7 Tips to Solve Limiting Reactant Worksheet Easily
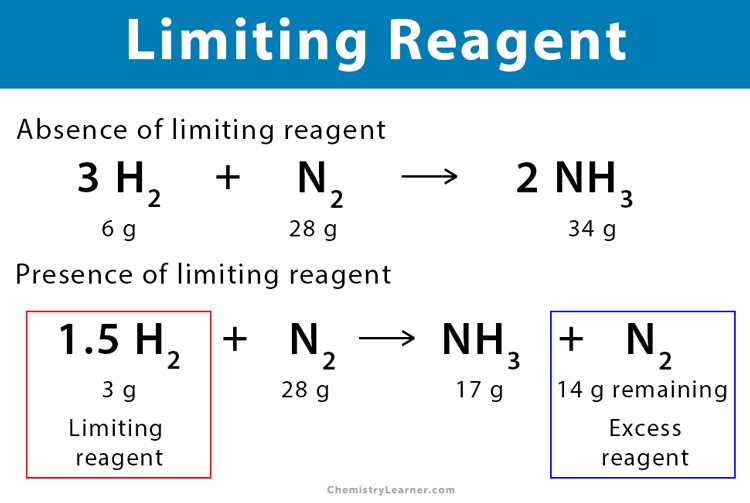
Understanding Limiting Reactants
When working with chemical reactions, it’s essential to understand the concept of limiting reactants. A limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed. Identifying the limiting reactant is crucial in determining the yield of a reaction. In this article, we will provide 7 tips to solve limiting reactant worksheet easily.
Tip 1: Write Down the Balanced Equation
The first step in solving a limiting reactant problem is to write down the balanced equation for the reaction. This will help you identify the mole ratio of the reactants and products.
📝 Note: Make sure to double-check the balancing of the equation, as an unbalanced equation can lead to incorrect calculations.
Tip 2: Identify the Given Information
Next, identify the given information in the problem, such as the masses or moles of the reactants, and the mole ratio from the balanced equation.
- Given Information:
- Mass of Reactant A: 50 g
- Mass of Reactant B: 75 g
- Balanced Equation: 2A + 3B → 2C
Tip 3: Calculate the Moles of Reactants
Now, calculate the moles of each reactant using the given masses and molar masses.
- Molar Mass of Reactant A: 40 g/mol
- Molar Mass of Reactant B: 30 g/mol
- Moles of Reactant A: 50 g / 40 g/mol = 1.25 mol
- Moles of Reactant B: 75 g / 30 g/mol = 2.5 mol
Tip 4: Determine the Limiting Reactant
Use the mole ratio from the balanced equation to determine which reactant is limiting.
- Mole Ratio of Reactant A to Reactant B: 2:3
- Moles of Reactant A: 1.25 mol
- Moles of Reactant B: 2.5 mol ( excess reactant)
- Limiting Reactant: Reactant A
Tip 5: Calculate the Yield of Product
Once you have identified the limiting reactant, calculate the yield of product using the mole ratio from the balanced equation.
- Mole Ratio of Reactant A to Product C: 2:2
- Moles of Reactant A: 1.25 mol
- Moles of Product C: 1.25 mol
Tip 6: Use the Limiting Reactant to Calculate the Mass of Product
Finally, use the limiting reactant to calculate the mass of product.
- Molar Mass of Product C: 50 g/mol
- Mass of Product C: 1.25 mol x 50 g/mol = 62.5 g
Tip 7: Practice, Practice, Practice!
Practice is key when it comes to solving limiting reactant problems. The more you practice, the more comfortable you will become with identifying the limiting reactant and calculating the yield of product.
What is the purpose of identifying the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction?
+The limiting reactant determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed in a chemical reaction.
How do you calculate the yield of product in a limiting reactant problem?
+Use the mole ratio from the balanced equation to calculate the yield of product.
What is the significance of the mole ratio in a limiting reactant problem?
+The mole ratio helps to identify the limiting reactant and calculate the yield of product.
By following these 7 tips, you will be able to solve limiting reactant worksheet easily and accurately. Remember to practice regularly to become more confident in your ability to identify the limiting reactant and calculate the yield of product.
Related Terms:
- Percent yield worksheet answers
- Limiting reactant quiz Answers
- Limiting reagents Worksheet
- Limiting and excess reactant pdf