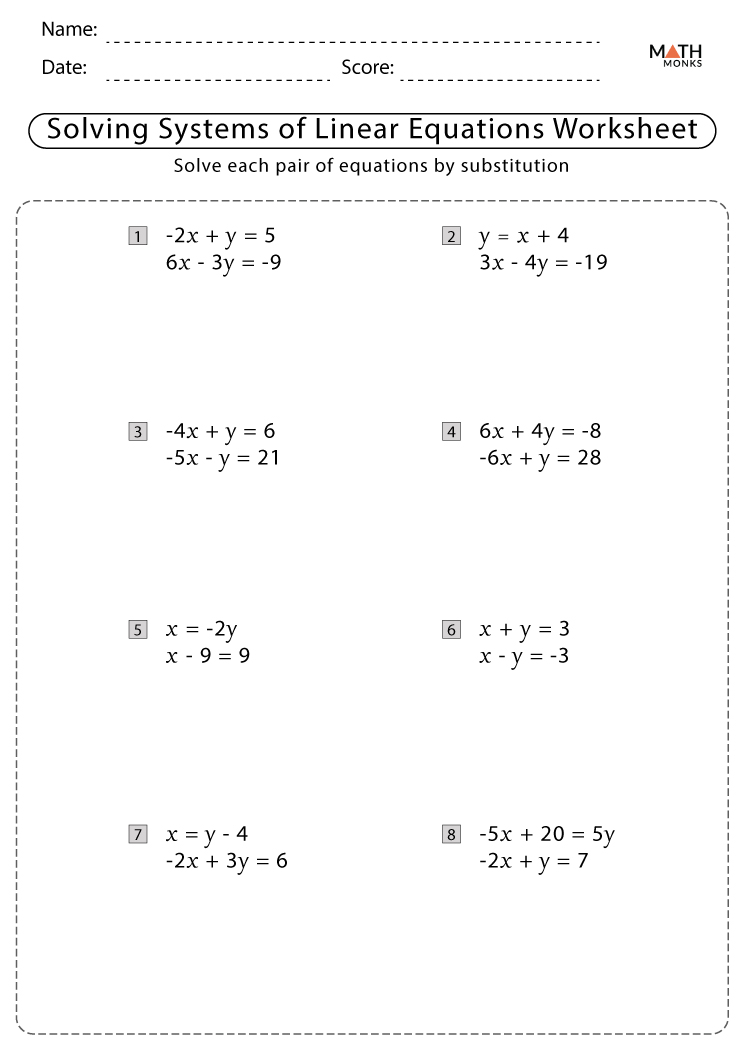
| Equation | Solution |
|---|---|
| x + 2 = 9 | x = 9 - 2 = 7 |
| 3x = 24 | x = 24 ÷ 3 = 8 |
| x/4 = 5 | x = 5 × 4 = 20 |
| 2x + 5 = 11 | x = (11 - 5) ÷ 2 = 3 |
📝 Note: Remember to check your solutions by plugging them back into the original equation.
Conclusion
Linear equations with one variable are a fundamental concept in algebra, and understanding how to solve them is crucial for success in mathematics and science. By following the step-by-step solutions outlined in this article, you can solve linear equations with one variable with confidence.
What is the difference between a linear equation and a quadratic equation?
+A linear equation is an equation in which the highest power of the variable is 1, while a quadratic equation is an equation in which the highest power of the variable is 2.
How do I know if an equation is linear or not?
+An equation is linear if it can be written in the form ax = b, where ‘a’ and ‘b’ are constants, and ‘x’ is the variable.
Can I use a calculator to solve linear equations?
+Yes, you can use a calculator to solve linear equations, but it’s recommended to understand the step-by-step solutions to build a strong foundation in algebra.
Related Terms:
- System of linear Equations pdf
- Linear equation worksheet Grade 8
- Linear equation one variable questions
- Linear equation in two variables
- Linear equation GRADE 7
- Solving expressions worksheet pdf