6 Simple Steps to Master Lewis Dot Structures
Understanding Lewis Dot Structures
Lewis dot structures are a fundamental concept in chemistry, used to represent the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. They provide a visual representation of the arrangement of electrons, helping chemists understand the properties and behavior of molecules. Mastering Lewis dot structures is essential for any chemistry student, and with these 6 simple steps, you can become proficient in creating and interpreting them.
Step 1: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons
To create a Lewis dot structure, you need to know the total number of valence electrons in the molecule. This can be calculated by summing the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule. For main group elements, the number of valence electrons is equal to the group number in the periodic table.
- Group 1A (1): 1 valence electron
- Group 2A (2): 2 valence electrons
- Group 3A (13): 3 valence electrons
- Group 4A (14): 4 valence electrons
- Group 5A (15): 5 valence electrons
- Group 6A (16): 6 valence electrons
- Group 7A (17): 7 valence electrons
- Group 8A (18): 8 valence electrons (noble gases)
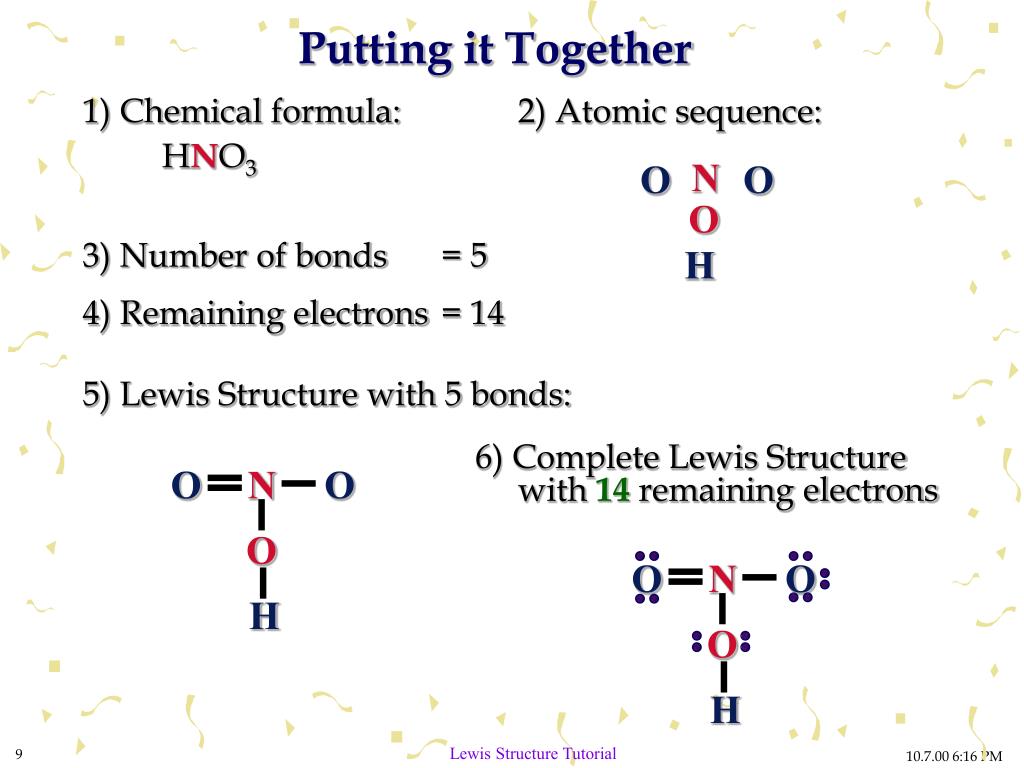
For example, if you want to create a Lewis dot structure for CO2 (carbon dioxide), you would calculate the total number of valence electrons as follows:
- Carbon © has 4 valence electrons (Group 4A)
- Oxygen (O) has 6 valence electrons (Group 6A)
- Total valence electrons = 4 © + 2 x 6 (O) = 16
Step 2: Determine the Central Atom
The central atom is the atom that will be at the center of the Lewis dot structure. In most cases, the central atom is the least electronegative atom in the molecule. If there are multiple atoms of the same element, choose one as the central atom.
- Electronegativity values:

Element Electronegativity Hydrogen (H) 2.2 Carbon © 2.5 Nitrogen (N) 3.0 Oxygen (O) 3.4 Fluorine (F) 4.0
In the case of CO2, carbon is the least electronegative atom, so it will be the central atom.
Step 3: Draw Single Bonds to the Central Atom
Draw single bonds from the central atom to each of the surrounding atoms. This will represent the sigma (σ) bonds between the atoms.
- Single bond: represented by a single line (-)
For CO2, draw single bonds from the central carbon atom to each of the two oxygen atoms.
Step 4: Distribute the Remaining Valence Electrons
Distribute the remaining valence electrons around the surrounding atoms, ensuring that each atom has a full octet (8 electrons) if possible. This can be achieved by adding double or triple bonds between atoms.
- Double bond: represented by two lines (=)
- Triple bond: represented by three lines (≡)
In CO2, there are 16 valence electrons remaining. Distribute 4 electrons to each oxygen atom, forming a double bond between the carbon and oxygen atoms.
Step 5: Check the Octet Rule
Verify that each atom has a full octet (8 electrons) if possible. If not, consider adding lone pairs to the central atom or rearranging the bonds to satisfy the octet rule.
- Octet rule: each atom should have 8 electrons in its valence shell
In CO2, the carbon atom has 8 electrons (4 from the double bonds and 4 from the lone pairs), and each oxygen atom has 8 electrons (4 from the double bond and 4 from the lone pairs).
Step 6: Verify the Lewis Dot Structure
Verify that the Lewis dot structure is correct by checking the following:
- The total number of valence electrons is equal to the sum of the valence electrons of each atom.
- The central atom has the correct number of bonds and lone pairs.
- Each surrounding atom has a full octet (8 electrons) if possible.
By following these 6 simple steps, you can master the creation of Lewis dot structures and improve your understanding of molecular chemistry.
📝 Note: Practice creating Lewis dot structures for different molecules to become more comfortable with the process.
What is the purpose of Lewis dot structures?
+Lewis dot structures provide a visual representation of the arrangement of electrons in a molecule, helping chemists understand the properties and behavior of molecules.
How do I determine the central atom in a Lewis dot structure?
+The central atom is usually the least electronegative atom in the molecule. If there are multiple atoms of the same element, choose one as the central atom.
What is the octet rule in Lewis dot structures?
+The octet rule states that each atom should have 8 electrons in its valence shell, if possible. This can be achieved by adding lone pairs to the central atom or rearranging the bonds.
In conclusion, mastering Lewis dot structures is an essential skill for chemistry students, and by following these 6 simple steps, you can improve your understanding of molecular chemistry and create accurate Lewis dot structures. Remember to practice creating Lewis dot structures for different molecules to become more comfortable with the process.