5 Essential Parts to Label on a Microscope Worksheet
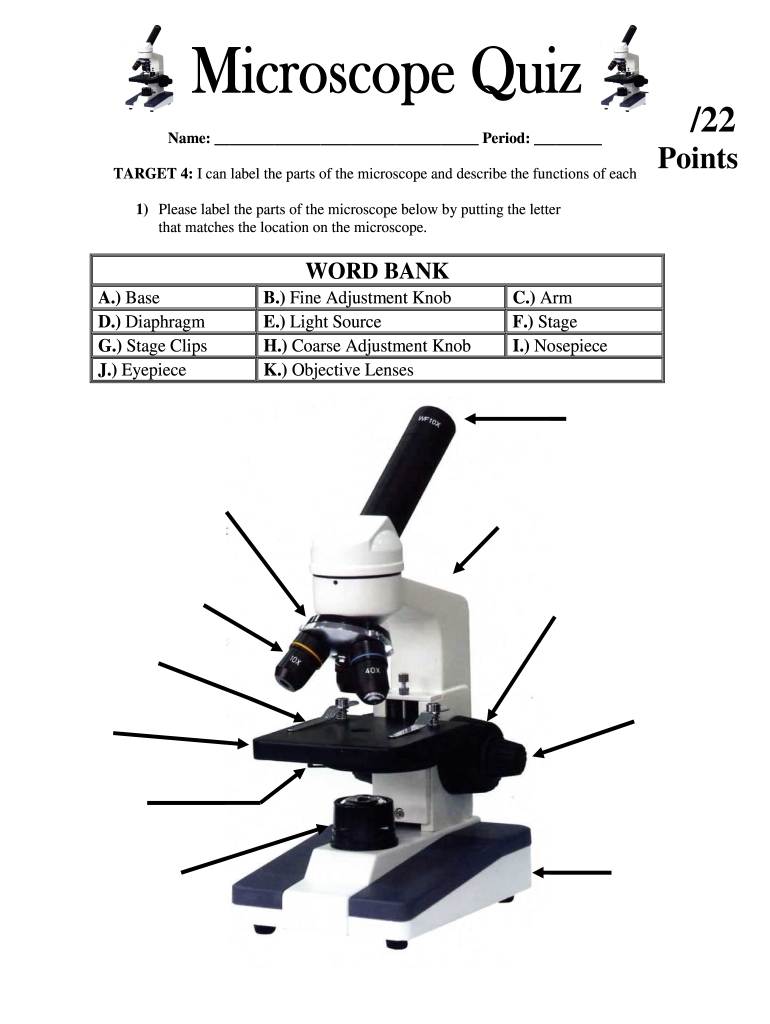
Understanding the Components of a Microscope
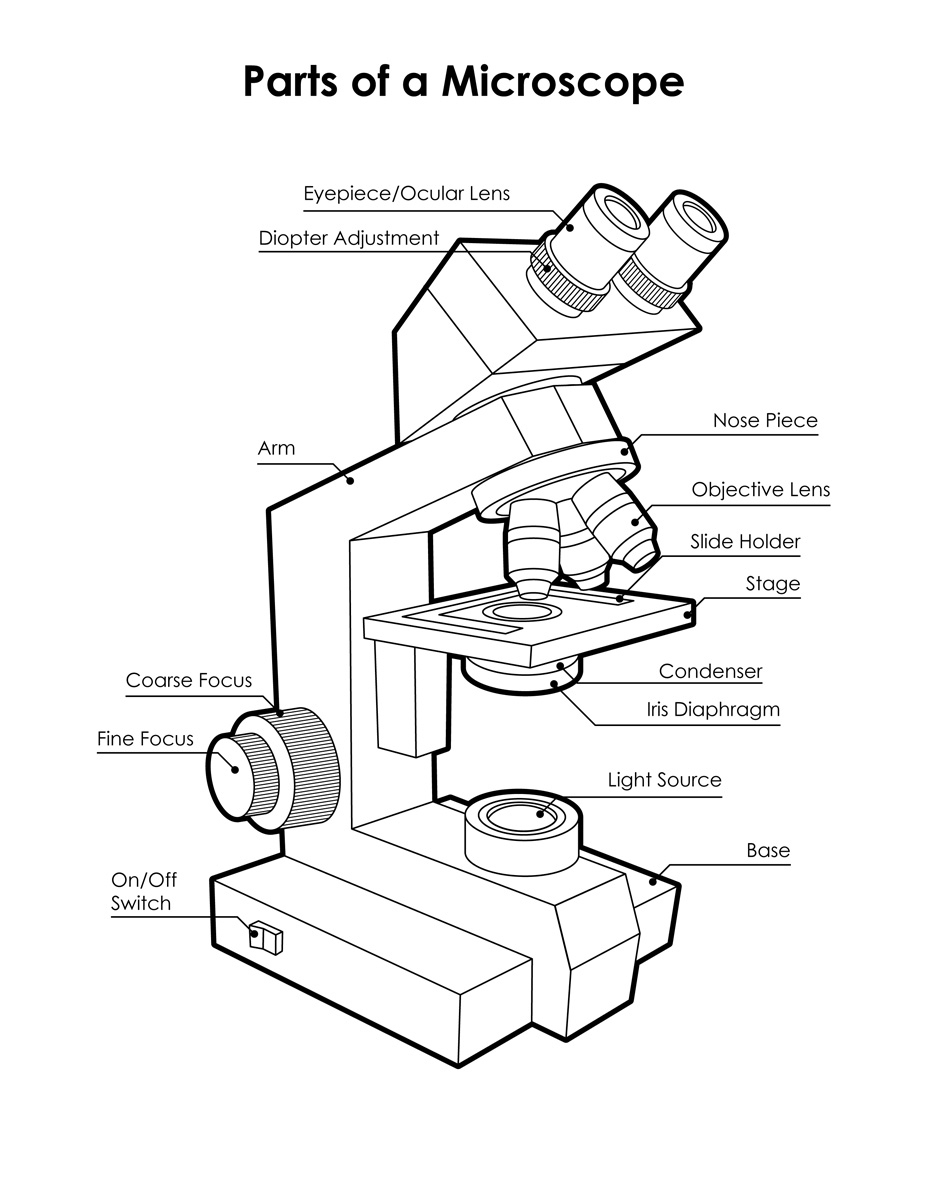
Microscopes are fascinating instruments that allow us to explore the microscopic world, revealing the intricate details of tiny structures and organisms. However, to fully appreciate and utilize a microscope, it’s essential to understand its various components and their functions. In this article, we’ll focus on the five essential parts to label on a microscope worksheet, ensuring that you become familiar with the fundamental anatomy of a microscope.
1. Ocular Lens (Eyepiece)
The ocular lens, also known as the eyepiece, is the part of the microscope that you look directly into to observe the specimen being examined. It’s usually a cylindrical lens that magnifies the image formed by the objective lens. The ocular lens typically has a magnification power of 10x or 15x, and it’s usually adjustable to accommodate different interpupillary distances.
🔍 Note: The ocular lens is not to be confused with the objective lens. While both lenses are essential for magnification, they serve distinct purposes.
2. Objective Lenses
The objective lenses are a set of lenses located near the specimen being observed. They collect light from the specimen and form an image that is then magnified by the ocular lens. There are usually three to four objective lenses on a standard microscope, each with a different magnification power (e.g., 4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x oil immersion).
- 4x objective lens: Provides a low magnification power, often used for observing larger specimens or surveying the specimen’s overall structure.
- 10x objective lens: Offers a moderate magnification power, commonly used for observing cells, tissues, and small organisms.
- 40x objective lens: Provides a higher magnification power, often used for observing detailed structures, such as cell organelles or microorganisms.
- 100x oil immersion objective lens: Offers the highest magnification power, used for observing tiny structures or microorganisms that require oil immersion to reduce light scattering.
3. Stage
The stage is a flat platform that holds the specimen in place during observation. It’s usually movable in the x, y, and z axes, allowing you to position the specimen precisely under the objective lens. The stage may also feature clips or a mechanical stage to secure the specimen in place.
4. Coarse and Fine Adjustment Knobs
