Line Plot Worksheet: Visualize and Learn with Easy Exercises

Introduction to Line Plots
A line plot, also known as a line graph, is a type of chart used to show information that has distinct trends or patterns over time. It is a simple yet effective way to visualize data, making it easy to understand and analyze. In this article, we will explore the world of line plots through a series of exercises and examples.
What is a Line Plot?
A line plot is a graphical representation of data that displays the relationship between two variables. It consists of a series of points connected by lines, with the x-axis representing the independent variable and the y-axis representing the dependent variable. Line plots are commonly used in various fields, such as finance, science, and engineering, to track changes and trends over time.
Benefits of Using Line Plots
Line plots offer several benefits, including:
- Easy to read and understand: Line plots are simple and intuitive, making it easy to visualize and comprehend complex data.
- Identify trends and patterns: Line plots help identify trends and patterns in data, allowing for better analysis and decision-making.
- Compare data: Line plots enable comparison of multiple datasets, making it easy to spot differences and similarities.
How to Create a Line Plot
Creating a line plot is a straightforward process that involves the following steps:
- Determine the data: Identify the data you want to plot, ensuring it has a clear independent variable (x-axis) and dependent variable (y-axis).
- Choose a scale: Select a suitable scale for both the x-axis and y-axis, ensuring it accurately represents the data.
- Plot the data: Mark the data points on the graph, connecting them with lines to create the line plot.
- Add labels and title: Include labels and a title to provide context and make the graph easy to understand.
📝 Note: When creating a line plot, ensure the data is accurate and reliable to avoid misinterpretation.
Line Plot Exercises
Practice makes perfect! Let’s work through some exercises to help you become more comfortable with line plots.
Exercise 1: Plotting a Simple Line Plot
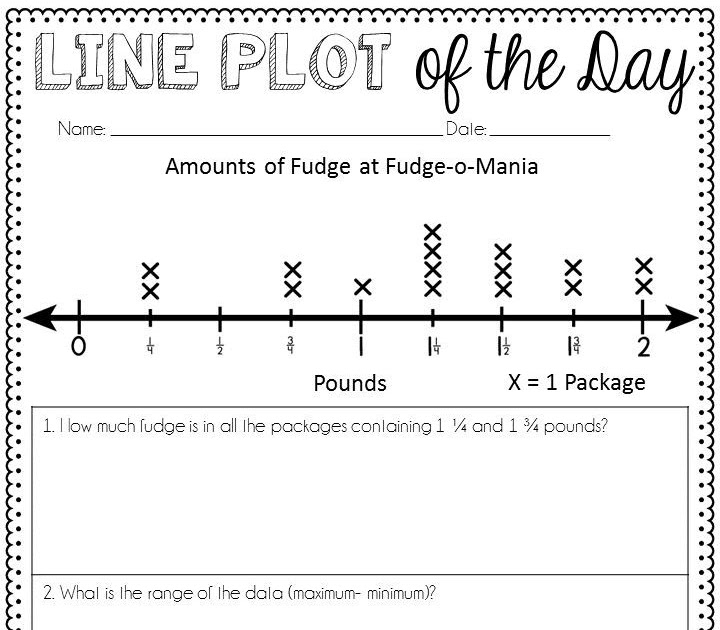
| Month | Sales |
|---|---|
| January | 100 |
| February | 120 |
| March | 150 |
| April | 180 |
| May | 200 |
Plot the sales data on a line plot, using the month as the independent variable and sales as the dependent variable.
Exercise 2: Interpreting a Line Plot
A company’s profit over the past year is shown on the line plot below.
| Month | Profit |
|---|---|
| January | 1000 |
| February | 1200 |
| March | 1500 |
| April | 1800 |
| May | 2000 |
- What is the overall trend of the company’s profit?
- Identify the month with the highest profit.
Exercise 3: Comparing Line Plots
Two friends, Alex and Ben, have been tracking their daily step count over the past week. Their data is shown on the line plots below.
| Day | Alex’s Steps | Ben’s Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Monday | 5000 | 6000 |
| Tuesday | 5500 | 6500 |
| Wednesday | 6000 | 7000 |
| Thursday | 6500 | 7500 |
| Friday | 7000 | 8000 |
- Compare the overall trend of Alex’s and Ben’s step count.
- Identify the day with the highest difference in step count between Alex and Ben.
Conclusion
Line plots are a powerful tool for visualizing and analyzing data. Through these exercises, you have learned how to create and interpret line plots, as well as compare multiple datasets. Remember to always ensure accurate and reliable data when working with line plots. With practice, you’ll become proficient in creating and analyzing line plots, unlocking new insights and perspectives in your data analysis journey.
What is the main purpose of a line plot?
+The main purpose of a line plot is to show the relationship between two variables, making it easy to identify trends and patterns over time.
How do I choose the right scale for my line plot?
+Choose a scale that accurately represents the data, ensuring it is neither too large nor too small. Consider the range of values and the differences between data points.
Can I use line plots to compare multiple datasets?
+Yes, line plots can be used to compare multiple datasets. This allows for easy identification of differences and similarities between the datasets.