Lewis Dot Diagram Worksheet and Answers
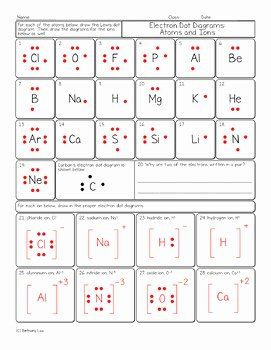
Lewis Dot Diagrams: A Comprehensive Guide
Lewis dot diagrams, also known as electron dot diagrams, are a fundamental concept in chemistry that represents the valence electrons of atoms within a molecule. These diagrams provide a visual representation of the electrons and help us understand the bonding between atoms. In this worksheet, we will explore the basics of Lewis dot diagrams, learn how to draw them, and practice creating diagrams for various molecules.
What are Lewis Dot Diagrams?
Lewis dot diagrams are a graphical representation of the valence electrons of an atom or a molecule. They are used to show the arrangement of electrons around an atom and help us understand the chemical bonding between atoms. The diagrams are named after Gilbert N. Lewis, who introduced this concept in 1916.
How to Draw Lewis Dot Diagrams
Drawing Lewis dot diagrams involves several steps:
- Determine the total number of valence electrons: Calculate the total number of valence electrons in the molecule by adding the valence electrons of each atom.
- Draw the skeletal structure: Draw the basic structure of the molecule, including the arrangement of atoms.
- Add valence electrons: Add the valence electrons to the diagram, starting with the atom that has the lowest electronegativity.
- Follow the octet rule: Ensure that each atom has a full outer energy level (octet) by adding electrons to the diagram.
- Check for multiple bonds: If necessary, add multiple bonds to the diagram to satisfy the octet rule.
Examples of Lewis Dot Diagrams
Let’s practice drawing Lewis dot diagrams for some simple molecules:
Example 1: Hydrogen Fluoride (HF)
- Total valence electrons: 1 (H) + 7 (F) = 8
- Skeletal structure: H-F
- Add valence electrons: H· · · · · ·F:
- Follow the octet rule: H-F:
Example 2: Methane (CH4)
- Total valence electrons: 4 © + 4 (H) x 4 = 20
- Skeletal structure: H-C-H
- Add valence electrons: H· · ·C· · · ·H
- Follow the octet rule: H-C-H
Example 3: Ammonia (NH3)
- Total valence electrons: 5 (N) + 3 (H) x 3 = 14
- Skeletal structure: H-N-H
- Add valence electrons: H· · ·N· · · ·H
- Follow the octet rule: H-N-H
Practice Time!
Try drawing Lewis dot diagrams for the following molecules:
- CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
- H2O (Water)
- CH3OH (Methanol)
- NH3 (Ammonia)
- C2H6 (Ethane)
👀 Note: When drawing Lewis dot diagrams, make sure to follow the octet rule and check for multiple bonds. This will help you create accurate diagrams.
Solutions to Practice Problems
Here are the solutions to the practice problems:
1. CO2 (Carbon Dioxide)
- Total valence electrons: 4 © + 2 (O) x 6 = 20
- Skeletal structure: O-C-O
- Add valence electrons: O· · ·C· · · ·O:
- Follow the octet rule: O=C=O
2. H2O (Water)
- Total valence electrons: 2 (H) + 6 (O) = 8
- Skeletal structure: H-O-H
- Add valence electrons: H· · ·O· · · ·H
- Follow the octet rule: H-O-H
3. CH3OH (Methanol)
- Total valence electrons: 4 © + 3 (H) x 3 + 6 (O) = 20
- Skeletal structure: H-C-H
- Add valence electrons: H· · ·C· · · ·H
- Follow the octet rule: H-C-O-H
4. NH3 (Ammonia)
- Total valence electrons: 5 (N) + 3 (H) x 3 = 14
- Skeletal structure: H-N-H
- Add valence electrons: H· · ·N· · · ·H
- Follow the octet rule: H-N-H
5. C2H6 (Ethane)
- Total valence electrons: 4 © x 2 + 6 (H) x 2 = 20
- Skeletal structure: H-C-C-H
- Add valence electrons: H· · ·C· · · ·C· · · ·H
- Follow the octet rule: H-C-C-H
Conclusion
In this worksheet, we learned the basics of Lewis dot diagrams and how to draw them for various molecules. We also practiced drawing diagrams for several molecules, including CO2, H2O, CH3OH, NH3, and C2H6. Remember to always follow the octet rule and check for multiple bonds when drawing Lewis dot diagrams.
What is the purpose of Lewis dot diagrams?
+Lewis dot diagrams are used to show the arrangement of electrons around an atom and help us understand the chemical bonding between atoms.
How do I determine the total number of valence electrons in a molecule?
+Calculate the total number of valence electrons by adding the valence electrons of each atom in the molecule.
What is the octet rule in Lewis dot diagrams?
+The octet rule states that each atom should have a full outer energy level (octet) by adding electrons to the diagram.
Related Terms:
- Lewis dot Diagram Worksheet pdf
- Lewis dot Structure ws
- Lewis dot structure quiz