The coarse and fine adjustment knobs are used to adjust the distance between the objective lens and the specimen. The coarse adjustment knob makes larger adjustments, while the fine adjustment knob makes finer adjustments to focus the image.
- Coarse adjustment knob: Used for larger adjustments, often to bring the specimen into rough focus.
- Fine adjustment knob: Used for finer adjustments, to achieve precise focus and optimize image quality.
5. Light Source
The light source is a critical component of a microscope, providing the illumination necessary to observe the specimen. The type of light source may vary, but common types include:
- Incandescent light: Uses a bulb to produce light, often with a variable intensity control.
- LED light: Uses light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to produce light, often with a fixed intensity.
- Fluorescent light: Uses a fluorescent bulb to produce light, often with a variable intensity control.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Ocular Lens (Eyepiece) | Magnifies the image formed by the objective lens |
| Objective Lenses | Collect light from the specimen and form an image |
| Stage | Holds the specimen in place during observation |
| Coarse and Fine Adjustment Knobs | Adjust the distance between the objective lens and the specimen |
| Light Source | Provides illumination to observe the specimen |
In conclusion, understanding the five essential parts to label on a microscope worksheet is crucial for effectively using a microscope and exploring the microscopic world. By familiarizing yourself with the ocular lens, objective lenses, stage, coarse and fine adjustment knobs, and light source, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the fascinating realm of microscopy.
What is the purpose of the ocular lens in a microscope?
+The ocular lens, also known as the eyepiece, is used to magnify the image formed by the objective lens. It typically has a magnification power of 10x or 15x and is adjustable to accommodate different interpupillary distances.
What is the difference between the coarse and fine adjustment knobs?
+The coarse adjustment knob is used for larger adjustments, often to bring the specimen into rough focus. The fine adjustment knob is used for finer adjustments to achieve precise focus and optimize image quality.
What types of light sources are commonly used in microscopes?
+Common types of light sources used in microscopes include incandescent light, LED light, and fluorescent light. Each type of light source has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the choice of light source often depends on the specific application and requirements.